
(a)
The reactance of the capacitor and the inductor.
(a)
Answer to Problem 93P
The reactance of the capacitor is
Explanation of Solution
Write an expression for the capacitive reactance.
Here,
Write an expression for the inductive reactance.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the reactance of the capacitor is
(b)
The impedance.
(b)
Answer to Problem 93P
The impedance is
Explanation of Solution
Write an expression for the impedance.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Thus, the impedance is
(c)
The rms current.
(c)
Answer to Problem 93P
The rms current is
Explanation of Solution
Write an expression for the rms current.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Thus, the rms current is
(d)
The current amplitude.
(d)
Answer to Problem 93P
The current amplitude is
Explanation of Solution
Write an expression for the current amplitude.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Thus, the current amplitude is
(e)
The phase angle.
(e)
Answer to Problem 93P
The phase angle is
Explanation of Solution
Write an expression for the phase angle.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Thus, the phase angle is
(f)
The rms voltage across each of the circuit elements.
(f)
Answer to Problem 93P
The rms voltage across the resistance is
Explanation of Solution
Write an expression for the rms voltage across the resistance.
Here,
Write an expression for the rms voltage across the inductor.
Here,
Write an expression for the rms voltage across the capacitor.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the rms voltage across the resistance is
(g)
If the current leads or lags the voltage.
(g)
Answer to Problem 93P
The current lags the voltage.
Explanation of Solution
From the values of the capacitive reactance and inductive reactance, the inductive reactance is greater than the capacitive reactance.
Conclusion:
As the dominant element is the inductor, the current lags the voltage.
Thus, the current lags the voltage.
(h)
Sketch the phasor diagram.
(h)
Answer to Problem 93P
The phasor diagram is shown in figure 1.
Explanation of Solution
The voltages of the different circuit elements found in part (f) is used to draw the phasor diagram.
The rms voltage across the resistance
The rms voltage across the inductor
The rms voltage across the capacitor
As the dominant element is the inductor, the current lags the voltage.
Conclusion:
The difference between the voltage across the inductor and the voltage across the capacitor is zero.
Sketch the phasor diagram.
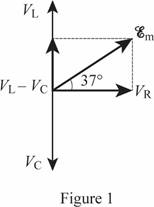
Thus, the phasor diagram is shown in figure 1.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 21 Solutions
Student Solutions Manual for Physics
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





