
(a)
The magnitude and direction of the resultant velocity vector
Answer to Problem 39QAP
The resultant velocity vector
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The magnitude and the directions of the velocity vectors
Formula used:
If
The magnitude of the vector
The angle the vector makes with the x axis is given by,
Calculation:
Assume the +x axis to be directed along the East and the +yaxis along the North.
Draw a vector diagram for the velocities.
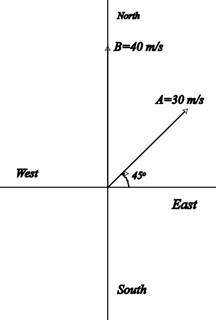
The vector
The velocity vector
Calculate the x and y components of the vector
Calculate the magnitude of the resultant velocity vector
Calculate the angle made by the vector with the +x axis (East).
Conclusion:
The resultant velocity vector
(b)
The magnitude and direction of the resultant velocity vector
Answer to Problem 39QAP
The resultant velocity vector
Explanation of Solution
Given:
From part (a), the components of the vectors
Formula used:
If
The magnitude of the vector
The angle made by the vector with the x axis is given by,
Calculation:
Calculate the x and y components of the vector
Calculate the magnitude of the vector
Calculate the angle made by the vector
Since the y component of
Conclusion:
The resultant velocity vector
(c)
The magnitude and the direction of the resultant velocity vector
Answer to Problem 39QAP
The resultant velocity vector
Explanation of Solution
Given:
From part (a), the components of the vectors
Formula used:
If
The magnitude of the vector
The angle made by the vector with the x axis is given by,
Calculation:
Calculate the x and y components of the vector
Calculate the magnitude of the vector
Calculate the angle made by the vector
Conclusion:
The resultant velocity vector
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
COLLEGE PHYSICS
- The maximum horizontal distance a boy can throw a ball is 50 m. Assume he can throw with the same initial speed at all angles. How high does he throw the ball when he throws it straight upward?arrow_forwardAn electron moves with a constant horizontal velocity of 3.0*10^6 m/s and no initial vertical velocity as it enters a deflector inside a TV tube. The electron strikes the screen after traveling 22cm horizontally and 40cm vertically upward with no horizontal acceleration. What is the constant vertical acceleration provided by the deflector? (The effects of gravity can be ignored.)arrow_forwardYou can use any coordinate system you like to solve a projectile motion problem. To demonstrate the truth of this statement, consider a ball thrown off the top of a building with a velocity v at an angle with respect to the horizontal. Let the building be 50.0 m tall, the initial horizontal velocity be 9.00 m/s, and the initial vertical velocity be 12.0 m/s. Choose your coordinates such that the positive y-axis is upward, the x-axis is to the right, and the origin is at the point where the ball is released, (a) With these choices, find the balls maximum height above the ground and the time it takes to reach the maximum height. (b) Repeat your calculations choosing the origin at the base of the building.arrow_forward
- Suppose you first walk 12.0 m in a direction 20° west of north and then 20.0 m in a direction 40.0° south of west. How far are you from your starting point, and what is the compass direction of a line connecting your starting point to your final position? (If you represent the two legs of the walk as vector displacements A and B, as in Figure 3.56, then this problem finds their sum R=A+B. )arrow_forwardRepeat the problem above, but reverse the order of the two legs of the walk; show that you get the same final result. That is, you first walk leg B, which is 20.0 m in a direction exactly 40° south of west, and then leg A, which is 12.0 m in a direction exactly 20° west of north. (This problem shows that A+B=B+A .)arrow_forwardIn a game of American football. a quarterback takes the ball from the line of scrimmage. runs backward a distance of 10.0 yards, and then runs sideways parallel to the line of scrimmage for 15.0 yards. At this point, he throws a forward pass downfield 50.0 yards perpendicular to the line of scrimmage. What is the magnitude of the football's resultant displacement?arrow_forward
- Suppose you walk 18.0 m straight west and then 25.0 m straight north. How far are you from your starting point, and what is the compass direction of a line connecting your starting point to your final position? (If you represent the two legs of the walk as vector displacements A and B as in Figure 3.55, then this problem asks you to find their sum R=A+B .)arrow_forwardYou can use any coordinate system you like to solve a projectile motion problem. To demonstrate the truth of this statement, consider a ball thrown off the top of a building with a velocity v at an angle with respect to the horizontal. Let the building be 50.0 m tall, the initial horizontal velocity be 9.00 m/s, and the initial vertical velocity be 12.0 m/s. Choose your coordinates such that the positive y-axis is upward, the x-axis is to the right, and the origin is at the point where the ball is released, (a) With these choices, find the balls maximum height above the ground and the time it takes to reach the maximum height. (b) Repeat your calculations choosing the origin at the base of the building.arrow_forwardSuppose you take two steps A and B (that is, two nonzero displacements). Under what circumstances can you end up at your starting point? More generally, under what circumstances can two nonzero vectors add to give zero? Is the maximum distance you can end up from the starting point A+B the sum of the lengths of the two steps?arrow_forward
- The world long jump record is 8.95 m (Mike Powell, USA, 1991). Treated as a projectile, what is the maximum range obtainable by a person if he has a take-off speed of 9.5 m/s? State your assumptions.arrow_forwardYou drive 7.50 km in a straight line in a direction 15° east of north. (a) Find the distances you would have to drive straight east and then straight north to arrive at the same point. (This determination is equivalent to find the components of the displacement along the east and north directions.) (b) Show that you still arrive at the same point if the east and north legs are reversed in order.arrow_forwardTwo students air on a balcony a distance h above the street. One student throws a ball vertically down-ward at a speed v0; at the same time, the other student throws a ball vertically upward at the same speed. Answer the following symbolically in terms of v0, g, h, and t. (a) Write the kinematic equation for the y-coordinate of each ball, (b) Set the equations found in part (a) equal to height 0 and solve each for t symbolically using the quadratic formula. What is the difference in the two balls' time in the air? (c) Use the time-independent kinematics equation to find the velocity of each ball as it strikes the ground, (d) How far apart are the balls at a time t after they are released and before the strike the ground?arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning




