
Concept explainers
(a)
The electric potential of the configuration of the three fixed charges.
(a)
Answer to Problem 17P
The potential energy of the configuration is
Explanation of Solution
The following figure shows the placement of charges
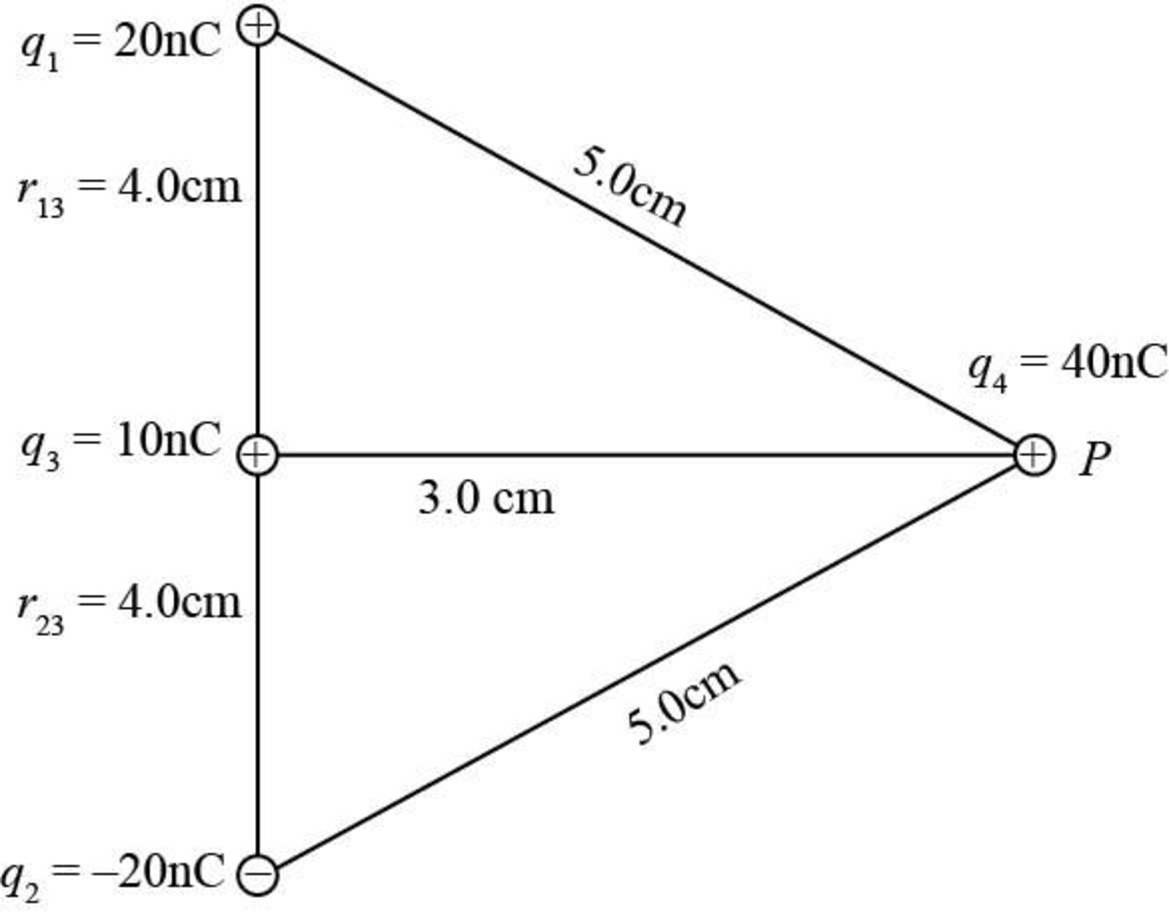
Figure-(1)
Write the expression for the configuration of the three fixed point’s electric potential energy.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Further solve the above equation.
Therefore, the potential energy of the configuration is
(b)
The speed of the fourth particle, after it has moved freely to a very large distance away from its point.
(b)
Answer to Problem 17P
The particle’s speed is
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the distance between the charges,
Write the expression for Pythagoras theorem.
Here,
Write the expression for net potential due to the three charges at point
Here,
Write expression when kinetic energy is converted into potential energy in the equilibrium position.
Here,
Rewrite the above equation for
Conclusion:
Consider triangle
Substitute
Further solve the above equation.
Substitute
Substitute
Further solve the above equation.
Therefore, the particle’ speed is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 25 Solutions
PHYSICS:F/SCI...W/MOD..-UPD(LL)W/ACCES
- Given two particles with 2.00-C charges as shown in Figure P20.9 and a particle with charge q = 1.28 1018 C at the origin, (a) what is the net force exerted by the two 2.00-C charges on the test charge q? (b) What is the electric field at the origin due to the two 2.00-C particles? (c) What is the electric potential at the origin due to the two 2.00-C particles? Figure P20.9arrow_forwardFour charged particles are at rest at the corners of a square (Fig. P26.14). The net charges are q1 = q2 = 2.65 C and q3 = q4 = 5.15 C. The distance between particle 1 and particle 3 is r13 = 1.75 cm. a. What is the electric potential energy of the four-particle system? b. If the particles are released from rest, what will happen to the system? In particular, what will happen to the systems kinetic energy as their separations become infinite? FIGURE P26.14 Problems 14, 15, and 16.arrow_forwardFour charged particles are at rest at the corners of a square (Fig. P26.14). The net charges are q1 = q2 = +2.65 C and q3 = q4 = 5.15 C. The distance between particle 1 and particle 3 is r13 = 1.75 cm. a. What is the electric potential energy of the four-particle system? b. If the particles are released from rest, what will happen to the system? In particular, what will happen to the systems kinetic energy?arrow_forward
- Given two particles with 2.00-C charges as shown in Figure P25.19 and a particle with charge q = 1.28 10-18 C at the origin, (a) what is the net force exerted by the two 2.00-C; charges on the charge q? (b) What is the electric field at the origin due to the two 2.00-C particles? (c) What is the electric potential at the origin due to the two 2.00-C particles?arrow_forwardFIGURE P26.14 Problems 14, 15, and 16. Four charged particles are at rest at the corners of a square (Fig. P26.14). The net charges are q1 = q2 = 2.65 C and q3 = q4 = 5.15 C. The distance between particle 1 and particle 3 is r13 = 1.75 cm. a. What is the electric potential energy of the four-particle system? b. If the particles are released from rest, what will happen to the system? In particular, what will happen to the systems kinetic energy as their separations become infinite?arrow_forwardThree particles with equal positive charges q are at the corners of an equilateral triangle of side a as shown in Figure P20.10. (a) At what point, if any, in the plane of the particles is the electric potential zero? (b) What is the electric potential at the position of one of the particles due to the other two particles in the triangle? Figure P20.10arrow_forward
- A proton is released from rest at the origin in a uniform electric field in the positive x direction with magnitude 850 N/C. What is the change in the electric potential energy of the protonfield system when the proton travels to x = 2.50 m? (a) 3.40 1016 J (b) 3.40 1016 J (c) 2.50 1016 J (d) 2.50 1016 J (e) 1.60 1019 Jarrow_forwardA positive point charge q = +2.50 nC is located at x = 1.20 m and a negative charge of 2q = 5.00 nC is located at the origin as in Figure P16.18. (a) Sketch the electric potential versus x for points along the x-axis in the range 1.50 m x 1.50 m. (b) Find a symbolic expression for the potential on the x-axis at an arbitrary point P between the two charges. (c) Find the electric potential at x = 0.600 m. (d) Find the point along the x-axis between the two charges where the electric potential is zero.arrow_forwardA proton is located at the origin, and a second proton is located on the x-axis at x = 6.00 fm (1 fm = 10-15 m). (a) Calculate the electric potential energy associated with this configuration. (b) An alpha particle (charge = 2e, mass = 6.64 1027 kg) is now placed at (x, y) = (3.00, 3.00) fm. Calculate the electric potential energy associated with this configuration. (c) Starting with the three-particle system, find the change in electric potential energy if the alpha particle is allowed to escape to infinity while the two protons remain fixed in place. (Throughout, neglect any radiation effects.) (d) Use conservation of energy to calculate the speed of the alpha particle at infinity. (e) If the two protons are released from rest and the alpha panicle remains fixed, calculate the speed of the protons at infinity.arrow_forward
- A filament running along the x axis from the origin to x = 80.0 cm carries electric charge with uniform density. At the point P with coordinates (x = 80.0 cm, y = 80.0 cm), this filament creates electric potential 100 V. Now we add another filament along the y axis, running from the origin to y = 80.0 cm, carrying the same amount of charge with the same uniform density. At the same point P, is the electric potential created by the pair of filaments (a) greater than 200 V, (b) 200 V, (c) 100 V, (d) between 0 and 200 V, or (e) 0?arrow_forwardA uniformly charged insulating rod of length 14.0 cm is bent into the shape of a semicircle as shown in Figure P25.44. The rod has a total charge of 7.50 C. Find the electric potential at O, the center of the semicircle.arrow_forwardFor the arrangement described in Problem 26, calculate the electric potential at point B, which lies on the perpendicular bisector of the rod a distance b above the x axis. Figure P20.26arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





