
Equity as an Option and
a. What is the value of the firm’s equity and debt if Project A is undertaken? If Project B is undertaken?
b. Which project would the stockholders prefer? Can you reconcile your answer with the NPV rule?
c. Suppose the stockholders and bondholders are, in fact, the same group of investors. Would this affect your answer to (b)?
d. What does this problem suggest to you about stockholder incentives?
a.
To compute: Value of the firm’s equity and debt under project A and project B.
Option Pricing:
Option pricing helps in determining correct or fair price in the market. It is the value of one share on the basis of which option is traded. Black-Scholes is one of the pricing methods. Further, equity is also used as an option.
Explanation of Solution
Project A
Given,
Stock price is
Exercise price is 20,000.
Risk free rate is 0.05.
Time to expire is 1 year.
Formula to calculate the value of equity by using Black Scholes model is,
Where,
- S is stock price.
- E is exercise price.
- R is risk free rate.
- T is time to expire.
Substitute $22,900 for S, $20,000 for E, 0.05 for R, and 1 for T.
Formula to calculate the value of debt is,
Substitute $22,900 as value of firm and $9,019.78 as value of equity.
Project B
Given,
Stock price is $21,700.
Exercise price is 20,000.
Risk free rate is 0.05.
Time to expire is 1 year.
Formula to calculate the value of equity by using Black Scholes model is,
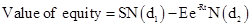
Where,
- S is stock price.
- E is exercise price.
- R is risk free rate.
- T is time to expire.
Substitute $21,700 for S, $20,000 for E, 0.05 for R, and 1 for T.
Formula to calculate the value of debt is,
Substitute $21,700 as value of firm and $4,285.82 as value of equity.
Working Note:
Formula to calculate
Calculation of
From normal distribution table
Calculation of
From normal distribution table
Formula to calculate
Calculation of
From normal distribution table
Calculation of
From normal distribution table
Hence, for Project A the value of firm’s equity is $9,019.78, value of firm’s debt is$13,880.22 and for Project B the value of firm’s equity is $4,285.82 and value of firm’s debt is $17,414.18.
b.
To identify: Project that would be preferred by stockholders.
Answer to Problem 22QP
- Here, equity’s value is higher in Project A than Project B.
- Project A does not create more bondholders.
Explanation of Solution
- If Project A is considered, it has increased the firm’s assets to$1,200.
- If Project B is considered, it has increased the firm’s assets to$1,600.
- NPV rules say Project B should be accepted, but value of equity is more in the case of Project A rather than Project B, which shows that Project A has less of bondholders.
- Thus, Project A is more attractive.
Hence, the stockholders prefer Project A.
c.
To identify: Project that would be preferred by stockholders if both stockholders and bondholders are same.
Answer to Problem 22QP
As Project B adds more value to the firm, this would be a good option.
Explanation of Solution
- If stockholders and bondholder would be the same, in that case their interest would also be the same and they can get benefits equally.
- Since Project A increases the firm’s assets to$1,200 and Project B increases the firm’s assets to$1,600.
- Thus, Project B is more attractive.
Hence, the stockholders prefer Project B.
d.
To explain: The effect on stockholders incentives.
Answer to Problem 22QP
In case of leveraged firm, stockholders would definitely prefer those projects, which would increase value of equity.
Explanation of Solution
- Reason for opting equity source is that in the case of debt source, risk is borne by the bondholders and benefits are limited to their debt value, which is not happening in the case of equity sources.
- All benefits after paying the debt, goes to the stockholders pocket.
- Thus, the stockholders incentive would relate to the project that adds more value to the equity.
