
Concept explainers
Given that only about 5% of the galaxies visible in the Hubble Deep Field are bright enough for astronomers to study spectroscopically, they need to make the most of the other 95%. One technique is to use their colors and apparent brightnesses to try to roughly estimate their redshift. How do you think the inaccuracy of this redshift estimation technique (compared to actually measuring the redshift from a spectrum) might affect our ability to make maps of large-scale structures such as the filaments and voids shown in Figure 28.21?
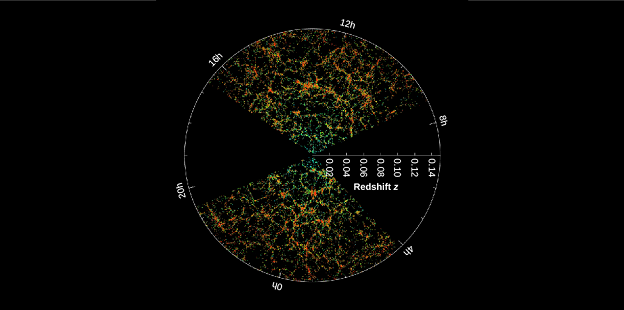
Figure 28.21 Sloan Digital Sky Survey Map of the Large-Scale Structure of the Universe. This image shows slices from the SDSS map. The point at the center corresponds to the Milky Way and might say “You Are Here!” Points on the map moving outward from the center are farther away. The distance to the galaxies is indicated by their redshifts (following Hubble’s law), shown on the horizontal line going right from the center. The redshift
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 28 Solutions
Astronomy
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Essential University Physics: Volume 2 (3rd Edition)
Conceptual Integrated Science
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
College Physics
The Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals (2nd Edition)
An Introduction to Thermal Physics
- When comparing two isolated spiral galaxies that have the same apparent brightness, but rotate at different rates, what can you say about their relative luminosity?arrow_forwardUsing the information from Example 28.1, how much fainter an object will you have to be able to measure in order to include the same kinds of galaxies in your second survey? Remember that the brightness of an object varies as the inverse square of the distance.arrow_forwardWhat is the most useful standard bulb method for determining distances to galaxies?arrow_forward
- Suppose you were Hubble and Humason, working on the distances and Doppler shifts of the galaxies. What sorts of things would you have to do to convince yourself (and others) that the relationship you were seeing between the two quantities was a real feature of the behavior of the universe? (For example, would data from two galaxies be enough to demonstrate Hubble’s law? Would data from just the nearest galaxies-in what astronomers call “the Local Group”-suffice?)arrow_forwardWhy can we not determine distances to galaxies by the same method used to measure the parallaxes of stars?arrow_forwardA galaxy is observed to recede at speed 140 km/s. If the Hubble constant is 70 km/s/ Mpc, how far is the galaxy?arrow_forward
- An astronomer observed the motions of some galaxies. Based on his observations, he made the following statements. Which one of them is most likely to be false? Take Hubble's constant to be 67 km/s/Mpc. A. A galaxy observed to be moving away from us at a speed of 70 km/s is at a distance of about 1 Mpc from us. B. A galaxy observed to be moving away from us at a speed of 700 km/s is at a distance of about 10 Mpc from us. C. A galaxy observed to be moving away from us at a speed of 7000 km/s is at a distance of about 100 Mpc from us. D. A galaxy observed to be moving away from us at a speed of 70000 km/s is at a distance of about 1 Gpc from us. Is the answer D? Thank you!arrow_forwardWhy is it that there doesn't seem to be an equivalent to the H-R diagram of stars for galaxies?arrow_forwardWhat is the redshift z of a galaxy 156 Mpc away from us? Note: Assume a value of the Hubble constant of 70.7 km/s/Mpcarrow_forward
- What is the redshift z of a galaxy 172 Mpc away from us? Note: Assume a value of the Hubble constant of 71.1 km/s/Mpc Round your answer to three decimal places.arrow_forwardA certain galaxy is observed to be receding from the Sun at a rate of 8000 km/sec. The distance to this Galaxy is measured independently and found to be 1.4 x 10 to the eighth power pc. Using this data, what is the value of the Hubble constant ?arrow_forwardPretend that galaxies are spaced evenly, 7.0 Mpc apart, and the average mass of a galaxy is 1.0 ✕ 1011 M. What is the average density (in kg/m3) of matter in the universe? (Note: The volume of a sphere is 4/3pieR^3 and the mass of the sun is 2.0 ✕ 1030 kg.) ______ kg/m^3 Which model universe does this density value support? A: open B: flat C: closedarrow_forward
 AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax
AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax Stars and Galaxies (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399944Author:Michael A. SeedsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Stars and Galaxies (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399944Author:Michael A. SeedsPublisher:Cengage Learning Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399920Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399920Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning


