
Concept explainers
Figure 21-11 shows (1) four situations in which five charged particles are evenly spaced along an axis. The charge values are indicated except for the central particle, which has the same charge in all four situations. Rank the situations according to the magnitude of the net electrostatic force or the central particle, greatest first.
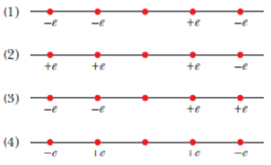
Figure 21-11 Question 1.
To rank:
The situations according to the magnitude of net electrostatic force exerted on the central particle by four given particles.
Answer to Problem 1Q
Solution:
Rank based on net electrostatic force is F3>F1>F2>F4
Explanation of Solution
1) Concept:
The net force acting on a particle due to more than one particle is the sum of forces exerted by each of the particles.
2) Formulae:
Electrostatic force between two charges q1 and q2,
k- Coulomb’s constant constant=8.99 x 109
d- distance of separation between particles.
3) Given:
a. The five particles are evenly spaced on an axis.
b. The charges on four particles are given except for the central particle.
Situation 1: Charges on right side = -e, -e Charges on left side =-+e, -e
Situation 2: Charges on right side = +e, +e Charges on left side =+e, -e
Situation 3: Charges on right side = -e, -e Charges on left side =+e, +e
Situation 4: Charges on right side = -e, +e Charges on left side =+e, -e
c. The central particle has same charge in all the 4 situations.
4) Calculation:
Let us consider that each of the particles is located at d distance apart.
Let us consider that the central particle has a charge +e.
According to Coulomb’s law, the magnitude of force F acting on the central particle due to the particles at distance d is,
Situation 1:
In the situation 1, the free body diagram of force acting on central particle, due to other particles is drawn as shown below.
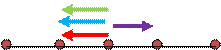 |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
The particles located at distance 2d on either side, exert equal and opposite forces on the central particle. So they nullify each other’s effect on the central particle. Meanwhile, the particles at distance d exert equal forces towards the same direction, and hence the exerted forces add up to 2F.
Hence net force, F1= 2F
Situation 2:
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
Force exerted by particles at distance d on either side nullifies each other. Hence, the net force on the central particle due to the particles at 2d distance,
F2 =
=
=
Situation 3:
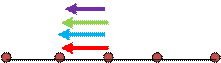 |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
Here the particles at distance ‘d’ exert equal force on same direction as in situation 1. Hence the force exerted by these particles on central particle is 2F. The particles that are at 2d distance on either sides again exert same force in same direction as in situation 2. Hence the force exerted by them on central particle is 0.5F.
Net force, F3= F1+F2 = 2F +0.5 F = 2.5 F
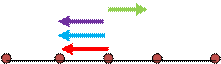
Situation 4:
 |
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
Here the particles at distance ‘2d’ nullifies each other’s effect and also that are at distance ‘d’ again cancel the force exerted by each other. Therefore, the net force acting on the particle is zero.
Net force, F4=0
Conclusion:
We can find net electrostatic force acting on a particle by knowing the magnitude and direction of the forces exerted by each of the particles present in the system.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
FUND. OF PHYSICS FOR LSU WILEY+ NEXT GEN
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Essential University Physics: Volume 1 (3rd Edition)
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
Mathematical Methods in the Physical Sciences
University Physics (14th Edition)
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student Edition
University Physics with Modern Physics (14th Edition)
- A circular plastic disk with radius R = 2.00 cm has a uniformly distributed charge Q=+(2.00 * 10^6)e on one face. A circular ring of width 30 mm is centered on that face, with the center of that width at radius r = 0.50 cm. In coulombs, what charge is contained within the width of the ring?arrow_forwardA charged nonconducting rod, with a length of 2.00 m and a cross-sectional area of 4.00 cm2, lies along the positive side of an x axis with one end at the origin. The volume charge density r is charge per unit volume in coulombs per cubic meter. How many excess electrons are on the rod if r is (a) uniform, with a value of -4.00 mC/m3, and (b) nonuniform, with a value given by r = bx2, where b=-2.00 mC/m5?arrow_forwardThe charges and coordinates of two charged particles held fixed in an xy plane are q1 = 2.15 μC, x1 = 3.60 cm, y1 = 0.902 cm and q2 = -5.64 μC, x2 = -1.91 cm, y2 = 2.49 cm. Find the (a) magnitude and (b) direction (with respect to +x-axis in the range (-180°;180°]) of the electrostatic force on particle 2 due to particle 1. At what (c) x and (d) y coordinates should a third particle of charge.arrow_forward
- The charges and coordinates of two charged particles held fixed in an xy plane are q1 = 2.69 μC, x1 = 3.17 cm, y1 = 0.823 cm and q2 = -5.84 μC, x2 = -2.66 cm, y2 = 1.14 cm. Find the (a) magnitude and (b) direction (with respect to +x-axis in the range (-180°;180°]) of the electrostatic force on particle 2 due to particle 1. At what (c) x and (d) y coordinates should a third particle of charge q3 = 4.20 μC be placed such that the net electrostatic force on particle 2 due to particles 1 and 3 is zero?arrow_forwardA solid conducting cylinder of radius R1 = 1.0 cm is surrounded by a thin conducting shell of radius R2 = 3.0 cm. Both cylinders have length L = 20.0 cm, and there is empty space between R1 and R2. If the inner cylinder has charge q = +3.0μC and the outer shell has charge -3.0μC, find the followingarrow_forwardIn Fig-1, there are two infinite planes A and B, parallel to the YZ plane. Their surface charge densities are σA = −47nC/m2 and σB = 28nC/m2. The separation between the planes A and B is d = 10m. a) Now, we place a conducting spherical shell of radius R=0.1d in between the planes. The spherical shell conductor carries a surface charge density σ = −25μC/m2. The coordinates of the center(d/2,d/2,0), P1 (4d/5, d/2, 0) and P2 (d/2, d/4, 0). Find the net electric field at points P1 and P2 in unit vector notation.arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





