
a.
Prepare the general ledger account with June 1 beginning balances.
a.
Explanation of Solution
T-account:
T-account is the form of the ledger account, where the
The components of the T-account are as follows:
a) The title of the account
b) The left or debit side
c) The right or credit side
Prepare the T-account with June 1 beginning balance:
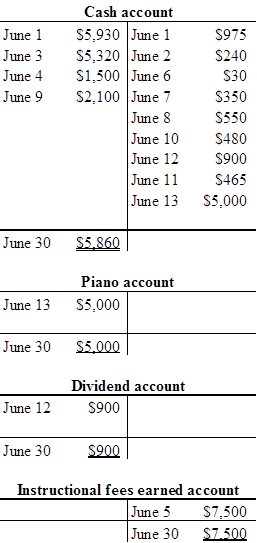
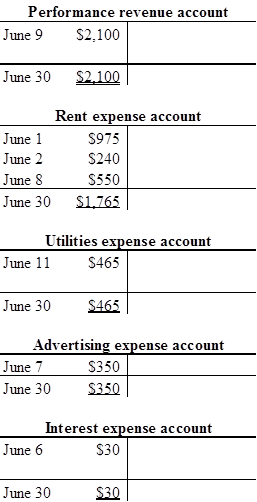
b.
Prepare the
b.
Explanation of Solution
Trial balance:
Trial balance is the summary of accounts, and their debit and credit balances at a given time. It is usually prepared at end of the accounting period. Debit balances are listed in left column and credit balances are listed in right column. The totals of debit and credit column should be equal. Trial balance is useful in the preparation of the financial statements.
Prepare the trial balance as of June 30.
| M Dance studio | ||
| Trial Balance | ||
| As of June 30 | ||
| Accounts | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash | 5,860 | |
| 10,180 | ||
| Piano | 5,000 | |
| Notes payable | 5,080 | |
| Common stock | 7,870 | |
| Dividends | 900 | |
| Instruction fees earned | 7,500 | |
| 2,000 | ||
| Performance revenue | 2,100 | |
| Advertising expense | 350 | |
| Rent expense | 1,765 | |
| Utilities expense | 465 | |
| Interest expense | 30 | |
| Total | 24,550 | 24,550 |
Table (1)
Working note:
Calculate the amount of accounts receivable:
Amount of accounts receivable in balance sheet is $8,000
Amount collected from students is $5,320
Amount billed for instructional fess is $7,500
Thus, the amount of accounts receivable is $10,180.
c.
Prepare the income statement for the month ended June.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement: The financial statement which reports revenues and expenses from business operations and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period is referred to as income statement.
Prepare an income statement for the month of June.
|
M Dance studio Income statement For the month ended June | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Revenues: | ||
| Instructional fee earned | 7,500 | |
| Performance revenue | 2,100 | |
| Total revenue | 9,600 | |
| Less: Expenses | ||
| Advertising expense | 350 | |
| Rent expense | 1,765 | |
| Utilities expense | 465 | |
| Interest expense | 30 | |
| Total Expenses | (2,610) | |
| Net Income | 6,990 | |
Table (2)
d.
Prepare a statement of
d.
Explanation of Solution
Statement of stockholders’ equity: The statement which reports the changes in stock, paid-in capital, retained earnings, and
Prepare a statement of stockholders’ equity for the month of June.
| M Dance studio | |||
| Statement of Stockholders’ Equity | |||
| For the month of June | |||
| Common Stock | Retained Earnings | Total | |
| Balance, June 1 | $7,870 | $2,000 | $9,870 |
| Add: Net Income | $6,990 | $6,990 | |
| Less: Dividends | $(900) | $(900) | |
| Balance, June 30 | $7,870 | $8,090 | $15,960 |
Table (3)
e.
Prepare the balance sheet as of June 30.
e.
Explanation of Solution
Balance sheet: This financial statement reports a company’s resources (assets) and claims of creditors (liabilities) and stockholders (stockholders’ equity) over those resources. The resources of the company are assets which include money contributed by stockholders and creditors. Hence, the main elements of the balance sheet are assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity.
Prepare a balance sheet as of January 31.
| M Dance studio | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| As of June 30 | ||
| Particulars |
Amount ($) |
Amount ($) |
| ASSETS | ||
| Current Assets: | ||
| Cash | 5,860 | |
| Account receivable | 10,180 | |
| Total Current Assets | 16,040 | |
| Piano | 5,000 | |
| Total Assets | 21,040 | |
| LIABILITIES | ||
| Notes payable | 5,080 | |
| Total liabilities | 5,080 | |
| Stockholders’ equity | ||
| Common stock | 7,870 | |
| Retained earnings | 8,090 | |
| Total Stockholders’ Equity | 15,960 | |
| Total Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity | 21,040 | |
Table (4)
f.
Prepare the closing entries to close the accounts using the retained earnings account and compute the balance in the retained earnings account.
f.
Explanation of Solution
Closing entries: The journal entries prepared to close the temporary accounts to Retained Earnings account are referred to as closing entries. The revenue, expense, and dividends accounts are referred to as temporary accounts because the information and figures in these accounts is held temporarily and consequently transferred to permanent account at the end of accounting year.
Prepare the closing entry for revenue accounts.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| June 30 | Instructional fee earned (E–) | 7,500 | ||
| Performance revenue(E–) | 2,100 | |||
| Retained earnings (E+) | 9,600 | |||
| (To record the closing for revenue accounts) |
Table (5)
In this closing entry, service revenue account and interest income is closed by transferring the amount of instructional fee earned and performance revenue to the retained earnings account in order to bring the revenue account balance to zero. Hence, debit the instructional fee earned and performance revenue account and credit retained earnings account.
Prepare the closing entry for expenses account.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| June 30 | Retained earnings (E–) | 2,610 | ||
| Rent Expense (E+) | 1,765 | |||
| Advertising Expense (E+) | 350 | |||
| Utilities Expense (E+) | 465 | |||
| Interest Expenses (E+) | 30 | |||
| (To record the closing entry for the expense accounts) |
Table (6)
In this closing entry, all the expenses account is closed by transferring the amount of expenses to the retained earnings in order to bring the expenses account balance to zero. Hence, debit the retained earnings account and credit all expenses account.
Prepare the closing entry for dividend account.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| December 31 | Retained Earnings (E–) | 900 | ||
| Dividends (E+) | 900 | |||
| (To close the dividends account) |
Table (7)
In this closing entry, dividend account is closed by transferring the amount of dividend to the retained earnings in order to bring the expense account balance to zero. Hence, debit the retained earnings and credit dividends account.
g.
Prepare the post-closing trial balance for the year ended 30th June.
g.
Explanation of Solution
Post-closing trial balance:
The post-closing trial balance is a summary of all ledger accounts, and it shows the debit and the credit balances after the closing entries are journalized and posted. The post-closing trial balance contains only permanent (balance sheet) accounts, and the debit and the credit balances of permanent accounts should agree.
Prepare the post-closing trial balance of Incorporation B.
| M Dance Studio | ||
| Post-Closing Trial Balance | ||
| For the year ended June 30 | ||
| Accounts | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash | 5,860 | |
| Accounts receivable | 10,180 | |
| Piano | 5,000 | |
| Notes payable | 5,080 | |
| Common stock | 7,870 | |
| Retained earnings | 8,090 | |
| Total | 21,040 | 21,040 |
Table (8)
The debit column and credit column of the post-closing trial balance are agreed, both having balance of $21,040.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Financial Accounting for Undergr. -Text Only (Instructor's)

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





