
(a)
The value of the unknown capacitor.
(a)
Answer to Problem 60P
The value of the unknown capacitor is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for phase angle.
Here,
Write the expression for capacitive reactance.
Here,
Write the expression for inductive reactance.
Here, 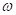 is the angular frequency and
is the angular frequency and
Conclusion:
Substitute the equation (III) and (II) in the equation (I).
Substitute
Here,
Substitute
Therefore, the value of the unknown capacitor is
(b)
If person F should connect a second capacitor in parallel across the first capacitor or in series in the circuit.
(b)
Answer to Problem 60P
Person F needs to add another capacitor in series to reduce the equivalent capacitance.
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the power proportional to the cosine of the phase angle.
Here,
The impedance of the
Since
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Since the capacitive reactance must be increased. Thus,
The capacitive reactance is too small, so person F needs to add another capacitor in series to reduce the equivalent capacitance, thereby increasing the capacitive reactance.
(c)
The value of the capacitor requited to get maximum power.
(c)
Answer to Problem 60P
The value of the capacitor requited to get maximum power is
Explanation of Solution
For the maximum power, the capacitive reactance should be equal to the inductive reactance. Since
The required capacitance of the additional capacitor is.
Here,
Replace
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the maximum power needed for the value of capacitor is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Package: Physics With 1 Semester Connect Access Card
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





