
Concept explainers
SSM In crystals of the salt cesium chloride, cesium ions Cs+ form the eight corners of a cube and a chlorine ion Cl− is at the cube’s center (Fig. 21-36). The edge length of the cube is 0.40 nm. The Cs+ ions are each deficient by one electron (and thus each has a charge of +e), and the Cl− ion has one excess electron (and thus has a charge of −e). (a) What is the magnitude of the net electrostatic force exerted on the Cl− ion by the eight Cs+ ions at the corners of the cube? (b) If one of the Cs+ ions is missing, the crystal is said to have a defect; what is the magnitude of the net electrostatic force exerted on the Cl− ion by the seven remaining Cs+ ions?
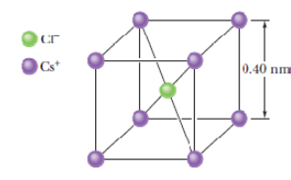
Figure 21-36 Problem 35.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 21 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics, Volume 1, Chapter 1-20
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Matter and Interactions
Physics: Principles with Applications
MODERN PHYSICS (LOOSELEAF)
University Physics Volume 1
- An object of mass 5 × 10-6 g is placed over a thin positively charged sheet of surface density of charge σ = 4.0 × 10-6C/m2 (figure shown below). Estimate the charge that should be given to this object so that upon release it will not fall down. Calculate the number of electrons that is to be removed to give this charge. How much mass loss is caused by this removal of electrons?arrow_forwardSome types of molecules that do not possess an intrinsic electric dipole moment can be given one by an external electric field in a process called charge separation, or polarization. In this process, their internal charge distribution becomes distorted by the field, which results in the region of a molecule on the side in the direction of the field gaining a positive net charge and the region on the other side gaining a negative net charge. Both charges have equal magnitudes, and the electric neutrality of the molecule as a whole is maintained. The electric field is said to induce an electric dipole moment in such a molecule. When the field is canceled, the molecule reverts to its unpolarized state and loses its electric dipole moment. The electric behavior of such a molecule can be modeled by a pair of ±1.60×10−19 C±1.60×10−19 C charges connected by a spring with force constant 0.000613 N/m.0.000613 N/m. The spring must be imagined as possessing zero relaxed length so that normally…arrow_forwardA charged nonconducting rod has a length L of 2.0 m and a cross-sectional area A of 8.0 cm?; it is placed along the positive side of an x axis with one end at the origin. The volume charge density p is the charge per unit volume, with the units of coulomb per cubic meter. a) How many excess electrons are on the rod if the rod's volume charge density pu is uniform with a value of –10 µC/m³? How does that compare to the total number of electrons you would estimate would be in the rod? (By compare, just a ballpark estimate- to within several orders of magnitude, factors of ten). b) What is an expression for the number of excess electrons on the rod if the rod's volume charge is nonuniform and is given instead by pN=ax³ where a is a constant? c) What value of a is necessary for the rod in part b to have the same number of excess electrons as the rod in part a)?arrow_forward
- The water molecule's dipole moment is 6.17×10-30C⋅m. What would be the separation distance if the molecule consisted of charges ±e? (The effective charge is actually less because H and O atoms share the electrons.) Express answer with appropriate units.arrow_forward5 In Fig. 23-25, an electron is released between two infinite nonconducting sheets that are horizontal and have uniform surface charge densities oay ando ,as indicated. The electron is subjected to the following three situations involving surface charge densities and sheet separations Rank the magnitudes of the electron's acceleration,greatest first. Situation O4) O(-) Separation +40 -40 2 +70 4d 3 +30 -5o 9darrow_forwardTwo small spheres separated by a distance equal to 20.0 cm have equal charges. How many excess electrons must be present in each sphere so that the modulus of the repulsion force between them is equal to 3.33x10-21N?arrow_forward
- The surfaces of a lipid bi-layer forming the membrane around a cell with a radius of 1.2 µm has a residual charge qr = 9x10-15 C on outside of the bi-layer, and the same amount of negative charge on the inside. What is the force in pN (×10-12 N) on a singly-charged positive ion (q =1.6 x10-19 C) located on the outer surface of this membrane? Hint: Use F = q E = q (o/e) with o = qr/A = qr/ (4Tt r²) and ɛ, = 8.85 x 10-12 F-m-1. Answer: 8.99180 Farrow_forwardThree distribution of charges are present in free: space with: A uniform line charge of p₁ = 3 μC/m lies along z-axis. MC/m 3 μC / m 3 A concentric circular cylinder of radius 2 m has p, = 5 A concentric circular cylinder of radius 4 ≤r ≤ 5 has pv Find D at a) r=1 b) r-3 c) r=6 (a) 0.0477*10^-6 C/m^2, (b) 3.05*10^-6 C/m^2, (c) 0.0022*10^-6 O C/m^2 (a) 4.77*10^-6 C/m^2, (b) 3.5*10^-6 O C/m^2, (c) 0.22*10^-6 C/m^2 (a) 0.477*10^-6 C/m^2, (b) 3.5*10^-6 C/m^2, (c) 0.022*10^-6 C/m^2 (a) 0.477*10^-5 C/m^2, (b) 3.5*10^-6 C/m^2, (c) 0.022*10^-5 O C/m^2arrow_forwardA charged nonconducting rod, with a length of 3.52 m and a cross-sectional area of 5.94 cm2, lies along the positive side of an x axis with one end at the origin. The volume charge density p is charge per unit volume in coulombs per cubic meter. How many excess electrons are on the rod if p is (a) uniform, with a value of -2.46 µC/m³, and (b) nonuniform, with a value given by p = bx2, where b = -2.26 µC/m3? (a) Number Units (b) Number Unitsarrow_forward
- Three distribution of charges are present in free space with: iC/m lies along z-axis. 5 Cm A uniform line charge of pL = 3 A concentric circular cylinder of radius 2 m has es A concentric circular cylinder of radius 4arrow_forwardIn a conductor, one or more electrons from each atom are free to roam throughout the volume of the conductor. Does this contradict the statement that any excess charge on a solid conductor must reside on its surface? Why or why not?arrow_forwardSuppose a capacitor consists of two coaxial thin cylindrical conductors. The inner cylinder of radius ra has a charge of +Q, while the outer cylinder of radius rp has charge -Q. The electric field E at a radial distance r from the central axis is given by the function: E = aer/ao + B/r + bo %| where alpha (a), beta (B), ao and bo are constants. Find an expression for its capacitance. First, let us derive the potential difference Vab between the two conductors. The potential difference is related to the electric field by: Va Edr= Edr Calculating the antiderivative or indefinite integral, Vab = (-aaoe-r/ao + B + bo By definition, the capacitance C is related to the charge and potential difference by: C = Evaluating with the upper and lower limits of integration for Vab, then simplifying: C = Q/( (e-"b/ao - era/ao) + B In( ) + bo ( ))arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning


