
Concept explainers
Devise efficient syntheses of each of the following compounds from the designated startingmaterials. You may also use any necessary organic or inorganic reagents.

Interpretation:
Efficient syntheses are to be designed for each of the five compounds with designated starting materials and necessary organic or inorganic compounds.
Concept introduction:
Synthesis of amines can be done in a variety of ways, based on forming a bond between a carbon and a nitrogen.
Nucleophilic substitution reactions on alkyl halides or alcohols by a nitrogen containing reagent is one of the common methods.
Primary amines can be synthesized by nucleophilic substitution of an alkyl halide with cyanide. The resulting compound, called a nitrile, yields a primary amine on catalytic reduction with hydrogen.
Secondary and particularly tertiary amines can be formed by reaction between ammonia and an excess of alkyl halide.
Another method involves nucleophilic addition of simpler amines to an aldehyde or a ketone.
Carboxylic acid derivatives such as acid halides, anhydrides, and esters undergo nucleophilic substitution by ammonia or a variety of simpler amines to give amides. The amides on reduction gives amines.
Benzyl radical is stabilized by delocalization of the unpaired electron on to the benzene ring. This helps in selective radical substitution of hydrogens and halogens in benzylic position.
Answer to Problem 45P
Solution:
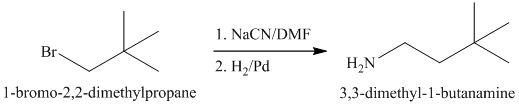
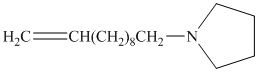 from
from
c)
 from
from 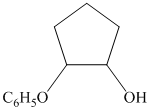 :
:
d)
e)
 from
from 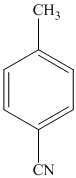 :
:
Explanation of Solution
a)
The substrate is a primary alkyl halide; therefore, substitution of the bromine requires a strong nucleophile such as cyanide ion via an
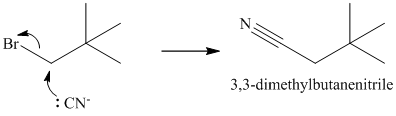
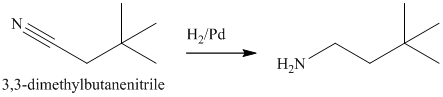
The nitrile yields the desired amine on catalytic reduction.
b)
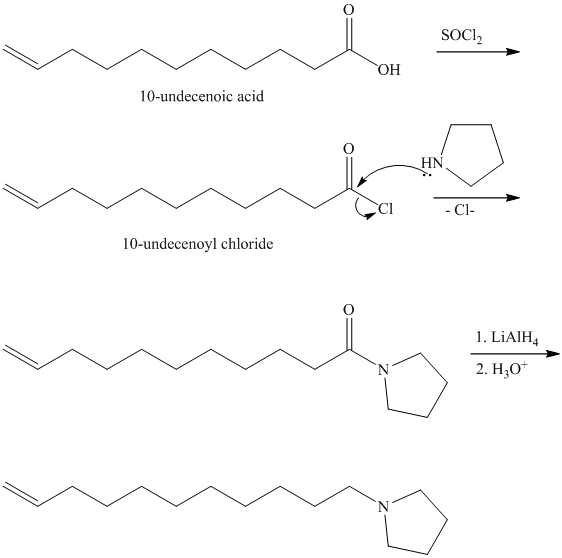
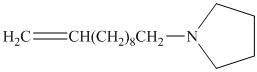 from
from
Carboxylic acids and amines can react to form amides by nucleophilic substitution of the hydroxyl group by the amine. However, carboxylic acids are poor electrophiles and are relatively unreactive. The first step is then to activate the acid by converting it to a stronger electrophile such as an acid chloride.
