
Concept explainers
Light is incident on a prism as shown in Figure P38.31. The prism, an equilateral triangle, is made of plastic with an index of refraction of 1.46 for red light and 1.49 for blue light. Assume the apex angle of the prism is 60.00°.
- a. Sketch the approximate paths of the rays for red and blue light as they travel through and then exit the prism.
- b. Determine the measure of dispersion, the angle between the red and blue rays that exit the prism.
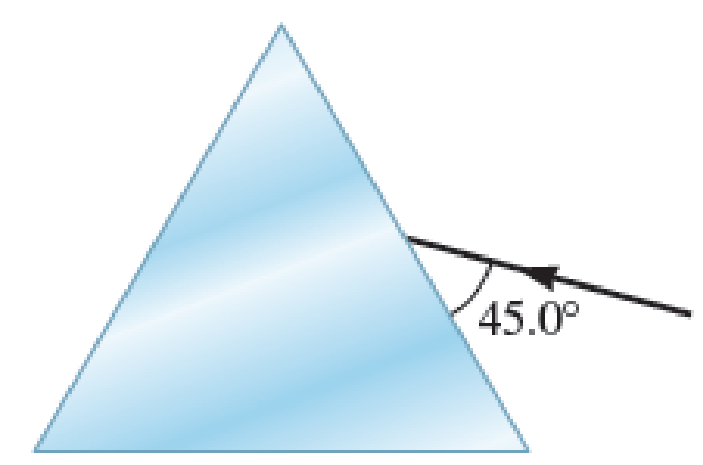
Figure P38.31
(a)
The sketch of the appropriate path of the red and blue light rays through the prism.
Answer to Problem 31PQ
The sketch of the appropriate path of the red and blue light rays through the prism is as shown below.
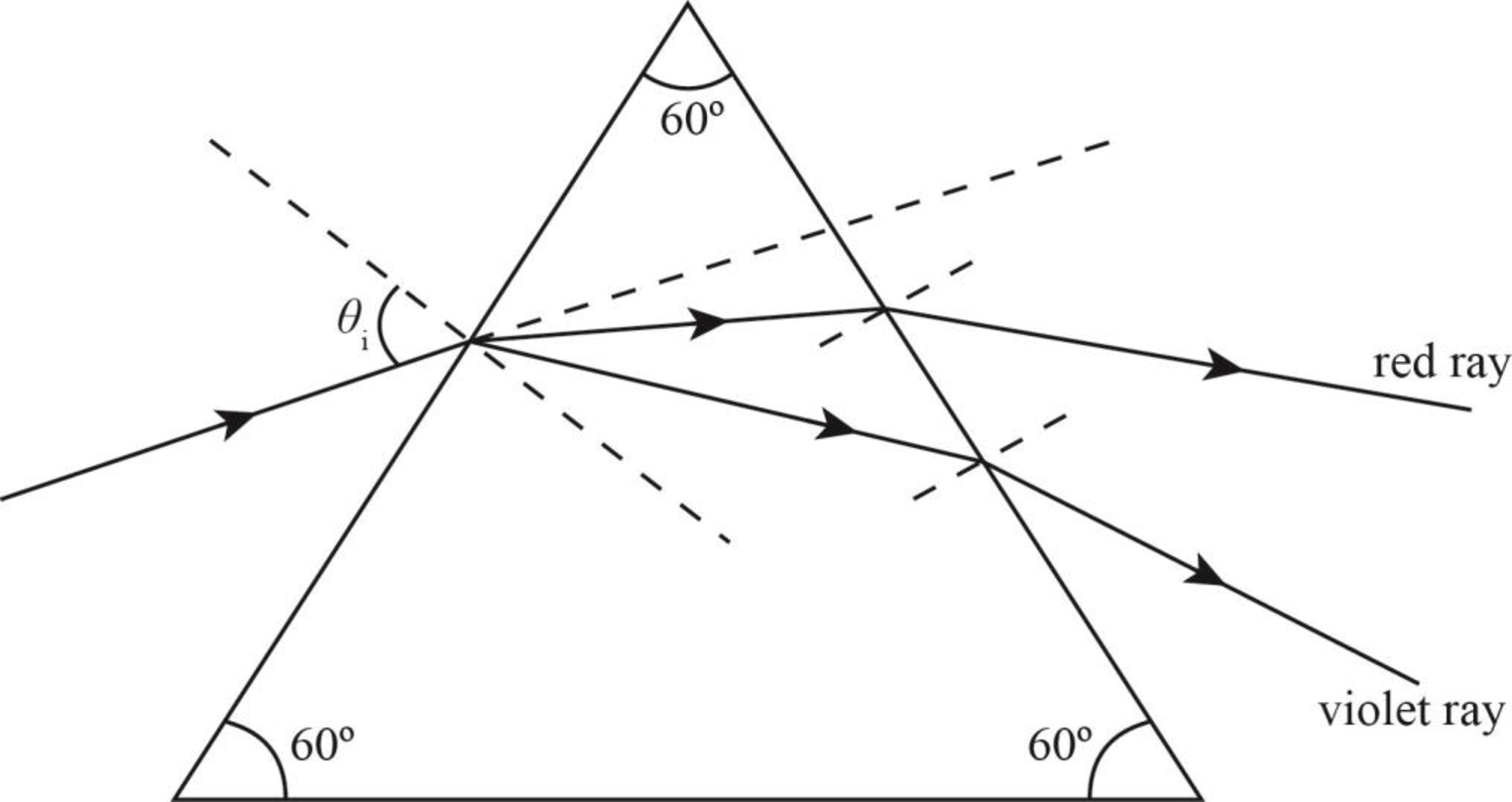
Explanation of Solution
The wavelength of the violet light is
The wavelength of light is inversely proportion to the refractive index of the material through which it is passing.
The wavelength of the violet light is lesser than the wavelength of the red light. Hence, the refractive index of the violet light is more as compared to the refractive index for the red light.
