
Concept explainers
(a)
The
(a)
Answer to Problem 18P
The
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The charge of particle
The diagram for the given condition is shown below.
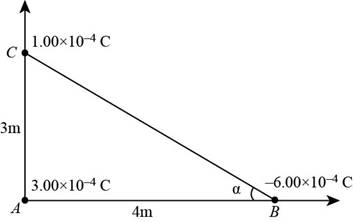
Figure 1
The formula to calculate the electrical force is,
Here,
The particle
The distance from the
Thus, the
Conclusion:
Therefore, the
(b)
The
(b)
Answer to Problem 18P
The
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The charge of particle
The formula to calculate the electrical force is,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the
(c)
The magnitude of the force exerted by
(c)
Answer to Problem 18P
The magnitude of the force exerted by
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The charge of particle
By Pythagoras theorem the distance between
Thus, the distance between
The formula to calculate the electrical force is,
Here,
Substitute
The magnitude of the force exerted by
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnitude of the force exerted by
(d)
The
(d)
Answer to Problem 18P
The
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The charge of particle
From part (c), the magnitude of the force exerted by
Resolve the side
From Figure I
The formula to calculate the
Here,

Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the
(e)
The
(e)
Answer to Problem 18P
The
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The charge of particle
From part (c), the magnitude of the force exerted by
Resolve the side
From Figure I,
The formula to calculate the
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the
(f)
The resultant
(f)
Answer to Problem 18P
The resultant
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The charge of particle
From part (a), the
From part (d), the
The formula to calculate the resultant force acting on the particle
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the resultant
(g)
The resultant
(g)
Answer to Problem 18P
The resultant
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The charge of particle
From part (b), the
From part (e), the
The formula to calculate the resultant force acting on the particle
Here,
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the resultant
(h)
The magnitude and direction of the resultant electric force acting on
(h)
Answer to Problem 18P
The magnitude and direction of the resultant electric force acting on
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The charge of particle
From part (g), the resultant
From part (f), the resultant
The formula to calculate the resultant force acting on the particle
Here,
Substitute
The formula to calculate the direction of the resultant force acting on
Here,
Substitute
The direction of the resultant force is counterclockwise from
Conclusion:
Therefore, the magnitude and direction of the resultant electric force acting on
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 23 Solutions
Physics For Scientists And Engineers With Modern Physics, 9th Edition, The Ohio State University
- A particle with charge q on the negative x axis and a second particle with charge 2q on the positive x axis are each a distance d from the origin. Where should a third particle with charge 3q be placed so that the magnitude of the electric field at the origin is zero?arrow_forwardTwo particles with charges q1 and q2 are separated by a distance d, and each exerts an electric force on the other with magnitude FE. a. In terms of these quantities, what separation distance would cause the magnitude of the electric force to be halved? b. In terms of these quantities, what separation distance would cause the magnitude of the electric force to be doubled?arrow_forwardPanicle A of charge 3.00 104 C is at the origin, particle B of charge 6.00 104 C is at (4.00 m, 0), and panicle C of charge 1.00 104 C is at (0, 3.00 m). (a) What is the x-component of the electric force exerted by A on C? (b) What is the y-component of the force exerted by A on C? (c) Find the magnitude of the force exerted by B on C. (d) Calculate the x-component of the force exerted by B on C. (e) Calculate the y-component of the force exerted by B on C. (f) Sum the two x-components to obtain the resultant x-component of the electric force acting on C. (g) Repeat part (f) for the y-component. (h) Find the magnitude and direction of the resultant electric force acting on C.arrow_forward
- Particle A of charge 3.00 104 C is at the origin, particle B of charge 6.00 101 C is at (4.00 m, 0), and particle C of charge 1.00 104 C is at (0, 3.00 in). We wish to find the net electric force on C. (a) What is the x component of the electric force exerted by A on C? (b) What is the y component of the force exerted by A on C? (c) Kind the magnitude of the force exerted by B on C. (d) Calculate the x component of the force exerted by B on C. (e) Calculate the y component of the force exerted by B on C. (f) Sum the two x components from parts (a) and (d) to obtain the resultant x component of the electric force acting on C. (g) Similarly, find the y component of the resultant force vector acting on C. (h) Kind the magnitude and direction of the resultant electric force acting on C.arrow_forwardA point charge of 4.00 nC is located at (0, 1.00) m. What is the x component of the electric field due to the point charge at (4.00, 2.00) m? (a) 1.15 N/C (b) 0.864 N/C (c) 1.44 N/C (d) 1.15 N/C (e) 0.864 N/Carrow_forwardPanicle A of charge 3.00 104 C is at the origin, particle B of charge 6.00 104 C is at (4.00 m, 0), and panicle C of charge 1.00 104 C is at (0, 3.00 m). (a) What is the x-component of the electric force exerted by A on C? (b) What is the y-component of the force exerted by A on C? (c) Find the magnitude of the force exerted by B on C. (d) Calculate the x-component of the force exerted by B on C. (e) Calculate the y-component of the force exerted by B on C. (f) Sum the two x-components to obtain the resultant x-component of the electric force acting on C. (g) Repeat part (f) for the y-component. (h) Find the magnitude and direction of the resultant electric force acting on C.arrow_forward
- A 1.75-nC charged particle located at the origin is separated by a distance of 0.0825 m from a 2.88-nC charged particle located farther along the positive x axis. If the 1.75-nC particle is kept fixed at the origin, where along the positive x axis should the 2.88-nC particle be located so that the magnitude of the electrostatic force it experiences is twice as great as it was in Problem 27?arrow_forwardA circular ring of charge of radius b has a total charge q uniformly distributed around it. Find the magnitude of the electric field in the center of the ring. (a) 0 (b) keq/b2 (c) keq2/b2 (d) keq2/b (e) None of these answers is correct.arrow_forwardThree charged particles are located at the corners of an equilateral triangle as shown in Figure P19.9. Calculate the total electric force on the 7.00-C charge.arrow_forward
- Is it possible for a conducting sphere of radius 0.10 m to hold a charge of 4.0 C in air? The minimum field required to break down air and turn it into a conductor is 3.0 106 N/C.arrow_forwardCharges A, B, and C are arranged in the xy plane with qA = 5.60 C, qB = 4.00 C, and qC = 2.30 /C (Fig. P23.43). What are the magnitude and direction of the electrostatic force on charge B? Figure P23.43arrow_forwardA Two positively charged particles, each with charge Q, are held at positions (a, 0) and (a, 0) as shown in Figure P23.73. A third positively charged particle with charge q is placed at (0, h). a. Find an expression for the net electric force on the third particle with charge q. b. Show that the two charges Q behave like a single charge 2Q located at the origin when the distance h is much greater than a. Figure P23.73 Problems 73 and 74.arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning