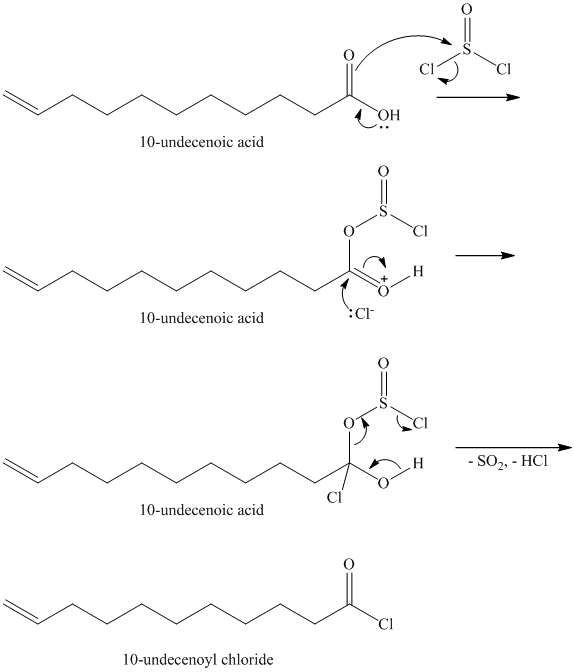
The chloride then undergoes substitution by
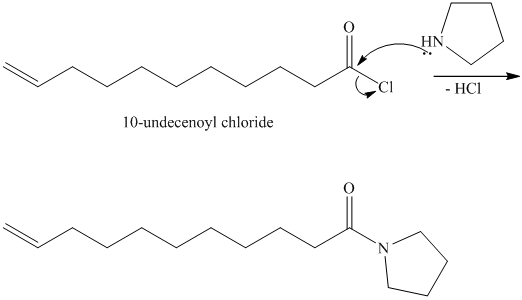
This contains both a carbonyl group that needs to be reduced to a methylene and a double bond. Catalytic reduction will result in reduction of the carbonyl group as well as an unwanted reduction of the double bond. Therefore, reduction of the carbonyl to methylene bridge is done with lithium aluminum hydride.
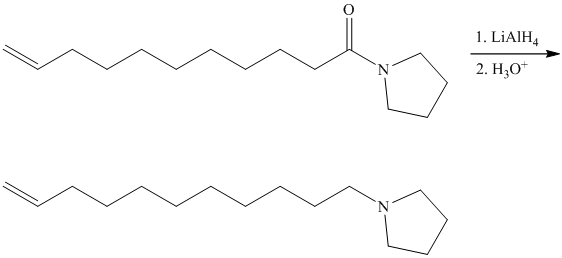
The hydride ion (
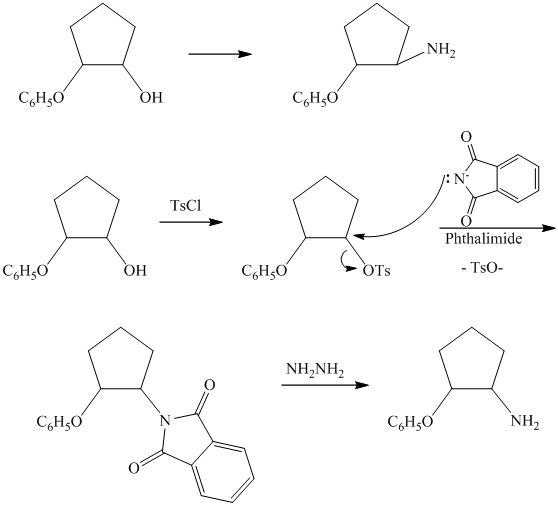
c)
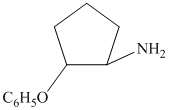
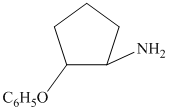 from
from 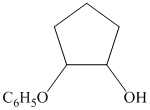 :
:
The synthesis requires substitution of the hydroxyl group of the substrate. Hydroxyl group is a poor leaving group as the hydroxide ion is a strong base. It first needs to be converted to a better leaving group. This is done by reaction with tosyl chloride, to give a tosylate.
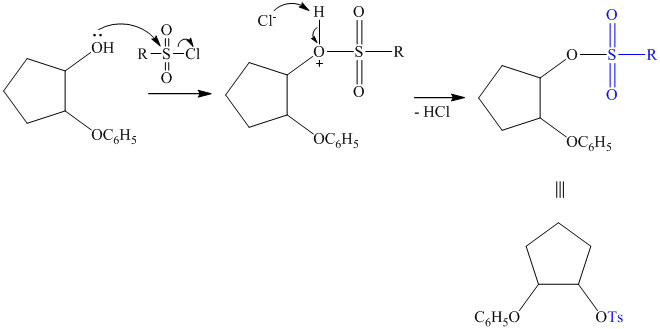
Tosylate ion is the conjugate base of a strong acid, so it can be easily replaced by a suitable nucleophile like phthalimide.
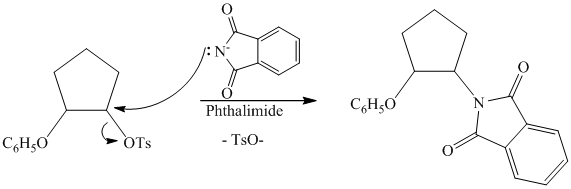
Reaction of the tosylate with phthalimide is an
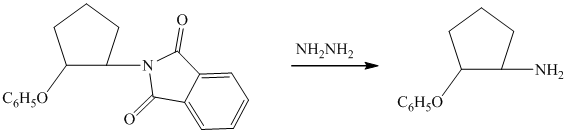
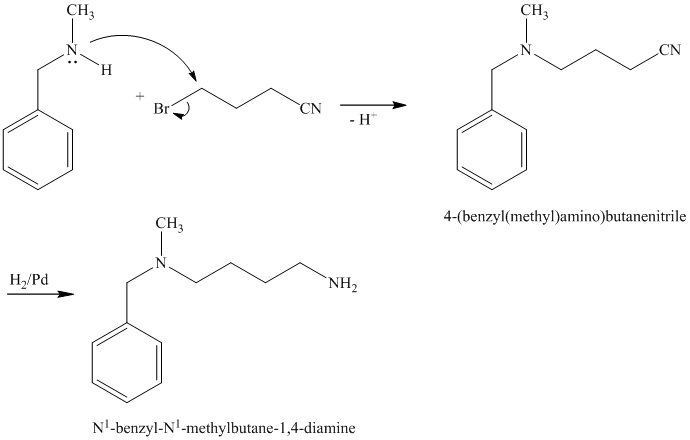
d)
The first of the designated starting compounds
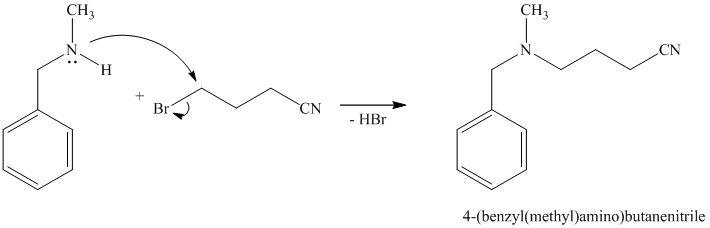
The nitrile (cyanide) function can then be reduced with hydrogen over palladium to yield the desired product.
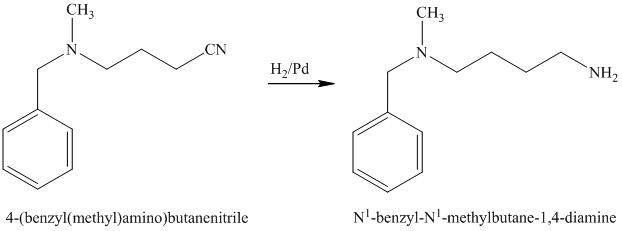
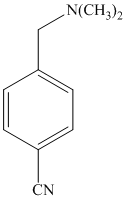
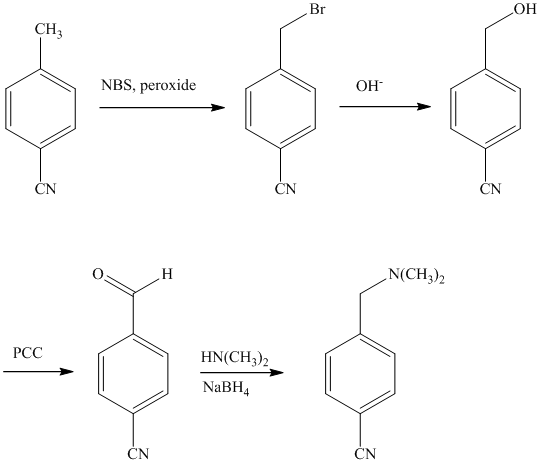
e)
The methyl substituent on the benzene ring needs to be converted to an amine. This requires first converting it to an alkyl halide. This is a substitution of a hydrogen in a benzylic position. A convenient method is to treat it with
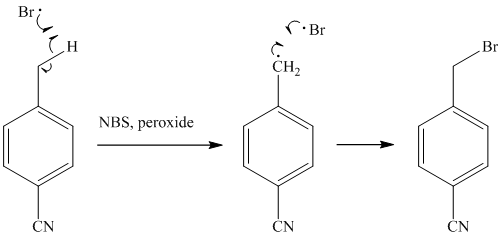
The resulting bromide can be reacted directly with dimethyl amine to yield the product. However, there is a possibility of formation of a quaternary ammonium compound. Therefore, the bromide is converted to a primary alcohol by reacting it with hydroxide.
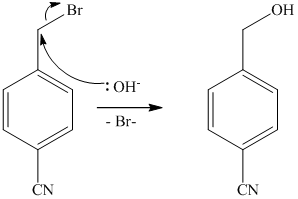
The alcohol is then oxidized to aldehyde using pyridiniumchlorochromate.
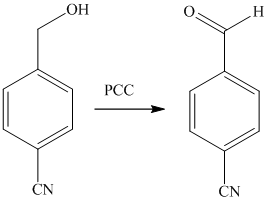
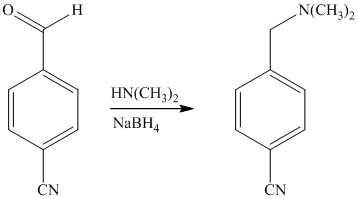
Reaction of the aldehyde can then be subjected to reductive amination, reaction with dimethyl amine in the presence of sodium borohydride, to yield the desired product. The reaction initially forms an imine, but that is directly reduced by sodium borohydrideinstead of isolating it.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 22 Solutions
Organic Chemistry - Standalone book
- The following bicyclic ketone has two -carbons and three -hydrogens. When this molecule is treated with D2O in the presence of an acid catalyst, only two of the three -hydrogens exchange with deuterium. The -hydrogen at the bridgehead does not exchange. How do you account for the fact that two -hydrogens do exchange but the third does not? You will find it helpful to build models of the enols by which exchange of -hydrogens occurs.arrow_forwardWhen warmed in dilute sulfuric acid, 1-phenyl-1,2-propanediol undergoes dehydration and rearrangement to give 2-phenylpropanal. (a) Propose a mechanism for this example of a pinacol rearrangement (Section 10.7). (b) Account for the fact that 2-phenylpropanal is formed rather than its constitutional isomer, 1-phenyl-1-propanone.arrow_forwardAuthentic skunk spray has become valuable for use in scent-masking products. Show how you would synthesize the two major components of skunk spray (3-methylbutane-1-thiol and but-2-ene-1-thiol) from any of the readily available butenes or from buta-1,3-diene.arrow_forward
- Deuterium (D, or 2H) is an isotope of hydrogen with atomic mass=2. Deuterium can be introduced into organic compounds by using reagents in which hydrogen has been replaced by deuterium. Outline preparation of the following compounds from the same alkene using appropriate deuterium-containing reagents.arrow_forwardStarting with benzene, toluene, or phenol as the only sources of aromatic rings, show how to synthesize the following. Assume in all syntheses that mixtures of ortho-para products can be separated into the desired isomer. Q.) 1-Bromo-3-nitrobenzenearrow_forwardTo synthesize trans-cinnamic acid from benzaldehyde (PhCHO) and acetic anhydride (Ac2O) under basic, refluxing conditions to exemplify the Perkin condensation. 1. Draw the complete chemical reaction to be carried out. 2. Provide a complete arrow-pushing mechanism for the synthesis of trans-cinnamic acid. 3. Briefly describe the role of water, Na2CO3, and HCl in the isolation of the product. Draw the structure of the product at basic pH (after Na2CO3 addition) and at acidic pH (after HCl addition).arrow_forward
- Show how you might synthesize the following compounds, using acetylene and anysuitable alkyl halides as your starting materials. If the compound given cannot besynthesized by this method, explain why. cyclodecynearrow_forwardGive the appropriate reagents for each of the following synthetic conversions......?arrow_forwardThe sex pheromone of the common house fly has the molecular formula C23H46. It can be synthesized in the lab using the following synthetic sequence. Give the structures of the pheromone and the intermediates A and B. n-C13H27C≡CH + n-butyl lithium → A (C15H27Li) A + n-C8H17Br → B (C23H44) B + H2 with Lindlar catalyst → the pheromonearrow_forward
- Syntheses of each of the following compounds have been reported in the chemical literature. Using the indicated starting material and any necessary organic or inorganic reagents, describe short sequences of reactions that would be appropriate for each transformation. (a) 1,1,5-Trimethylcyclononane from 5,5-dimethylcyclononanonearrow_forwardThe following compound may be synthesized through alkylation of an appropriate enamine with an alkyl bromide, followed by hydrolysis of the resulting immonium ion. Using this strategy, provide the necessary starting materials for the synthesis. (Note that a portion of the starting enamine is given.)arrow_forwardWrite equations showing how to prepare each of the following from benzene or toluene and any necessary organic or inorganic reagents. If an ortho, para mixture is formed in any step of your synthesis, assume that you can separate the two isomers. (a) Isopropylbenzene (b) p-Isopropylbenzenesulfonic acid (c) 2-Bromo-2-phenylpropane (d) 4-tert-Butyl-2-nitrotoluene (e) m-Chloroacetophenone (f) p-Chloroacetophenone (g) 3-Bromo-4-methylacetophenone (h) 2-Bromo-4-ethyltoluene (i) 3-Bromo-5-nitrobenzoic acid (j) 2-Bromo-4-nitrobenzoic acid (k) 1-Phenyloctane (l) 1-Phenyl-1-octene (m) 1-Phenyl-1-octyne (n) 1,4-Di-tert-butyl-1,4-cyclohexadienearrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
