
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The explanation for alanine which has different optical rotation in water,
Concept introduction:
The amino acid is made of two functional groups an
Answer to Problem 27.61AP
Each solvent rotates the alanine molecule to a different angle due to the formation of different complex formation and so it gives rise to different optical rotation in different solvents.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of alanine is shown below.
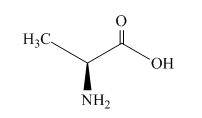
Figure 1
Alanine is an optically active compound. It rotates the plane of polarized light. The reaction of alanine with water,
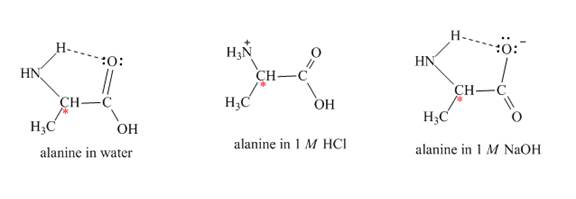
Figure 2
The optical rotation of alanine is measure by Circular Dichroism (CD). It involves circularly polarized light absorption. It measures the angle at which the plane-polarized light is rotated by the molecule. Each solvent rotates the alanine molecule to a different angle, due to this it gives rise to different optical rotation in different solvents.
The alanine has different optical rotation in water,
(b)
Interpretation:
The explanation for two known mono
Concept introduction:
The amino acid is made of two functional groups an amine group,
Answer to Problem 27.61AP
Due to the presence of two amine groups in lysine molecule. It may undergo acetylation reaction from either side and form mono
Explanation of Solution
The structure of amino acid lysine is shown below.
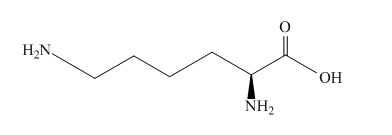
Figure 3
The structure of the lysine molecule contains two amine group one at the
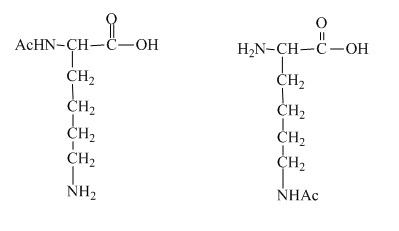
Figure 4
The two mono
(c)
Interpretation:
The explanation for fact that the peptide
Concept introduction:
The amino acid is made of two functional groups an amine group
Answer to Problem 27.61AP
The compound urea under basic conditions acts as a denaturation agent which breakdown the protein molecule bonding. Due to this, the peptide,
Explanation of Solution
The protein molecule is composed of four types of structure primary, secondary, tertiary and quarternary. The enzyme trypsin hydrolyzes the peptide,
The peptide
(d)
Interpretation:
The explanation for the peptide containing cysteine on reaction with
Concept introduction:
The amino acid is made of two functional groups an amine group,
Answer to Problem 27.61AP
The generation of lysine type molecule at the end of the reaction which is cleaved by trypsin enzyme. Due to this, the peptide containing cysteine on reaction with
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the cysteine molecule is shown below.
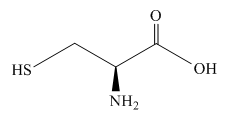
Figure 5
The same molecule in peptides exists as a disulfide bond. The disulfide bond of cysteine in the protein molecule is shown below.
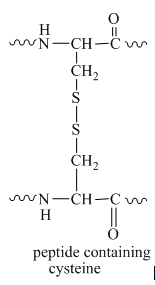
Figure 6
When this protein molecule with a disulfide bond is treated with
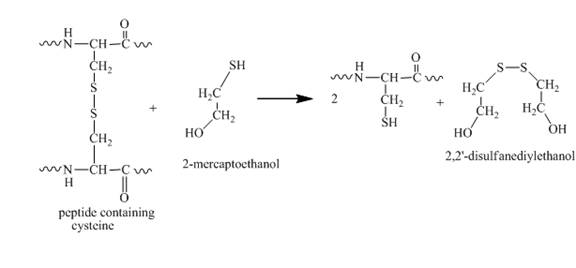
Figure 7
The thiol group is then reacted with the aziridine molecule which results in the formation of a lysine type molecule. This reaction is shown below.
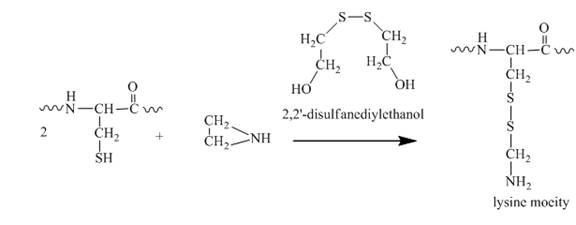
Figure 8
This lysine type molecule then reacts with trypsin enzyme which cleaves arginine and lysine molecule. Due to this, the trypsin enzyme reacts with the modified cysteine residues.
The peptide containing cysteine on reaction with
(e)
Interpretation:
The explanation for the formation of two separable methionine sulfoxides from the oxidation of
Concept introduction:
The amino acid is made of two functional groups an amine group,
Answer to Problem 27.61AP
The application of a certain amount of energy which converts one form to another form of structure. Due to this, the formation of two separable methionine sulfoxides from the oxidation of
Explanation of Solution
The structure of methionine is shown below.
