
AND gate:
The AND gate is denoted by “AND”, “.” or no symbol. The AND gate is always opposite to the OR gate.

Truth table:
Consider the truth table of AND gate is as follows:
| A | B | C = AB |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
Here, the Boolean expressions “AB” is equivalent to the expression “A.B” is read “A and B”. The result of the given expression is 1 only when both the inputs are 1, and 0 otherwise.
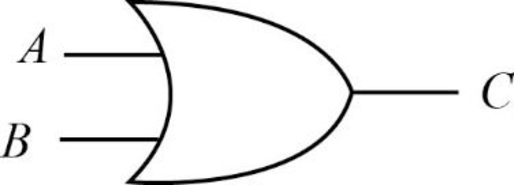
OR gate:
The OR gate is denoted by “OR” or “+”. The result of OR gate is 0 when both the inputs are 0, otherwise 1.
Truth table:
Consider the truth table of OR gate is as follows:
| A | B | C = A+B |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
Here, the Boolean expressions “A+B” then it is read “A or B”. The result of the given expression is 0 only when both the inputs are 0, and 1 otherwise.
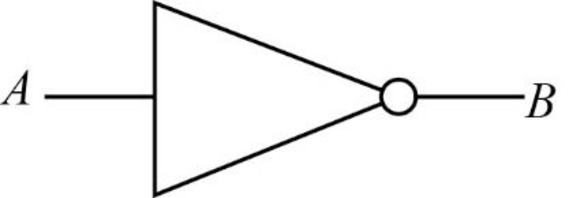
NOT gate:
The NOT gate denoted by negation symbol like “B’”. The result of NOT gate is 0 if the input is 1 and vice versa.
Truth table:
The truth table for NOT gate is given below:
| A | B' |
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 |
Here, the “B’” is simply opposite value of the input variable “A”.
Ex-OR gate:
The result of Ex-OR gate will be 1, if any of the input is 0. Otherwise 1.
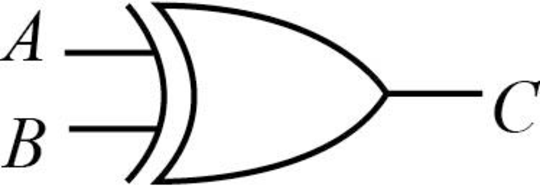
The truth table for XOR gate is given below:
| A | B | C = A |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
Here, the Boolean expression of “A
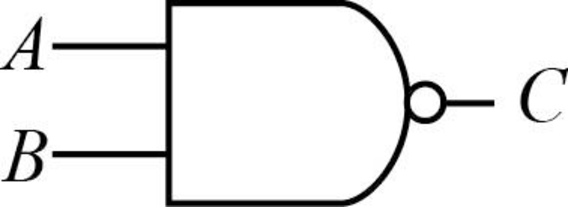
NAND gate:
The NAND gate is always opposite to the AND gate which means the result of NAND gate is 0 if both inputs are 1, otherwise 0.
Truth table:
Consider the truth table of NAND gate is as follows:
| A | B | C = (AB)’ |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
The result of the given expression is 0 only when both the inputs are 1, and 0 otherwise.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
Essentials of Computer Organization and Architecture
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