Therefore, violet light refracts more as compared to the red light as shown in the figure below.
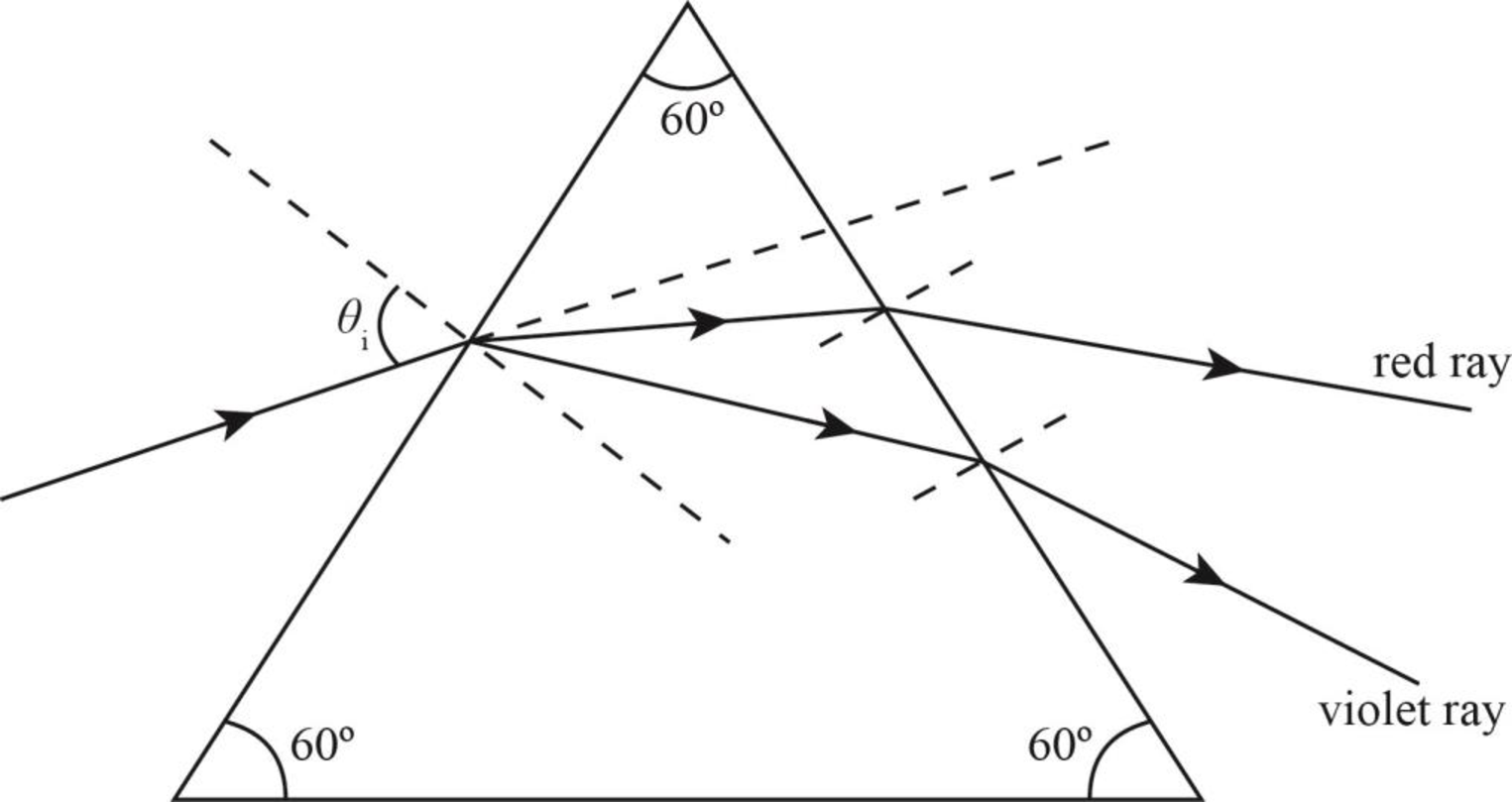
Figure-(1)
(b)
The dispersion angle between the red and blue rays when exit the prism.
Answer to Problem 31PQ
The dispersion angle between the red and blue rays when exit the prism is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for Snell’s law.
Here, incidence angle is
Further solve the above equation for
The prism diagram on which light is incident at an angle
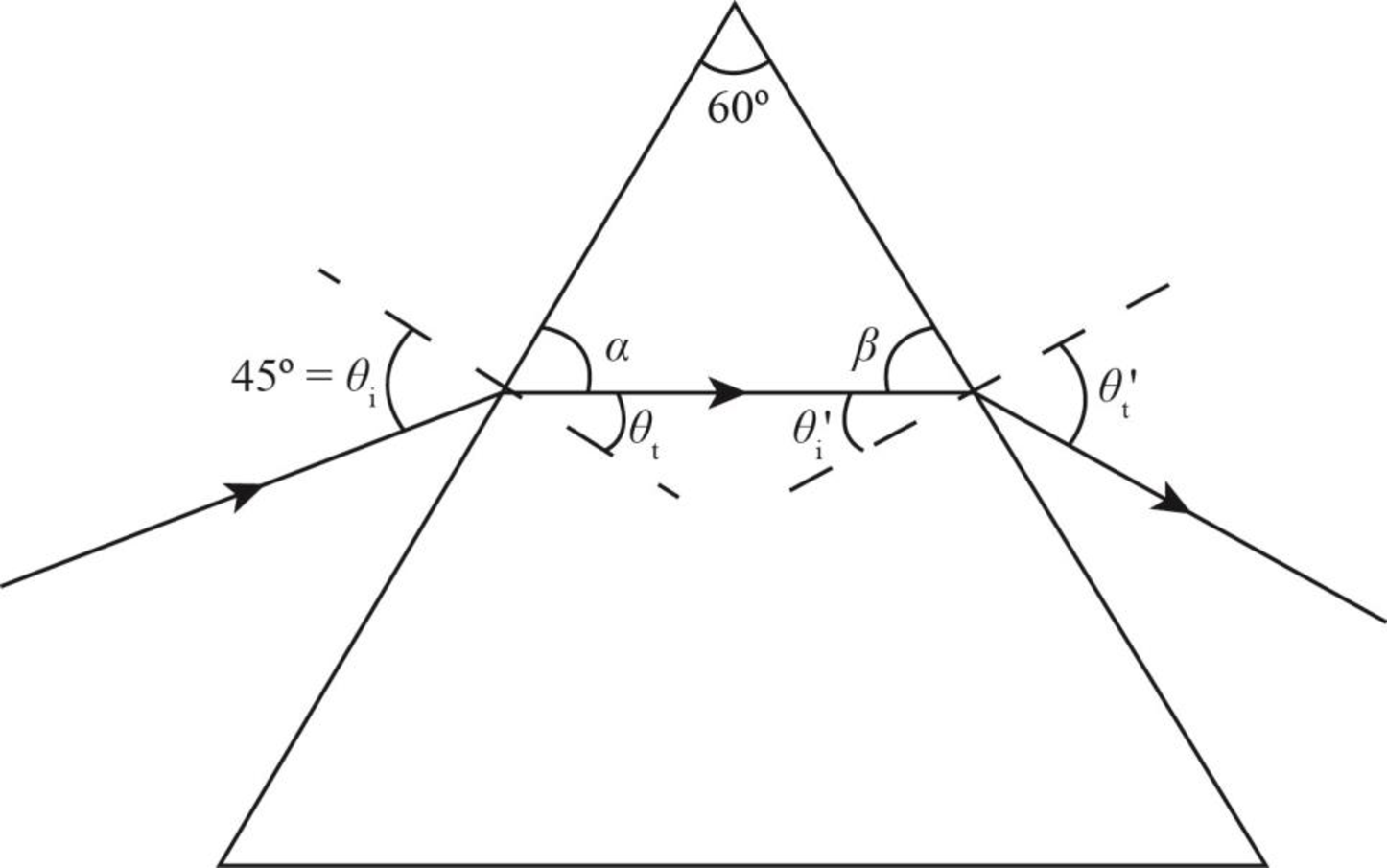
Figure-(1)
Write the expression for dispersion angle between the red and blue rays when exit the prism.
Here, dispersion angle between the red and blue rays when exit the prism is
Conclusion:
Case (i): For blue light.
Substitute
Solve for
Solve for
Solve for
Substitute
Case (ii): For red light.
Substitute
Solve for
Solve for
Solve for
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the dispersion angle between the red and blue rays when exit the prism is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 38 Solutions