Hence, stockholder’s incentives are more related with the project that contains equity.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
CORPORATE FINANCE (LL)-W/ACCESS
- What makes for a good investment? Use the approximate yield formula or a financial calculator to rank the following investments according to their expected returns. Buy a stock for $30 a share, hold it for three years, and then sell it for $60 a share (the stock pays annual dividends of $2 a share). Buy a security for $40, hold it for two years, and then sell it for $100 (current income on this security is zero). Buy a one-year, 5 percent note for $1,000 (assume that the note has a $1,000 par value and that it will be held to maturity).arrow_forwardConsider a market where the assumptions behind the Black-Scholes model hold. A non-dividend paying share is currently priced at $300. A put option is available on the share with a strike price of $320 and one year to expiry. Volatility of 15% and the risk-free rate is 5% per annum. What would be the fair price of the put option.arrow_forwardA risky $420,000 investment is expected to generate the following cash flows: Year 1 2 3 4$ 102,700 $ 163,030 $ 160,824 $ 135,200 If the firm’s cost of capital is 12 percent, should the investment be made?. Use a minus sign to enter a negative value, if any. Round your answer to the nearest dollar.NPV: $ Should The investment be made? An alternative use for the $420,000 is a four-year U.S. Treasury bond that pays $25,200 annually and repays the $420,000 at maturity. Management believes that the cash inflows from the risky investment are equivalent to only 70 percent of the certain investment, which pays 6 percent. Should the investment be made? Use Appendix B to answer the question. Do not round other intermediate calculations. NPV: $ Should The investment be made?arrow_forward
- Roundall dollar answers to 2 decimal places and record all interest rate, coupon rate and growth rate answers as a percentrounded to one decimal place 40. If the expected return on the market portfolio (i.e., Rm) is 18%, if the risk-free rate (i.e., Rf) is 8% and if thebeta of Homton, Inc. stock is 1.75, what is the equilibrium expected rate of return on Homton’s stockaccording to the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM)? (Record your answer rounded to 1 decimal place; forexample, record 18.29654% as 18.3).41. If the beta of Braxton, Inc. stock is 1.51, the risk-free rate (Rf) is 3.5%, and the market risk premium is 4.8%,what is the equilibrium expected rate of return on Braxton’s stock according to the Capital Asset PricingModel (CAPM)? (Record your answer rounded to 1 decimal place; for example, record 18.29654% as 18.3)arrow_forwardyou are considdering an investment in justus corporatiuon which is expected to pay a divident of $2.25 a share at the end of the year (D1=$2.25) and his a beta of 0.9 . the risk free rate is 4.9 and the market risk primum is 5% .justus currently sells $46.00 a share its divdent is expexted to grow at some constant rate g, assuming the market is in equilibrium , what does the market belive will be the stock price at the end of 3 year ?(that is what is p3?)arrow_forwardSuppose Firm 1 is 100% equity financed. Firm 1 has a project available that offers a 10% return on average and has the same systematic risk as Firm 1. Assume that the risk-free rate is 2%, the stock market return premium (Rm - Rf) is 7%, the CAPM beta is 1.3, and estimate the future required return for Firm 1 (when estimating the required return for Firm 1 going forward, assume an alpha of zero). All returns are on an annual basis. Should Firm 1 do its project?arrow_forward
- Assume that you are using the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) to find the expected return for a share of common stock. Your research shows the following: Beta = βi = 1.54 Risk free rate = Rf = 2.5% per year Market return = E(RM) = 6.5% per year Based on this information, answer the following: A. Based on the beta, how does the stock's risk compare to the market overall? On what do you base your answer? B. Based on the beta, how would you expect the stock's returns to react to a decrease in returns in the market overall? Why? C. According to the CAPM and the information given above, what is the expected return E(Ri) for this stock? D. If the required rate of return on this stock were 7% per year, would you invest? Why or why not?arrow_forwardExplain how a financial market operates? Which of the investment constraints is expected to have the most impact on your decision process? You plan to buy common stock and hold it for one year. You expect to receive both ₱150 and ₱260 from the sale of the stock at the end of the year. How much will you pay for the stock, if you want to a. Have a return of 8% b. A return of 20% c. A return of 15%arrow_forwardAn all-equity firm is considering the projects shown below. The T-bill rate is 4 percent and the market risk premium is 7 percent. If the firm uses its current WACC of 12 percent to evaluate the projects, which project(s), if any, will be incorrectly accepted? Expected Return Beta Project A 8.0% 0.5 Project B 19.0% 1.2 Project C 13.0% 1.4 Project D 17.0% 1.6arrow_forward
- An all-equity firm has a beta of 1.2. The firm is evaluating a project that will increase the output of the firm's existing products. The market risk premium is 6.5 percent and the risk-free rate is 3.5 percent. What discount rate should be assigned to this expansion project?arrow_forwardAssume that the Collins Company has a beta of 1.8 and that the risk-free rate of return is 2.5 percent. If the equity-risk premium is six percent, calculate the cost of equity for the Collins Company using the capital asset pricing model.arrow_forwardRanking investments by expected returns What makes for a good investment? Use the approximate yield formula or a financial calculator to rank the following investments according to their expected returns. Round the answers to two decimal places. Do not round intermediate calculations. Buy a stock for $45 a share, hold it for 3 years, then sell it for $75 a share (the stock pays annual dividends of $3 a share). % Buy a security for $25, hold it for 2 years, then sell it for $60 (current income on this security is zero). Do not round intermediate calculations. % Buy a 1-year, 12 percent note for $950 (assume that the note has a $1,000 par value and that it will be held to maturity). Do not round intermediate calculations. %arrow_forward
 EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning Pfin (with Mindtap, 1 Term Printed Access Card) (...FinanceISBN:9780357033609Author:Randall Billingsley, Lawrence J. Gitman, Michael D. JoehnkPublisher:Cengage Learning
Pfin (with Mindtap, 1 Term Printed Access Card) (...FinanceISBN:9780357033609Author:Randall Billingsley, Lawrence J. Gitman, Michael D. JoehnkPublisher:Cengage Learning




