
Interpretation:
A mechanism for the dehydration of 4-methylcyclohexanol catalyzed by phosphoric acid needs to be explained.
Concept Introduction:
A dehydration reaction takes place after the removal of water molecule/s from the reactant molecule. In the mechanism of any organic reaction, negative charge always attacks on the positive center, and removal of good leaving group takes place. The stability of a leaving group depends on the stability of the molecule which can be shown by inductive, hyperconjugation or resonance effect.
Explanation of Solution
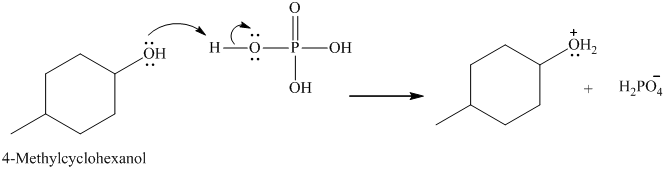
Below is the mechanism for the dehydration of 4-methyl cyclohexanol catalyzed by phosphoric acid:
In the first step, lone pair of electrons attack on the H atom which results in the formation positive charge on the O of the -OH group of 4-methyl cyclohexanol.
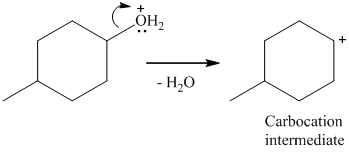
Here, the good leaving group is H2O. The derivative of hydronium ion removes a water molecule to form a carbocation intermediate.
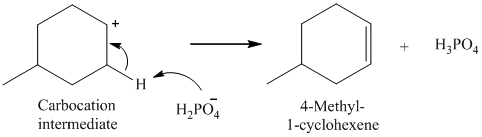
The nucleophile (H2PO4-) abstracts a proton from adjacent carbon of carbocation to form 4-methyl-1-cyclohexene.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
A Small Scale Approach to Organic Laboratory Techniques
- Write a mechanism for the enolization of a ketone. Show how acids and bases can act as catalysists of this reaction.arrow_forwardFollowing is a retrosynthetic analysis for an intermediate in the industrial synthesis of vitamin A. (a) Addition of one mole of HCl to isoprene gives 4-chloro-2-methyl-2-butene as the major product. Propose a mechanism for this addition and account for its regioselectivity. (b) Propose a synthesis of the vitamin A precursor from this allylic chloride and ethyl acetoacetate.arrow_forwardThe base-promoted rearrangement of an -haloketone to a carboxylic acid, known as the Favorskii rearrangement, is illustrated by the conversion of 2-chlorocyclohexanone to cyclopentanecarboxylic acid. It is proposed that NaOH first converts the a-haloketone to the substituted cyclopropanone shown in brackets and then to the sodium salt of cyclopentanecarboxylic acid. (a) Propose a mechanism for base-promoted conversion of 2-chlorocyclohexanone to the proposed intermediate. (b) Propose a mechanism for base-promoted conversion of the proposed intermediate to sodium cyclopentanecarboxylate.arrow_forward
- o - Nitroaniline is more soluble in ethanol than p - nitroaniline. Propose a scheme by which a pure sample of o-nitroaniline might be obtained from this reactionarrow_forwardWrite a mechanism for the formation of cyclic ketal under acid catalysis in benzene. The catalysis is p-toluenesulfonic acid.arrow_forwardWrite a mechanism that shows how isopropylidenecyclopentane is produced by the dehydration of 2,2-dimethylcyclohexanol in an acid medium.arrow_forward
- Propose mechanisms for the base-catalyzed hydration of acetone to form acetone hydrate.arrow_forwardwrite the mechanism for a decarboxylation and state the structural features necessary for a decarboxylation.arrow_forwardWrite the preparation of 2,4,4-trimethyl-2-pentenal using 2,2-dimethylpropanal and other necessary reagents, showing the reaction mechanism.arrow_forward
- Starting with benzene, outline a procedure for synthesizing m-chloroaniline.arrow_forwardPropose mechanisms for the acid-catalyzed hydration of chloral to form chloral hydrate.arrow_forwardGive a plausible mechanism for the reaction of o-bromobenzoic acid and 1-propanol (with HCI) to yield propyl o-bromobenzoate.arrow_forward
 EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

