
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEER
10th Edition
ISBN: 8220106906149
Author: Jewett
Publisher: Cengage Learning US
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 28, Problem 47AP
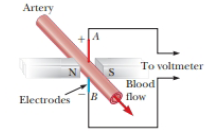
A heart surgeon monitors the flow rate of blood through an artery using an
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
An electric field exists between a pair of circular metal plates measuring 3.00 m in radius. The field is uniform across the surface of the
plates but increases in strength at a rate given by E(t) = At², starting at t = 0 and persisting for 33.0 seconds. The constant, A, has a
value of 69900 V.m¹.s². How strong will the magnetic field be on the edge of the plates at the end of the 33.0 second interval?
T
i
An electromagnetic rail gun uses magnetic forces to launch projectiles. (Figure 1) shows a 10-cm-long, 10 g metal wire that can slide without friction along 1.0-m-long horizontal rails. The rails are connected to a 300 V source, and a 0.10 T magnetic field fills the space between the rails. Each rail has linear resistivity λ = 0.10 Ω/m, which means that the resistance is λ multiplied by the length of rail through which current flows. Assume that the sliding wire and the left end, where the voltage source is, have zero resistance. The wire is initially placed at x0 = 30 cm, then the switch is closed. What is the wire's speed as it leaves the rails?
A rocket zooms past the earth at v =2.0×106m/s. Scientists on the rocket have created the electric and magnetic fields shown in the figure.(Figure 1) Assume that B = 1.2 T and E = 1.2×106 V/m .
a. What is the electric field strength measured by an earthbound scientist?
b. What is the magnetic field strength measured by an earthbound scientist?
Chapter 28 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEER
Ch. 28.1 - An electron moves in the plane of this paper...Ch. 28.2 - Prob. 28.2QQCh. 28.4 - A wire carries current in the plane of this paper...Ch. 28.5 - (i) Rank the magnitudes of the torques acting on...Ch. 28 - At the equator, near the surface of the Earth, the...Ch. 28 - Consider an electron near the Earths equator. In...Ch. 28 - Find the direction of the magnetic field acting on...Ch. 28 - A proton moving at 4.00 106 m/s through a...Ch. 28 - A proton travels with a speed of 5.02 106 m/s in...Ch. 28 - A laboratory electromagnet produces a magnetic...
Ch. 28 - A proton moves perpendicular to a uniform magnetic...Ch. 28 - An accelerating voltage of 2.50103 V is applied to...Ch. 28 - A proton (charge + e, mass mp), a deuteron (charge...Ch. 28 - Review. A 30.0-g metal hall having net charge Q =...Ch. 28 - Review. One electron collides elastically with a...Ch. 28 - Review. One electron collides elastically with a...Ch. 28 - Review. An electron moves in a circular path...Ch. 28 - A cyclotron designed to accelerate protons has a...Ch. 28 - Prob. 15PCh. 28 - Singly charged uranium-238 ions are accelerated...Ch. 28 - A cyclotron (Fig. 28.16) designed to accelerate...Ch. 28 - A particle in the cyclotron shown in Figure 28.16a...Ch. 28 - Prob. 19PCh. 28 - A straight wire earning a 3.00-A current is placed...Ch. 28 - A wire carries a steady current of 2.40 A. A...Ch. 28 - Why is the following situation impossible? Imagine...Ch. 28 - Review. A rod of mass 0.720 kg and radius 6.00 cm...Ch. 28 - Review. A rod of mass m and radius R rests on two...Ch. 28 - A wire having a mass per unit length of 0.500 g/cm...Ch. 28 - Consider the system pictured in Figure P28.26. A...Ch. 28 - A strong magnet is placed under a horizontal...Ch. 28 - In Figure P28.28, the cube is 40.0 cm on each...Ch. 28 - A magnetized sewing needle has a magnetic moment...Ch. 28 - A 50.0-turn circular coil of radius 5.00 cm can be...Ch. 28 - You are in charge of planning a physics magic show...Ch. 28 - You are working in your dream job: an assistant...Ch. 28 - A rectangular coil consists of N = 100 closely...Ch. 28 - A rectangular loop of wire has dimensions 0.500 m...Ch. 28 - A wire is formed into a circle having a diameter...Ch. 28 - A Hall-effect probe operates with a 120-mA...Ch. 28 - Prob. 37APCh. 28 - Figure 28.11 shows a charged particle traveling in...Ch. 28 - Within a cylindrical region of space of radius 100...Ch. 28 - Prob. 40APCh. 28 - Prob. 41APCh. 28 - (a) A proton moving with velocity v=ii experiences...Ch. 28 - A proton having an initial velocity of 20.0iMm/s...Ch. 28 - You have been called in as an expert witness in a...Ch. 28 - Prob. 45APCh. 28 - Why is the following situation impossible? Figure...Ch. 28 - A heart surgeon monitors the flow rate of blood...Ch. 28 - Review. (a) Show that a magnetic dipole in a...Ch. 28 - Consider an electron orbiting a proton and...Ch. 28 - Protons having a kinetic energy of 5.00 MeV (1 eV...Ch. 28 - Review. A wire having a linear mass density of...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Unreasonable results Frustrated by the small Hall voltage obtained in blood flow measurements, a medical physicist decides to increase the applied magnetic field strength to get a 0.500-V output for blood moving at 30.0 cm/s in a 1.50-cm-diameter vessel. (a) What magnetic field strength is needed? (b) What is unreasonable about this result? (C) Which premise is responsible?arrow_forwardA proton moving in the plane of the page has a kinetic energy of 6.00 MeV. A magnetic field of magnitude H = 1.00 T is directed into the page. The proton enters the magnetic field with its velocity vector at an angle = 45.0 to the linear boundary of' the field as shown in Figure P29.80. (a) Find x, the distance from the point of entry to where the proton will leave the field. (b) Determine . the angle between the boundary and the protons velocity vector as it leaves the field.arrow_forwardConsider the mass spectrometer shown schematically in Figure P19.36. The electric field between the plates of the velocity selector is 950 V/m, and the magnetic fields in both the velocity selector and the deflection chamber have magnitudes of 0.930 T. Calculate the radius of the path in the system for a singly charged ion with mass m = 2.18 × 10−26 kg. Hint: See Problem 35.arrow_forward
- A particle passes through a mass spectrometer as illustrated in Figure P19.36. The electric field between the plates of the velocity selector has a magnitude of 8 250 V/m, and the magnetic fields in both the velocity selector and the deflection chamber have magnitudes of 0.093 1 T. In the deflection chamber the particle strikes a photographic plate 39.6 cm removed from its exit point after traveling in a semicircle. (a) What is the mass-to-charge ratio of the particle? (b) What is the mass of the particle if it is doubly ionized? (c) What is its identity, assuming it’s an element?arrow_forwardAn electron in a TV CRT moves with a speed of 5.5 × 107 m/s, in a direction perpendicular to the Earth’s magnetic field, which has a strength of 5.75 × 10-5 T. Part (a) What electric field strength in kV/m must be applied perpendicular to the Earth’s magnetic field to make the electron moves in a straight line? Part (b) If this is done between plates separated by 1.1 cm, what is the voltage applied in V? (Note that TVs are usually surrounded by a ferromagnetic material to shield against external magnetic fields and avoid the need for such a correction.)arrow_forwardUsing an electromagnetic flowmeter (Fig. P19.69), aheart surgeon monitors the flow rate of blood through anartery. Electrodes A and B make contact with the outer surfaceof the blood vessel, which has interior diameter 3.00 mm. (a) For a magnetic field magnitude of 0.040 0 T, a potentialdifference of 160 µV appears between the electrodes. Calculatethe speed of the blood. (b) Verify that electrode A is positive,as shown. Does the sign of the emf depend on whetherthe mobile ions in the blood are predominantly positively ornegatively charged? Explain.arrow_forward
- Consider the mass spectrometer shown schematically inFigure P19.15. The electric field between the plates of thevelocity selector is 9.50 x 102 V/m, and the magnetic fieldsin both the velocity selector and the deflection chamber havemagnitudes of 0.930 T. Calculate the radius of the path in thesystem for a singly charged ion with mass m = 2.18 x 10-26 kg.arrow_forwardA 2.60-N metal bar, 0.850 m long and having a resistance of 10.0 Ω, rests horizontally on conducting wires connecting it to the circuit shown in Fig. P27.62. The bar is in a uniform, horizontal, 1.60-T magnetic field and is not attached to the wires in the circuit. What is the acceleration of the bar just after the switch S is closed?arrow_forwardAn electromagnetic rail gun uses magnetic forces to launch projectiles. (Figure 1) shows a 10-cm-long, 12 g metal wire that can slide without friction along 1.0-m-long horizontal rails. The rails are connected to a 300 V source, and a 0.10 T magnetic field fills the space between the rails. Each rail has linear resistivity λ = 0.10 /m, which means that the resistance is A multiplied by the length of rail through which current flows. Assume that the sliding wire and the left end, where the voltage source is, have zero resistance. The wire is initially placed at x0 = 30 cm, then the switch is closed. Figure Part A X X X x 10 cm х X X × 0.10 T X X + X X 300 V × ✗ ✗ X X ✗ ☑ × × × x What is the wire's speed as it leaves the rails? 1 of 1arrow_forward
- Figure P20.3 shows three edge views of a square loop withsides of length , l = 0.250 m in a magnetic field of magnitude 2.00 T. Calculate the magnetic flux through the loop oriented(a) perpendicular to the magnetic field, (b) 60.0° from themagnetic field, and (c) parallel to the magnetic field.arrow_forwardThe cross-sectional dimensions of the copper strip shown are 2.0 cm by 2.0 mm. The strip carries a current of 120 A, and it is placed in a magnetic field of magnitude B = 1.4 T. What are the value (in V) and polarity of the Hall potential in the copper strip? (Assume the charge carrier density of copper is 8.0 x 1028 electrons/m³). B 2.0 cm X 2.0 mm value polarity The ---Select--- of the strip is at a higher potential.arrow_forwardA metal strip 5.00 cm long, 0.800 cm wide, and 0.700 mm thick moves with constant velocity through a uniform magnetic field B = 1.00 T directed perpendicular to the strip, as shown in the figure. A potential difference of 4.70 mV is measured between points x and y across the width of the strip. Calculate the speed v (in m/s). Hint: How fast are the electrons moving through the magnetic field? Give your answer as only the numerical value in the SI units specified. e is interpreted as x10^ for use with large or small values; 1.01e2 is interpreted as 1.01 x 102. Barrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Magnets and Magnetic Fields; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IgtIdttfGVw;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY