Tutorials In Introductory Physics: Homework
1st Edition
ISBN: 9780130662453
Author: Lillian C. McDermott, Peter S. Shaffer
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 24.5, Problem 1dTH
To determine
Toexplain:
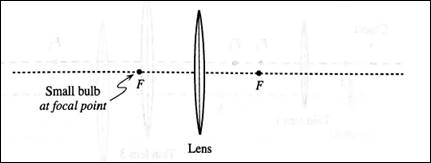
The location of the image formed by an object placed at focus of a converging lens.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
The diagram below shows the situation described in the problem. The focal length of the lens is labeled f; the scale on the
optical axis is in centimeters. Draw the three special rays, Ray1, Ray2, and Ray3 as described in the Tactics Box above,
and label each ray accordingly. Draw the rays from the tip of the object to the center vertical axis of the lens. Do not draw
the refracted rays.
Draw the vectors for the incident rays starting at the tip of the object to the center vertical axis of the lens. The
location and orientation of the vectors will be graded.
Vectors:
Ray3 Ray though center of lens
Ray2 Ray through near focal point
Rayl Ray parallel to axis
Unlabeled vector
Object
1.Place your object at a distance equal to the focal length (f) of your diverging lens. Where is your image located? Describe the type of image formed based on size, orientation, and condition and provide a screenshot of your set-up.
2.Place your object at a distance less than the focal length (f) of your diverging lens. Where is your image located? Describe the type of image formed based on size, orientation, and condition and provide a screenshot of your set-up.
Suppose you know the six cardinal points of an optical system (two focal points F1 and F2, two principal
points H1 and H₂ and two nodal points N₁ and N₂), complete the three special rays to locate the image
position formed by this system. Label the focal lengths, object distance and image distance. [Hint: A ray
parallel to optical axis, turns to the focal point F2 after passing through the principle plane H₂. A ray through
Fi will turn to parallel after H₁. A ray moving towards to N₁ will emerge at N₂ with the same angle. In a thick
lens, N overlaps with H point if the refractive index is the same on both sides of the lens.]
F₁
H1 N₁ H₂ N₂ F₂
Chapter 24 Solutions
Tutorials In Introductory Physics: Homework
Ch. 24.1 - On the diagram, sketch what you would see on the...Ch. 24.1 - The small bulb is replaced by three longfilament...Ch. 24.1 - The three longfilament bulbs are replaced by a...Ch. 24.1 - Predict the size and shape of the shadow that will...Ch. 24.1 - Is it possible to place the bulb in another...Ch. 24.1 - Prob. 2cTHCh. 24.1 - Prob. 2dTHCh. 24.1 - Prob. 3aTHCh. 24.1 - A student is looking at the building shown at...Ch. 24.1 - Prob. 4aTH
Ch. 24.1 - Suppose that this student were walking through the...Ch. 24.2 - The top view diagrams at right were drawn by a...Ch. 24.2 - Draw a ray diagram to determine the location of...Ch. 24.2 - Describe how you could use a ray diagram to...Ch. 24.2 - A pencil is placed in front of a plane mirror as...Ch. 24.2 - Prob. 3bTHCh. 24.3 - Prob. 1aTHCh. 24.3 - A pin is placed in front of a semicylindrical...Ch. 24.3 - Prob. 1cTHCh. 24.3 - Prob. 2aTHCh. 24.3 - A very small, very bright bulb is placed for from...Ch. 24.4 - The following are top view diagrams of solid...Ch. 24.4 - The following are top view diagrams of solid...Ch. 24.4 - The following are top view diagrams of solid...Ch. 24.4 - The following are top view diagrams of solid...Ch. 24.4 - Prob. 2THCh. 24.4 - Prob. 3aTHCh. 24.4 - Prob. 3bTHCh. 24.4 - Is the image(s) of the nail real or virtual?...Ch. 24.5 - Suppose that the bulb is placed as shown. Using...Ch. 24.5 - Prob. 1bTHCh. 24.5 - Prob. 1cTHCh. 24.5 - Prob. 1dTHCh. 24.5 - Prob. 2aTHCh. 24.5 - Treat the image produced by lens 1 as an object...Ch. 24.5 - Repeat parts a andb for the case in which lens 2...Ch. 24.6 - Reproduced below is a side view diagram of the...Ch. 24.6 - In section III of the tutorial Magnification, you...Ch. 24.6 - Two thin convex lenses and an object are arranged...Ch. 24.6 - Prob. 3bTHCh. 24.6 - Two thin convex lenses and an object are arranged...Ch. 24.6 - Prob. 3dTHCh. 24.6 - Two thin convex lenses and an object are arranged...