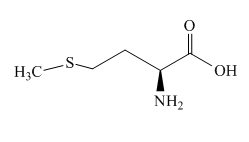
Figure 9
The resonance structure of sulfoxides with two different groups is shown below.
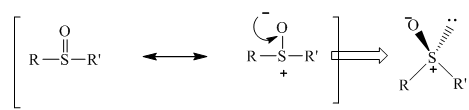
Figure 10
The conversion of one structure to another structure at room temperature requires a certain amount of energy. Therefore, on the application of that amount of energy, the two forms of
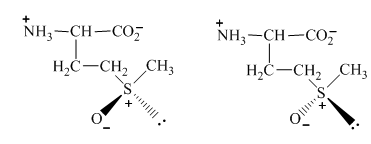
Figure 11
The formation of two separable methionine sulfoxides from the oxidation of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 27 Solutions
Organic Chemistry, Ebook And Single-course Homework Access
- Give the sequence of the following tetrapeptide:arrow_forwardOxytocin, a nonapeptide hormone secreted by the pituitary gland, functions by stimulating uterine contraction and lactation during childbirth. Its sequence was determined from the following evidence: 1. Oxytocin is a cyclic compound containing a disulfide bridge between two cysteine residues. 2. When the disulfide bridge is reduced, oxytocin has the constitution Asn, Cys2, Gln, Gly, Ile, Leu, Pro, Tyr. 3. Partial hydrolysis of reduced oxytocin yields seven fragments: Asp-Cys, Ile-Glu, Cys-Tyr, Leu-Gly, Tyr-Ile-Glu, Glu-Asp-Cys, and Cys-Pro-Leu. 4. Gly is the C-terminal group. 5. Both Glu and Asp are present as their side-chain amides (Gln and Asn) rather than as free side-chain acids. What is the amino acid sequence of reduced oxytocin? What is the structure of oxytocin itself?arrow_forwardWhat type of interaction (IMF) would be present between side chains of the following amino acid residues? Explain your answers. a) 2 phenylalanine residues b) Methionine and valine residues c) Glutamate and arginine residuesarrow_forward
- Determine the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide from the following data:Complete hydrolysis of the peptide yields Ala, Arg, Gly, 2 Lys, Met, Phe, Pro, 2 Ser, Tyr, and Val.Treatment with Edman’s reagent releases PTH-Val.Carboxypeptidase A releases Ala. Treatment with trypsin yields the following three peptides:1. Gly, Lys, Met, Tyr 2. Ala, Lys, Phe, Pro, Ser 3. Arg, Ser, Valarrow_forwardA peptide has the following amino acid composition: 2 Met, 2 Phe, 2 Glu, 1 Arg, 1 Lys, 1 Val, 1 Leu, 1 Gly, 1 Ser Reaction of the intact peptide with dansyl chloride followed by acid hydrolysis creates a derivative of Met. A specific cleavage of the intact peptide produces fragments with the following sequences: Fragment A: Glu-Gly-Lys-Phe Fragment B: Met-Ser-Leu-Arg Fragment C: Met-Val-Glu-Phe What information do this result give about the sequence of the peptide? Explain how you arrived on your answer. a) The sequence is: Met-Val-Glu-Phe-Glu-Gly-Lys-Phe-Met-Ser-Leu-Arg b) The sequence is: Met-Ser-Leu-Arg-Met-Val-Glu-Phe-Glu-Gly-Lys-Phe c) The sequence is: Met-Val-Glu-Phe-Met-Ser-Leu-Arg-Glu-Gly-Lys-Phe d) The sequence is: Met-Ser-Leu-Arg-Glu-Gly-Lys-Phe-Met Val-Glu-Phearrow_forwardShow the mechanism and explain how the Ala-Val-Ile peptide bond is formed.arrow_forward
- Although the bond energy for the hydrogen bond in a vacuum is estimated to be about 20 kJ/mol, we find that each hydrogen bond in a folded protein contributes much less--probably less that 5 kJ/mol--to the enthalpy of protein stabilization. Suggest an explanation for this difference. Explain briefly.arrow_forwardThe configuration of the chiral center in a-amino acids is most commonly specified using the d,l convention. It can also be identified using the R,S convention . Does the chiral center in l-serine have the R or S configuration?arrow_forwardReport the isoelectric point of the peptide, Gly-Asp-Lys-Ile?arrow_forward
- 5 ased on molecular weights of purified (no beta-Me) and (beta-Me) sample, which are 97.4 kDa and 47.2 kDa, what can be said about the number and size of the protein monomers, as well as the nature of the bonds holding together the complete quaternary structure of the proteins?arrow_forwardHis-Met-Asp-Tyr-Phe-Ser within this peptide, which amino acid residue is the most hydrophobic and why?arrow_forward1. Taking the structure of the amino acids into account, give a comparative discussion pK values where histidine=2 and alanine=2.arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