Bundle: Physics For Scientists And Engineers: Foundations And Connections, Volume 2, Loose-leaf Version + Webassign Printed Access Card For Katz's ... And Connections, Single-term Courses
- A light ray is incident on an interface between water (n = 1.333) and air (n = 1.0002926) from within the air. If the angle of incidence in the air is 30.0, what is the angle of the refracted ray in the water?arrow_forwardA beam of monochromatic light within a fiber optic cable is incident on one of the sides of the cable (n = 1.485) at an angle of incidence i. Assume the fiber is surrounded by air (n = 1.00029). a. What is the critical angle for total internal reflection so that the beam stays within the fiber? b. What would the critical angle be if the fiber were completely immersed in water (n = 1.33)?arrow_forwardConsider a light ray that enters a pane of glass with air on one side and water on the other side as shown in Figure P38.21. The light ray experiences refraction at the first interface when it enters the glass from the water and again at the second interface when it exits the glass into the air. Assume the index of refraction of the glass is 1.54. For a ray of light, find the angle of incidence 1 in the water such that the ray experiences total internal reflection when it strikes the glassair interface on the other side. FIGURE P38.21arrow_forward
- Curved glassair interfaces like those observed in an empty shot glass make it possible for total internal reflection to occur at the shot glasss internal surface. Consider a glass cylinder (n = 1.54) with an outer radius of 2.50 cm and an inner radius of 2.00 cm as shown in Figure P38.105. Find the minimum angle i such that there is total internal reflection at the inner surface of the shot glass. FIGURE P38.105 Problems 105 and 106.arrow_forwardA beam of light is incident upon a stack of four flat transparent materials with indices of refraction of n1 =1.8, n2 =1.5 , n3 =1.3 , and n4 =1.2, see figure. a. If θ1 is 29o, what angle θ2 does the beam make to the normal when in emerges into the air after passing through the entire stack? b. What must the incident angle θ1 be to have total internal reflection at the surface between medium n4 and n?arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning


