
Three network topologies, four different network types, along withthe uses and limitations of each.
Explanation of Solution
Network topologies defines the shape, structure and arrangement in which components of a network can be linked. Though, among networks transmission rate, distance between nodes, signal types and physical media uses for connection may differ, but they may have the same topology.
The three main popular network topologies used are star, bus and mesh topologies.
Star topology: In this topology, all nodes in a network are connected to a central node which is known as hub node. Start topology is very easy to implement and is used when lesser number of devices are required to be connected. The main drawback of star topology is that in case, there is failure of central node, the entire network will go down. The figure below shows devices connected in star topology:

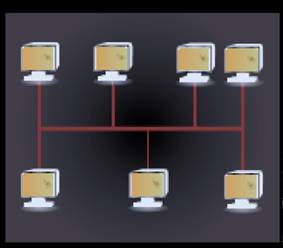
Bus topology: In this topology, every node on the network is connected through a common commnication channel known as Bus. For communication purposes, whenever any device needs to communicate with any other device, it sends braodcast messages through a communication link which goes to all devices but can only be accepted and processed by the intended receiving device. But topology is the easiest way to establishing a network and also,the cost of implementation is less. The main issue with bus topology is that for a large network, there is more amount of time needed for communication between devices at extreme ends than devices which are in close proximity. Also, in case of failure of bus, the whole network has to be restructured which is a very time consuming process. The following figure shows bus topology:
Mesh topology: In mesh topology, nodes can be connected on network using multiple access points. Each device on the network is directly linked with another device. In mesh topology, a connection is established between the sending device and receiving device by routing through node to node and make a continous connection which does not have any blocked nodes. Mesh topology is the most reliable type of

Based on physical distances between the connected nodes of a network, the networkscan be classified as personal area network, local area network, metropolitan area network and wide area network.
Personal area network (PAN): PAN is a wireless network which is setup near a person. A person can connect laptops, digital cameras, mobile phones, printers etc by using personal area. all together. PAN is also used in IoT connections for allowing sensors to receive data from your body and transmit it to your smartphone which can be used for health tracking, glucose monitoring, and pedometers.
Local area network (LAN): LAN network connects computing devices within an office, home or building. Typically, a LAN network, has hundreds of computing devices connected to the network. LAN network is used to create a private and secure network.
Metropolitan area network (MAN): MAN is used to connect multiple LAN networks spread across various small geographical locations together. Two or more LAN networks can be connected into a WAN network. MAN, networks can be used to connect multiple offices of an organization locatedin different locations.
Wide area network (WAN): WAN is used to connect large geographical regions. They are mainly used to provide communication over national borders. A WAN network can be either be privately owned or can be rented. WAN comes to picture when you try to make a phone call to somebody who is in any other international location. For establishing WAN, national and international laws need to be taken care while handling and monitoring data flow through these networks.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Bundle: Fundamentals of Information Systems, Loose-Leaf Version, 9th + MindTap MIS, 1 term (6 months) Printed Access Card
- What are the possible network topologies, and one would you recommend?arrow_forwardIn order for a network to function appropriately and effectively, what are the three components that have to be in place? Kindly provide your own interpretation of one of these, thank you.arrow_forwardWhich network topologies are feasible, and which do you advise?arrow_forward
 Fundamentals of Information SystemsComputer ScienceISBN:9781337097536Author:Ralph Stair, George ReynoldsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Information SystemsComputer ScienceISBN:9781337097536Author:Ralph Stair, George ReynoldsPublisher:Cengage Learning
