
Concept explainers
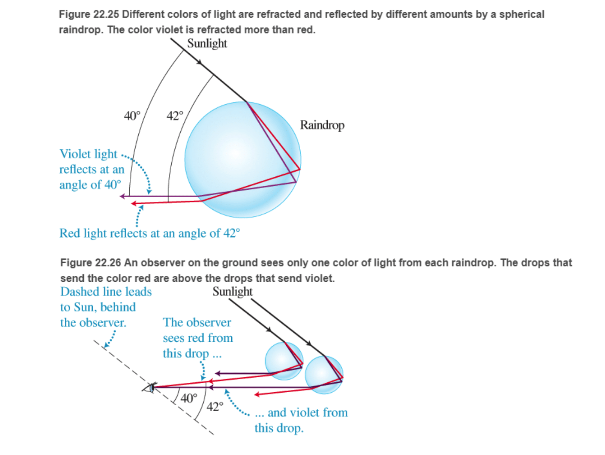
Rainbows How is a rainbow formed? Recall that the index of refraction of a medium is slightly different for different colors. When white light from the Sun enters a spherical raindrop, as shown in Figure 22.25, the light is refracted, or bent After reflecting off the back surface of the drop, the light is refracted again as it leaves the front surface.
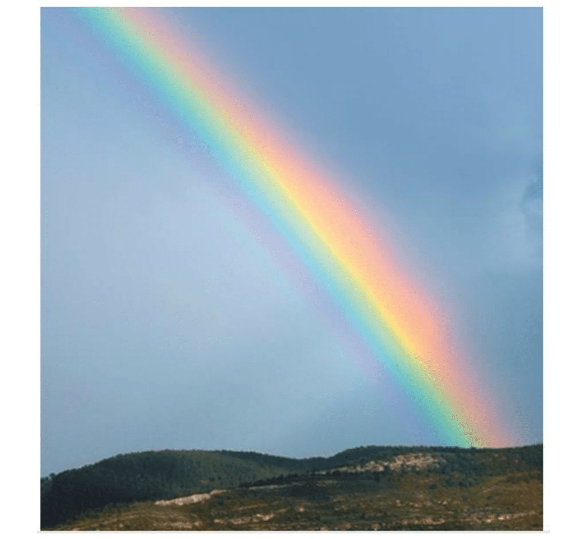

Each drop separates the colors of light. An observer on the ground with her back to the Sun sees at most one color of light coming from a particular drop (see Figure 22.26). If the observer sees rod light from a drop (for example, the top drop in Figure 22.26). the violet light for that same drop is deflected above her head. However, if she sees violet light coming from a drop lower in the sky the red light from that drop is defected below her eyes onto the ground She sees red light when her line of view makes an angle of
Earth energy balance Gases in Earth's atmosphere, such as carbon dioxide and water vapor act like a blanket that reduces the amount of energy that Earth radiates into space. This phenomenon is called the greenhouse effect. Without the greenhouse effect most of Earth would have a climate comparable to that of the polar or subpolar regions What would Earth's mean surface temperature be, in the absence of the gases causing the greenhouse effect?
The Sun continually irradiates our upper atmosphere with an intensity of about
About
To maintain a constant temperature, Earth's radiation rate must equal its energy absorption rate from the Sun A fairly simple calculation indicates that the two rates are equal when the average surface temperature of Earth is 255 K or about
Over the past two centuries the concentration of carbon dioxide in our atmosphere has increased from a pre- industrial level of about 270 parts per million to 380 parts per million. This increase in carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases has been caused by the burning of fossil fuels and the removal of forests, which absorb carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide concentration in the atmosphere is expected to reach 600-700 parts per million by 2100. If that occurs, it will be warmer in 2100 than at any time in the last half million years.
