
To label:
The features of the spinal cord and the surrounding structures.
Introduction:
The spinal cord is a thin, long, tubular structure. It is composed of nervous tissues that extend from medulla oblongata to the lumbar region of vertebral column. It is elliptical in cross section, being compressed dorsolaterally. The brain and spinal cord are protected by the three layers of tissue known as meninges.
Explanation of Solution
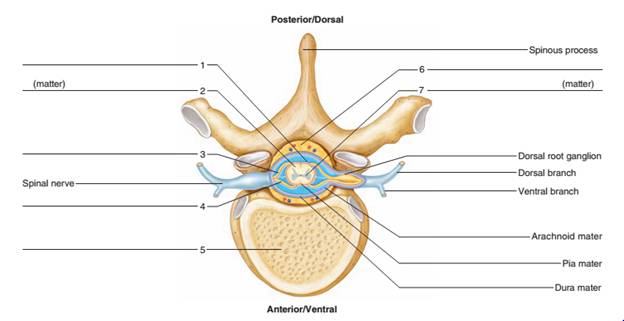
1. Subdural space
2. White matter
3. Dorsal root
4. Ventral root
5. Vertebral body
6. Epidural space
7. Gray matter
(1). Subdural space: It is a potential area between the spinal dura mater and the arachnoid mater. It doesn’t contain any bridging veins. That’s why hemorrhage in this area occurs very rarely.
(2). White matter: It consists of most of the glial cells and myelinated axons. It is white because of myelin (fatty substances) that surrounds the nerve fibers. It is located in the outer region of spinal cord surrounding the gray matter.
(3). Dorsal root: It emerges directly from spinal cord and expands to the dorsal root ganglion. It contains sensory fibers and carries the sensory information, forming afferent sensory root of a spinal nerve.
(4). Ventral root: It contains outgoing efferent motor fibers that carry the information destined to the control motor or to the glandular function. It joins with the dorsal root on the outside of the vertebral column to form a spinal nerve.
(5). Vertebral body: It is the main part of the vertebra and bears about the 80% of the load while standing. It provides an attachment to the discs in between the vertebrae.
(6). Epidural space: It is the area between the vertebral wall and the dura mater. It contains fat and blood vessels. The epidural space is found just outside the dural sac that surrounds the nerve roots and it is filled with the cerebrospinal fluid.
(7). Gray matter: It consists of neuronal cell bodies, glial cells, neuropil, capillaries, and synapses. It is found deep inside the core of spinal cord.
- Subdural space
- White matter
- Dorsal root
- Ventral root
- Vertebral body
- Epidural space
- Gray matter
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 28 Solutions
Laboratory Manual for Holes Human Anatomy & Physiology Fetal Pig Version
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





