
Concept explainers
Two infinitely long current-carrying wires run parallel in the xy plane and are each a distance d = 11.0 cm from the y axis (Fig. P30.83). The current in both wires is I = 5.00 A in the negative y direction.
- a. Draw a sketch of the magnetic field pattern in the xz plane due to the two wires. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field due to the two wires
- b. at the origin and
- c. as a function of z along the z axis, at x = y = 0?
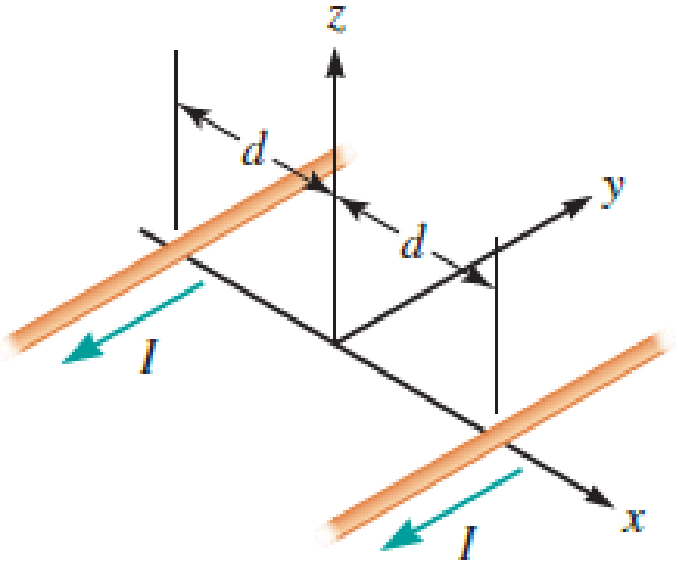
FIGURE P30.83
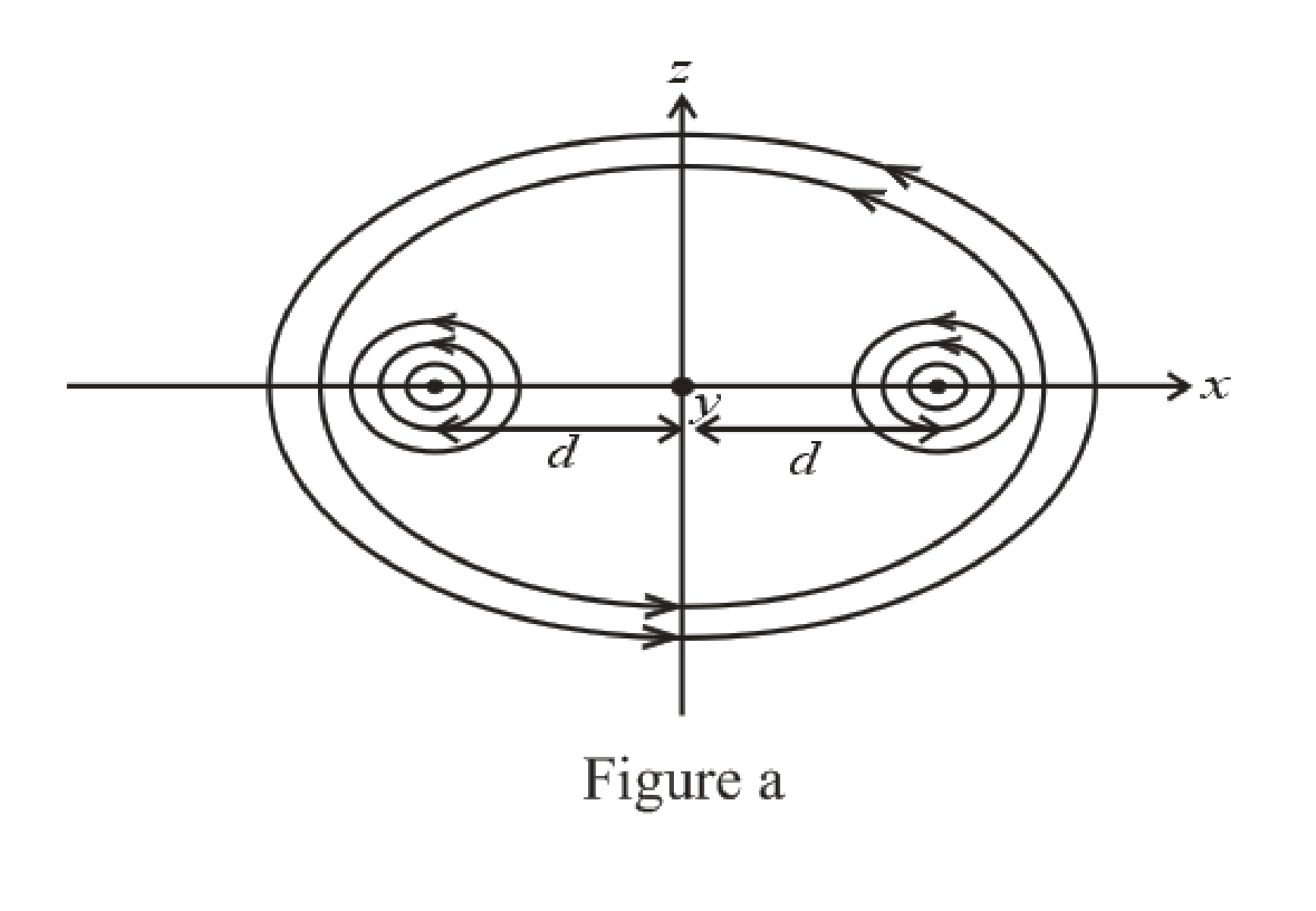
(a)
The sketch of the magnetic field pattern in the x-z plane due to the two wires.