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A lens has 2 focal points or foci as shown in the drawings below... A. A convex-convex lens is a converging lens. P rays that enter the lens from the left side will converge at and pass through the focal point on the right or far side. The focal point on the left or near side is not used. Sketch three P rays passing through the converging lens provided. Note: Instead of refracting the ray at each interface, assume the ray refracts only once, at the dashed central bisector of the lens B. A concave-concave lens is a diverging lens. P rays entering from the left will diverge away from the focal point on the left. The right side focal point is not used. Sketch 3 P rays passing through the diverging lens provided.arrow_forwardA converging (concave) mirror with a focal length of 7 cm is held 4 cm from your face. a. Determine the image location. Insert your solution here: b. What is the magnification of the image? Use the formula belowarrow_forwardSuppose you have a concave mirror as shown in the image below. If h = 1.6m is the height of an object (really the displacement of the top of the object from the axis) and h' = 4.05m is the height of the image, what is the magnitude of the transverse magnification (in units of meters)? Image Object Note: Do not explicitly include units in your answer (it is understood the unit is meter). Enter only a number. If you do enter a unit, your answer will be counted wrong.arrow_forward
- If the radius of curvature of the mirror in diagram A is 15 cm and the object which is 10 cm long is placed 20 cm away from the mirror, then, find: a. the location of image b. size of image. Reminder: Always show your solution.arrow_forwardAn object (represented by an upright arrow) is placed 15 cm from a converging, thin lens with a focal length f = 10 cm. The scaled diagram below represents this arrangement. 15 cm object - principal axis f f 10 cm 10 cm convex lens (a) Draw a ray diagram to find the location of the image. Be sure to include the image in your diagram (b) Solve, using the thin-lens equation, for the location of the image. (c) Determine the magnification m of the image using equations (and not your diagram).arrow_forwardAn object, pointing upwards, is placed outside the focal point F2 of a thin diverging lens. A student is using the diagram shown above and the graphical method to predict the image of the arrow. To draw a principal ray, which direction should the student follow? O Draw a ray from point Q through F, to the lens, then bend it so it is horizontal. O Draw a horizontal ray from point Q to the lens, then bend it so it appears to diverge from F2. O Draw a ray from point P to any position on the lens, then bend it so it is horizontal. Draw a ray from point Q to the center of the lens, then bend it so it is horizontal.arrow_forward
- Use the ray diagram method to locate and describe the images formed by spherical mirror. Use one color for the object, and another color for the image. Please label all the points. concave mirrorarrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwritten solution ...arrow_forwardAn object is positioned at a distance less than one focal length from a convex lens. Describe the image formation. O inverted, diminished and real O upright, enlarged and virtual O inverted, enlarged and real O upright, diminished and virtualarrow_forward
- i) Ray parallel to the optical axis; ii) Focal ray; iii) Central ray, iv) Draw the image of the arrow, v) Indicate in the same figure, from where to where di (image-lens distance) is. Use the figure, Do not substitute it with any other figure. Don't forget to put the direction on each ray, both the incident rays and the transmitted rays. Label each ray. Image characteristics for Case 3: Object distance d0=R. Choose the ones that apply: a) Virtual b) Real c) Inverted d) Increased e) No image is formed f) Equal size g) Reduced h) Erectarrow_forwardHelp.arrow_forwardDraw the figure shown abov onto the same page as the mathematical proofs of your answer. Using the upright arrow as your object, draw the three primary light rays (M-, F-, and P-rays) to determine where the image will be located. Finally draw in the image taking care to show the correct size and orientation of the image. The black dots in the diagram represent the focal points of the lens.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON