
Concept explainers
To determine:
The way in which bacteria generate new gene combinations in the absence of sexual reproduction.
Introduction:
Beneficial genes are transferred in bacterial cells through horizontal gene transfer. The genomes in the bacteria constantly show reshaping. The transfer of gene horizontally from one bacterial cell to another is through viruses.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation:
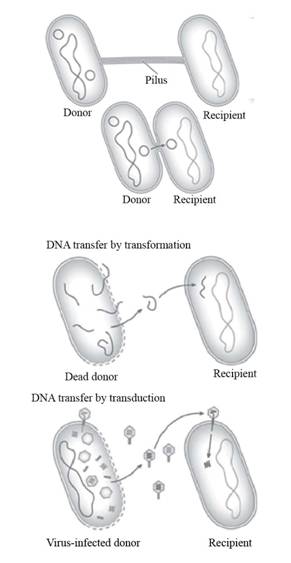
Fig.1: Horizontal gene transfer in bacteria.
Explanation:
As the eukaryotes are not able to produce genetic diversity through sexual reproduction, bacteria have special mechanisms of gene transfer. Through DNA, the bacteria are able to add or subtract the gene. There are three methods of gene transfer in bacteria without sexual reproduction, which are as follows:
- 1. Conjugation: The DNA is transferred from the donor bacterial cell to the recipient bacterial cell through a structure known as pilus. The pilus connects the donor cell with the recipient cell and brings them together. As the cells become close to each other, the DNA is transferred through a small opening to the recipient bacterial cell.
- 2. Transformation: The dead bacterial cell releases its DNA in the environment. The DNA from the environment is then taken up by another bacterial cell known as recipient bacterial cell. Here, no connection is made between the donor and the recipient cell. By using transformation, many of the harmless cells can also be converted into virulent strains.
- 3. Transduction: The process of horizontal gene transfer by means of viruses in the bacterial cell is known as transduction. In transduction, the bacteriophages play an important role, as they act as viruses which help in the transfer of DNA in the recipient bacterial cell.
When the DNA leaves the donor bacterial cell, it is packaged in the form of protein capsules in the viruses, which are directly released into the recipient bacterial cell. The release of DNA into the recipient cell is done when the viruses infect the cell.
Gene transfer in bacteria includes the mechanisms of conjugation, transformation and transduction.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 26 Solutions
Biology: How Life Works - Standalone book
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