Answer to Problem 83PQ
The direction of the magnetic field pattern in x-z plane is shown in figure (a).
Explanation of Solution
The direction of the magnetic field for a current carrying wire is given by the Right Hand Palm rule.
According to the right hand palm rule, the thumb of the right hand points in the direction of the current flowing in the wire, the fingers point along the point at which the magnetic field is to be calculated then the palm faces towards the direction of the magnetic field.
Here, the direction of magnetic field due to both wires is in anticlockwise direction.
Conclusion:
Thus, the direction of the magnetic field pattern in x-z plane is shown in figure (a).
(b)
The magnitude of the magnetic field due to the two wires at the origin.
Answer to Problem 83PQ
The magnitude of the magnetic field due to the two wires at the origin in zero.
Explanation of Solution
The direction of the magnetic field due to first wire and the second wire is shown as.
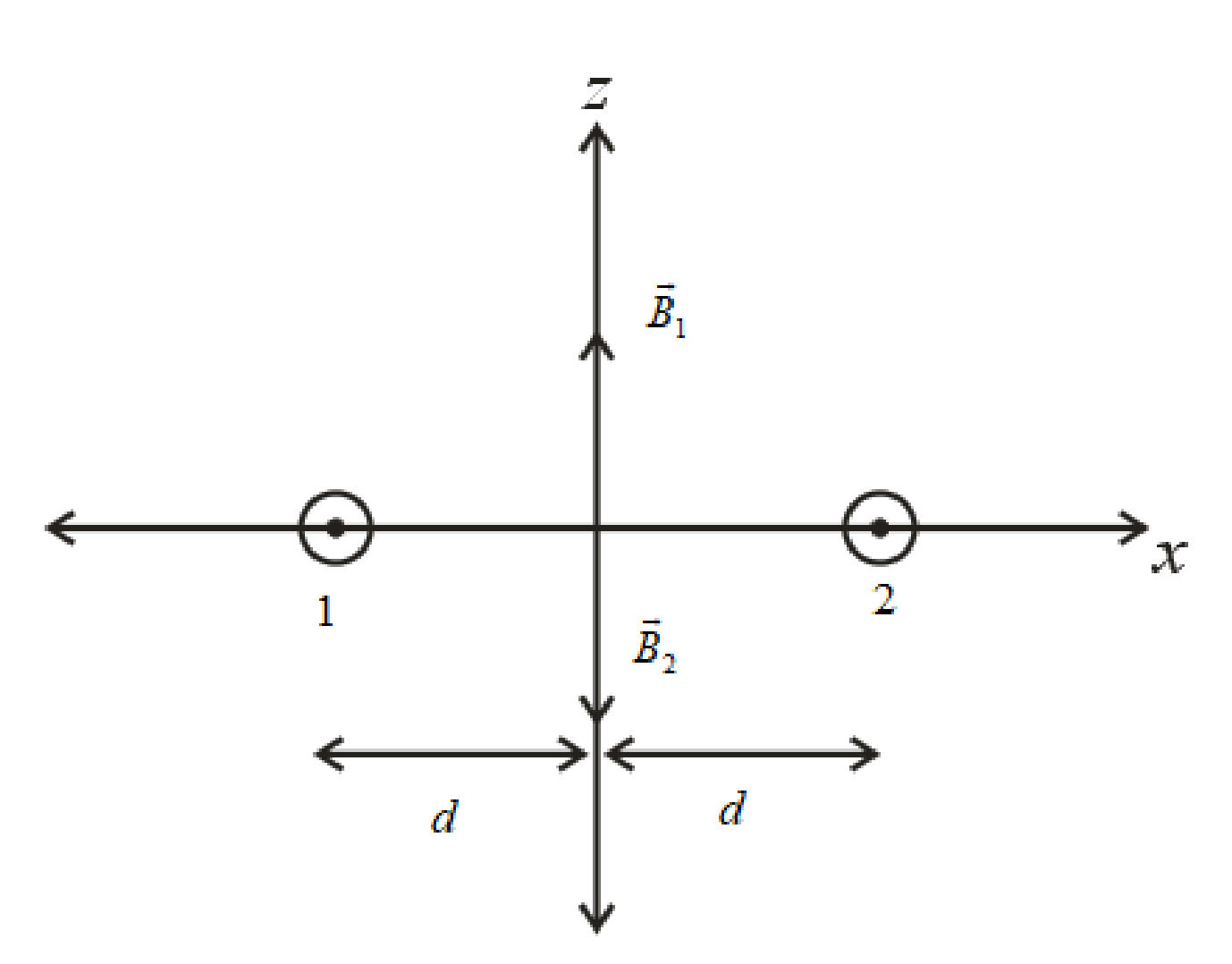
Write the expression forthe magnetic field due to first wire.
Here
Write the expression for the magnetic field due to second wire.
Here
Write the expression for the net magnetic field at the origin as.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Hence, the net magnetic field at the origin will be zero.
(c)
The magnitude of the magnetic field due to two wire as a function of z along the z-axis.
Answer to Problem 83PQ
The magnetic field due to two wires as a function of z along the Z-axis is
Explanation of Solution
The direction of the magnetic field for a current carrying wire is given by the Right Hand Palm rule.
The magnetic field due to both wires will be in negative X-direction at some point z above the origin.
Write the expression for the magnetic field due to first wire as.
Here,
The net magnetic field due to the second wire is same as that of the magnetic field due to the first wire.
Write the expression for the magnetic field due to second wire as.
Here,
The distance of the point along the Z-axis from the wire is given by the Pythagoras theorem.
Write the expression for the distance
Here,
Write the expression for the angle made by the position vector with the horizontal as.
Substitute
Write the expression for the net magnetic field as.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the magnetic field due to two wires as a function of z along the Z-axis is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 30 Solutions
Bundle: Physics For Scientists And Engineers: Foundations And Connections, Volume 2, Loose-leaf Version + Webassign Printed Access Card For Katz's ... And Connections, Single-term Courses
- One common type of cosmic ray is a proton traveling at close to the speed of light. If the proton is traveling downward, as shown in Figure P30.14, at a speed of 1.00 107 m/s, what are the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field at point B?arrow_forwardA Derive an expression for the magnetic field produced at point P due to the current-carrying wire shown in Figure P30.26. The curved parts of the wire are pieces of concentric circles. Point P is at their center.arrow_forwardFigure P31.13 shows a uniform magnetic field. a. Can you find a (nonzero area) loop through which the magnetic flux is zero? If so, draw the loop and the field. If not, explain why not. b. Can you find a loop through which the magnetic flux is nonzero? If so, draw the loop and the field. If not, explain why not.arrow_forward
- Figure P30.11 shows three configurations of wires and the resultant magnetic fields due to current in the wires. What is the direction of the current that gives the resultant magnetic field shown in each case?arrow_forwardFor both sketches in Figure P30.56, there is a 3.54-A current, a magnetic field strength B 0.650 T. and the angle is 32.0. Find the magnetic force per unit length (magnitude and direction) exerted on the current-carrying conductor in both cases.arrow_forwardA uniform magnetic field B=5.44104iT passes through a closed surface with a slanted top as shown in Figure P31.59. a. Given the dimensions and orientation of the closed surface shown, what is the magnetic flux through the slanted top of the surface? b. What is the net magnetic flux through the entire closed surface?arrow_forward
- A conducting rod is pulled with constant speed v on a smooth conducting rail as shown in Figure P32.77. A constant magnetic field B is directed into the page. If the speed of the bar is doubled, by what factor does the rate of heat dissipation change? FIGURE P32.77arrow_forwardA toroid has a major radius R and a minor radius r and is tightly wound with N turns of wire on a hollow cardboard torus. Figure P31.6 shows half of this toroid, allowing us to see its cross section. If R r, the magnetic field in the region enclosed by the wire is essentially the same as the magnetic field of a solenoid that has been bent into a large circle of radius R. Modeling the field as the uniform field of a long solenoid, show that the inductance of such a toroid is approximately L=120N2r2R Figure P31.6arrow_forwardA metal rod of mass M and length L is pivoted about a hinge at point O as shown in Figure P32.80. The axis of rotation passes through O into the page. A constant magnetic field B is applied into the page. Find the ratio of the maximum electric field inside the rod to the applied magnetic field when the rod is rotated with angular speed . Assume the speed of the rod is determined by the linear speed of its center of mass, and its mass is uniformly distributed. FIGURE P32.80arrow_forward
- The velocity vector of a singly charged helium ion (mHe = 6.64 1027 kg) is given by v=4.50105m/s. The acceleration of the ion in a region of space with a uniform magnetic field is 8.50 1012 m/s2 in the positive y direction. The velocity is perpendicular to the field direction. What are the magnitude and direction of the magnetic field in this region?arrow_forwardA current-carrying conductor PQ of mass m and length L is placed on an inclined plane with angle of inclination (Fig. P30.93). A uniform magnetic field B is directed upward as shown. Assume friction is negligible. a. Determine the magnitude and direction of the current in the conductor so that it remains in equilibrium. b. If the direction of the current is reversed, will the conductor still be in equilibrium? If not, find the magnitude of the initial acceleration of the conductor. FIGURE P30.93arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning



