
Concept explainers
Figure P26.35 shows four particles with identical charges of +5.75 μC arrayed at the vertices of a rectangle of width 25.0 cm and height 55.0 cm. What is the change in the electric potential energy of this system if particles A, B, and C are held in place and particle D is brought from infinity to the position shown in the figure?
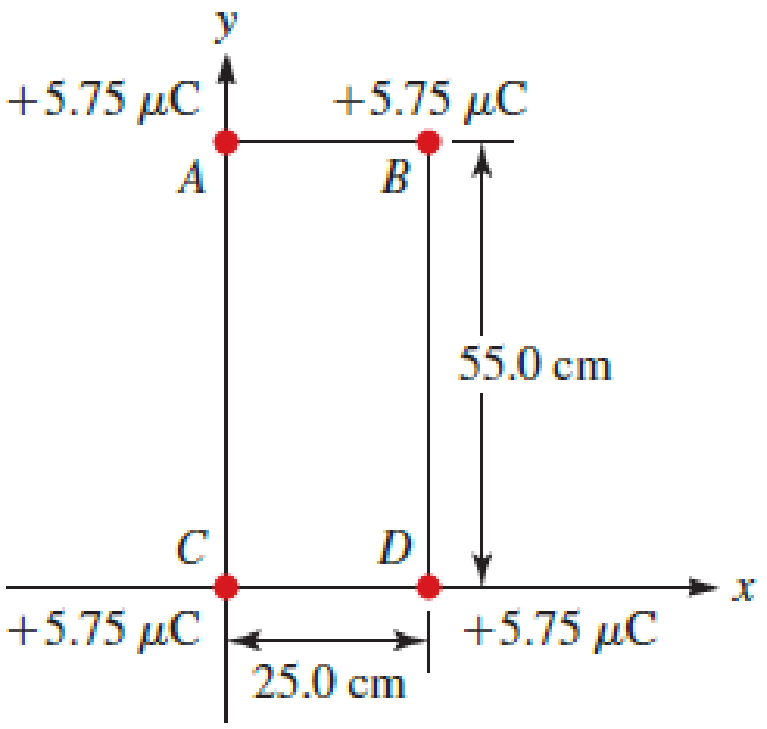
FIGURE P26.35
The change in the electric potential energy of the system if particles
Answer to Problem 35PQ
The change in the electric potential energy of the system if particles
Explanation of Solution
When additional charge is included in the system, the change in potential energy arises due to the effect of charge in existing potentials.
Write the expression for the change in potential energy due to bringing the charge to the point
Here,
Write the expression for
Here,
Write the expression for
Here,
Write the expression for
Here,
Use equations (II), (III) and (IV) in equation (I) to get change in potential energy.
Since all charges are identical, substitute
Write the expression for
Conclusion:
From figureP26.35, distance between point
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the change in the electric potential energy of the system if particles
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 26 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
- FIGURE P26.14 Problems 14, 15, and 16. Four charged particles are at rest at the corners of a square (Fig. P26.14). The net charges are q1 = q2 = 2.65 C and q3 = q4 = 5.15 C. The distance between particle 1 and particle 3 is r13 = 1.75 cm. a. What is the electric potential energy of the four-particle system? b. If the particles are released from rest, what will happen to the system? In particular, what will happen to the systems kinetic energy as their separations become infinite?arrow_forwardFour charged particles are at rest at the corners of a square (Fig. P26.14). The net charges are q1 = q2 = 2.65 C and q3 = q4 = 5.15 C. The distance between particle 1 and particle 3 is r13 = 1.75 cm. a. What is the electric potential energy of the four-particle system? b. If the particles are released from rest, what will happen to the system? In particular, what will happen to the systems kinetic energy as their separations become infinite? FIGURE P26.14 Problems 14, 15, and 16.arrow_forwardFigure P26.80 shows a wire with uniform charge per unit length = 2.25 nC/m comprised of two straight sections of length d = 75.0 cm and a semicircle with radius r = 25.0 cm. What is the electric potential at point P, the center of the semicircular portion of the wire? FIGURE P26.80arrow_forward
- Four charged particles are at rest at the corners of a square (Fig. P26.14). The net charges are q1 = q2 = +2.65 C and q3 = q4 = 5.15 C. The distance between particle 1 and particle 3 is r13 = 1.75 cm. a. What is the electric potential energy of the four-particle system? b. If the particles are released from rest, what will happen to the system? In particular, what will happen to the systems kinetic energy?arrow_forwardA charged particle is moved in a uniform electric field between two points, A and B, as depicted in Figure P26.65. Does the change in the electric potential or the change in the electric potential energy of the particle depend on the sign of the charged particle? Consider the movement of the particle from A to B, and vice versa, and determine the signs of the electric potential and the electric potential energy in each possible scenario.arrow_forwardTwo 5.00-nC charged particles are in a uniform electric field with a magnitude of 625 N/C. Each of the particles is moved from point A to point B along two different paths, labeled in Figure P26.65. a. Given the dimensions in the figure, what is the change in the electric potential experienced by the particle that is moved along path 1 (black)? b. What is the change in the electric potential experienced by the particle that is moved along path 2 (red)? c. Is there a path between the points A and B for which the change in the electric potential is different from your answers to parts (a) and (b)? Explain. FIGURE P26.65 Problems 65, 66, and 67.arrow_forward
- Figure P26.44 shows a rod of length = 1.00 m aligned with the y axis and oriented so that its lower end is at the origin. The charge density on the rod is given by = a + by, with a = 2.00 C/m2 and b = 1.00 C /m2. What is the electric potential at point P with coordinates (0, 25.0 cm)? A table of integrals will aid you in solving this problem.arrow_forwardTwo charged particles with q1 = 5.00 C and q2 = 3.00 C are placed at two vertices of an equilateral tetrahedron whose edges all have length s = 4.20 m (Fig. P26.37). Determine what charge q3 should be placed at the third vertex so that the total electric potential at the fourth vertex is 2.00 kV. FIGURE P26.37arrow_forwardFour particles are positioned on the rim of a circle. The charges on the particles are +0.500 C, +1.50 C, 1.00 C, and 0.500 C. If the electric potential at the center of the circle due to the +0.500 C charge alone is 4.50 104 V, what is the total electric potential at the center due to the four charges? (a) 18.0 104 V (b) 4.50 104 V (c) 0 (d) 4.50 104 V (e) 9.00 104 Varrow_forward
- Given two particles with 2.00-C charges as shown in Figure P20.9 and a particle with charge q = 1.28 1018 C at the origin, (a) what is the net force exerted by the two 2.00-C charges on the test charge q? (b) What is the electric field at the origin due to the two 2.00-C particles? (c) What is the electric potential at the origin due to the two 2.00-C particles? Figure P20.9arrow_forwardA 5.00-nC charged particle is at point B in a uniform electric field with a magnitude of 625 N/C (Fig. P26.65). What is the change in electric potential experienced by the charge if it is moved from B to A along a. path 1 and b. path 2?arrow_forwardA positive point charge q = +2.50 nC is located at x = 1.20 m and a negative charge of 2q = 5.00 nC is located at the origin as in Figure P16.18. (a) Sketch the electric potential versus x for points along the x-axis in the range 1.50 m x 1.50 m. (b) Find a symbolic expression for the potential on the x-axis at an arbitrary point P between the two charges. (c) Find the electric potential at x = 0.600 m. (d) Find the point along the x-axis between the two charges where the electric potential is zero.arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