The Sun irradiates Earth’s outer atmosphere at what rate?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 22 Solutions
College Physics
- In a laboratory accident, you spill two liquids onto different parts of a water surface. Neither of the liquids mixes with the water. Both liquids form thin films on the water surface. As the films spread and become very thin, you notice that one film becomes brighter and the other darker in reflected light. Why?arrow_forwardYou are working for an optical research company during a summer break. Part of the apparatus in one particular experiment is shown in Figure 34.7b. In fact, the experimenter used this text book to set up this part of the experiment, and also used the result in the What If? section to determine the angular change in direction of the light beam: =3602 (1) The experimenter is constantly grumbling that the measuring device to determine the angle on the inside of the mirrors is constantly getting in the wav of the light beam and making his life difficult. You quickly draw Figure P34.5 and then say. Then why dont you use the measuring device to measure the angle outside the mirror, and then your device wont get in the way of the light? The experimenter, who has never thought of this, tries to save face and says to you. Well, Smarty, then tell me how angle depends on angle ! You provide him the answer quickly. Figure P34.5arrow_forwardYou are working for a solar energy company. Your supervisor has asked you to investigate a new idea that has been proposed for a solar collector. A large sphere of glass focuses light on photocells, as shown in Figure P35.22. The photocells are moved by electronics along the curved track to the right of the sphere. Your supervisor would like to build a prototype of a material with index of refraction n, but needs for you to calculate the position at which the Suns rays focus and, therefore, to find where to locale the curved track. Figure P35.22arrow_forward
- Calculate the index of refraction for a medium in which the speed of light is 2.012108m/s , and identify the most likely substance based on Table 25.1.arrow_forwardIn placing a sample on a microscope slide, a glass cover is placed over a water drop on the glass slide. Light incident from above can reflect from the top and bottom of the glass cover and from the glass slide below the water drop. At which surfaces will there be a phase change in the reflected light?arrow_forwardThe speed of a water wave is described by v=gd, where d is the water depth, assumed to be small compared to the wavelength. Because their speed changes, water waves refract when moving into a region of different depth. (a) Sketch a map of an ocean beach on the eastern side of a landmass. Show contour lines of constant depth under water, assuming a reasonably uniform slope. (b) Suppose waves approach the coast from a storm far away to the northnortheast. Demonstrate that the waves move nearly perpendicular to the shoreline when they reach the beach. (c) Sketch a map of a coastline with alternating bays and headlands as suggested in Figure P34.26. Again make a reasonable guess about the shape of contour lines of constant depth. (d) Suppose waves approach the coast, carrying energy with uniform density along originally straight wave fronts. Show that the energy reaching the coast is concentrated at the headlands and has lower intensity in the bays. Figure P34.26arrow_forward
- Thomas Young’s conception of the fundamental nature of light differed from that of Newton. Compare these two views of light, and give some experimental or observational evidence to sustain each of these representations.arrow_forwardDoes the fact that the light flash from lightning teaches you before its sound prove that the speed of light is extremely large or simply that it is greater than the speed at sound? Discuss how you could use this effect to get an estimate of the speed of light.arrow_forwardA diverging lens has a focal length of 20.0 cm. Use graph paper to construct accurate ray diagrams for object distance of (a) 40.0cm and (b) 10.0 cm. In each case, determine the location of the image from the diagram and the image magnification, and state whether the image is uptight or inverted. (c) Estimate the magnitude of uncertainty in locating the points in the graph. Are your answers and the uncertainty consistent with the algebraic answers found in Problem 33?arrow_forward
- A beam in air strikes a glass ball as shown in Figure 37.8. Draw the reflected ray.arrow_forwardA layer of ice having parallel sides floats on water. If light is incident on the upper surface of the ice at an angle of incidence of 30.0, what is the angle of refraction in the water?arrow_forwardLight passes from air into flint glass at a nonzero angle of incidence. (a) Is it possible for the component of its velocity perpendicular to the interface to remain constant? Explain your answer. (b) What If? Can the component of velocity parallel to the interface remain constant during refraction? Explain your answer.arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





