
Engineering Mechanics: Statics
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780132915540
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: Prentice Hall
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3.4, Problem 60P
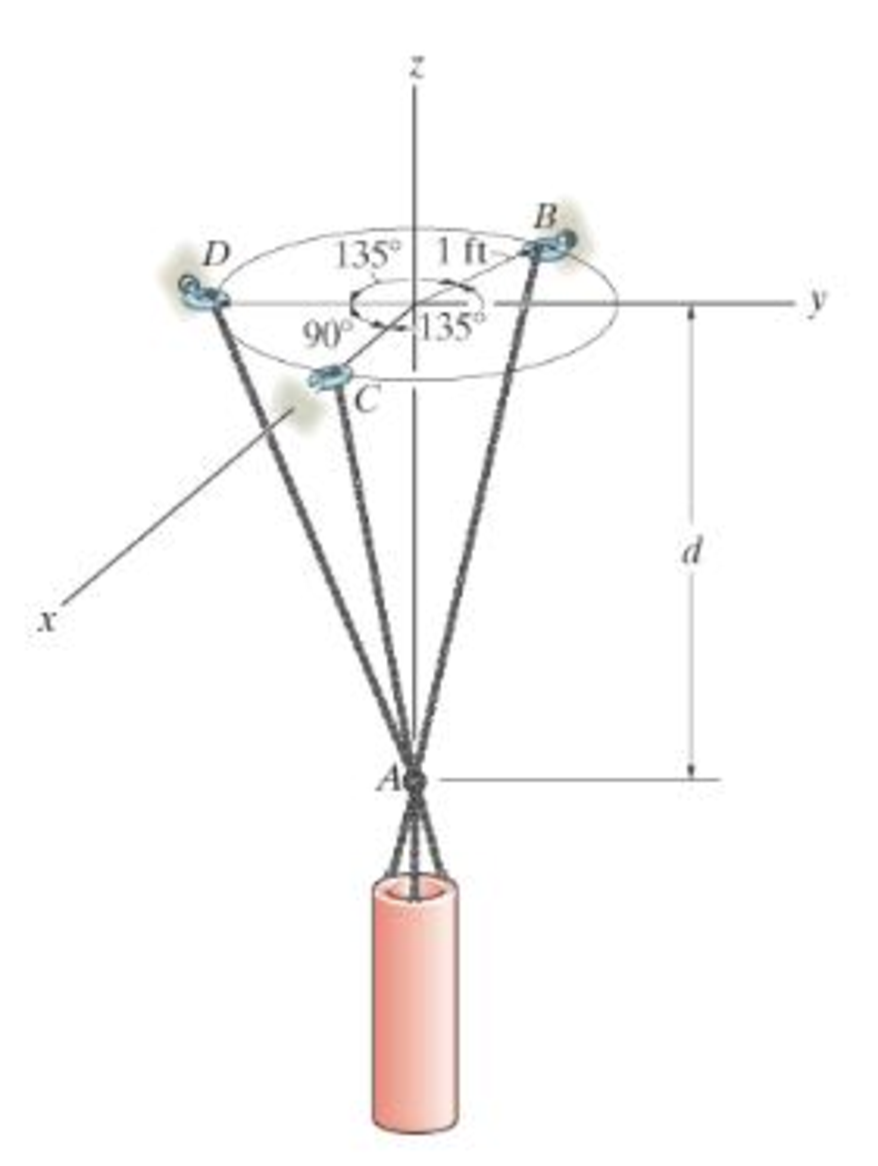
Determine the force in each chain for equilibrium. Take d = 1 ft
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule10:57
Students have asked these similar questions
The rope that makes up the system has a total length of 5 m.At D there is a load of weight W = 1320 N.Calculate the value of the load to be placed at B so that the system remains in equilibrium when S = 1,5 m.
If the length of cable CD is (5 ft), determine A) the tension in cable CD and B) what length of cable AC is required for static equilibrium
In each case, determine the force P required to maintain equilibrium. The block weighs 100 lb.
Chapter 3 Solutions
Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Ch. 3.3 - Determine the force in each supporting cable.Ch. 3.3 - Determine the shortest cable ABC that can be used...Ch. 3.3 - Neglect the size of the pulley.Ch. 3.3 - Determine the unstretched length of the spring.Ch. 3.3 - If the mass of cylinder C is 40 kg, determine the...Ch. 3.3 - Also, find the angle .Ch. 3.3 - Determine the magnitudes of F1 and F2 for...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the magnitude of F1 and its angle for...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the force in each of the cables AB and...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 4P
Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 5PCh. 3.3 - Prob. 6PCh. 3.3 - Prob. 7PCh. 3.3 - Prob. 8PCh. 3.3 - Determine the maximum weight of the flowerpot that...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 10PCh. 3.3 - Prob. 11PCh. 3.3 - Prob. 12PCh. 3.3 - Prob. 13PCh. 3.3 - Prob. 14PCh. 3.3 - Prob. 15PCh. 3.3 - Prob. 16PCh. 3.3 - Note that s = 0 when the cylinders are removed.Ch. 3.3 - The springs are shown in the equilibrium position.Ch. 3.3 - If the block is held in the equilibrium position...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the horizontal force F applied to the...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the displacement d of the cord from the...Ch. 3.3 - If the spring has an unstretched length of 2 ft,...Ch. 3.3 - Cord AB is 2 ft long. Take k = 50 lb/ft.Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 24PCh. 3.3 - Prob. 25PCh. 3.3 - Prob. 26PCh. 3.3 - Prob. 27PCh. 3.3 - Determine the tension developed in each cord...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the maximum mass of the lamp that the...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 30PCh. 3.3 - Prob. 31PCh. 3.3 - Prob. 32PCh. 3.3 - Prob. 33PCh. 3.3 - Prob. 34PCh. 3.3 - Determine the position x and the tension developed...Ch. 3.3 - Determine the position x and the tension in the...Ch. 3.3 - If the cable can be attached at either points A...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 38PCh. 3.3 - The cord is fixed to a pin at A and passes over...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 40PCh. 3.3 - Take F = 300 N and d = 1 m.Ch. 3.3 - If a force of F = 100 N is applied horizontally to...Ch. 3.3 - Establish appropriate dimensions and use an...Ch. 3.3 - If the maximum tension that can be supported by...Ch. 3.3 - If the angle between AB and BC is 30, determine...Ch. 3.3 - If the distance BC is 1.5 m, and AB can support a...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the magnitude of forces F1, F2, F3, so...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tension developed in cables AB, AC,...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tension developed in cables AB, AC,...Ch. 3.4 - F310. Determine the tension developed in cables...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the tension in these wires.Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 43PCh. 3.4 - If cable AB is subjected to a tension of 700 N,...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the magnitudes of F1, F2, and F3 for...Ch. 3.4 - If the bucket and its contents have a total weight...Ch. 3.4 - Each spring has on unstretched length of 2 m and a...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 48PCh. 3.4 - Prob. 49PCh. 3.4 - Prob. 50PCh. 3.4 - Prob. 51PCh. 3.4 - Prob. 52PCh. 3.4 - Prob. 53PCh. 3.4 - Determine the tens on developed in cables AB and...Ch. 3.4 - Also, what is the force developed along strut AD?Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 56PCh. 3.4 - Prob. 57PCh. 3.4 - Determine the tension developed in each cable for...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the maximum weight of the crate that can...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the force in each chain for equilibrium....Ch. 3.4 - If cable AD is tightened by a turnbuckle and...Ch. 3.4 - If cable AD is tightened by a turnbuckle and...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 63PCh. 3.4 - Prob. 64PCh. 3.4 - Prob. 65PCh. 3.4 - Prob. 66PCh. 3.4 - Prob. 67PCh. 3.4 - If the bolt exerts a force of 50 lb on the pipe in...Ch. 3.4 - Determine the magnitude of the applied vertical...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 70RPCh. 3.4 - Prob. 71RPCh. 3.4 - Prob. 72RPCh. 3.4 - Prob. 73RPCh. 3.4 - Also, what is the force in cord AB? Hint: use the...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 75RPCh. 3.4 - Determine the force in each cable needed to...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 77RP
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Comprehension Check 7-1
Express the following values using an appropriate Sl prefix such that there are only on...
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (3rd Edition)
What parts are included in the vehicle chassis?
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, and Service (5th Edition)
Determine the elastic curve for the cantilevered beam, which is subjected to the couple moment M0. Also calcula...
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
The support reactions. Also, draw the free body diagrams of Joints A, B, and C of the truss.
Engineering Mechanics: Statics & Dynamics (14th Edition)
What parts are included in the vehicle chassis?
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
6.6 Block A in the figure shown has a mass of 10 kg and block B has a mass of 20 kg. The coefficient of static ...
Applied Statics and Strength of Materials (6th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Determine the ratio P/Q of the forces that are required to maintain equilibrium of the mechanism for an arbitrary angle . Neglect the weight of the mechanism.arrow_forwardFind the stable equilibrium position of the system described in Prob. 10.56 if m = 2.06 kg.arrow_forwardThe 14-kN weight is suspended from a small pulley that is free to roll on the cable. The length of the cable ABC is 20 m. Determine the horizontal force P that would hold the pulley in equilibrium in the position x=5m.arrow_forward
- The spring attached to the sliding collar is capable of carrying tension and compression. The spring has a stiffness k = 1.5 lb/in., and its free length is 1.5L. If the System is known to be in equilibrium in the position =30, determine the weight W of the slider.arrow_forwardThe cable of mass 1.8 kg/m is attached to a rigid support at A and passes over a smooth pulley at B. If the mass M = 40 kg is attached to the free end of the cable, find the two values of H for which the cable will be in equilibrium. (Note: The smaller value of H represents stable equilibrium.)arrow_forwardDraw the FBDs for the entire structure and the member BDE. Count the total number of unknowns and the total number of independent equilibrium equations. Note that the cable that supports the 1200-lb weight runs over a smooth peg at D.arrow_forward
- The 40-kghomogeneous disk is placed on a frictionless inclined surface and held in equilibrium by the horizontal force P and a couple C (C is not shown on the figure). Find P and C.arrow_forwardNeglecting friction, determine the relationship between P and Q, assuming that the mechanism is in equilibrium in the position shown.arrow_forwardThe pulley system is used to lift a weight of 1.088 N. Determine the force P needed to bring the system into equilibrium.arrow_forward
- Determine the magnitude of the force P required to hold the 300-kg crate in equilibriumarrow_forwardThe ring weighs 5 N and is in equilibrium. The force F1 = 4.5 N. Determine the force F2 and the angle ∝.arrow_forwardBlocks D and F weigh 6 lb each and block E weighs 8 lb. Determine the sag s for equilibrium. Neglect the size of the pulleys.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
Engineering Basics - Statics & Forces in Equilibrium; Author: Solid Solutions - Professional Design Solutions;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dQBvQ2hJZFg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY