
Income Statement for Year Ended December 31, 2018 (Millions of Dollars)
| Net sales | $795.0 |
| Cost of goods sold | 660.0 |
| Gross profit | $135.0 |
| Selling expenses | 73.5 |
| EBITDA | $ 61.5 |
| 12.0 | |
| Earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) | $ 49.5 |
| Interest expenses | 4.5 |
| Earnings before taxes (EBT) | $ 45.0 |
| Taxes (40%) | 18.0 |
| Net income | $ 27.0 |
- a. Calculate the ratios you think would be useful in this analysis.
- b. Construct a DuPont equation, and compare the company’s ratios to the industry average ratios.
- c. Do the balance-sheet accounts or the income statement figures seem to be primarily responsible for the low profits?
- d. Which specific accounts seem to be most out of line relative to other firms in the industry?
- e. If the firm had a pronounced seasonal sales pattern or if it grew rapidly during the year, how might that affect the validity of your ratio analysis? How might you correct for such potential problems?
a.
To determine: The ratios that would be useful in this analysis.
Current Ratio:
Current ratio is a part of liquidity ratio, which reflects the capability of the company to payback its short-term debts. It is calculated based on the current assets and current liabilities that a company possess in an accounting period.
Ratio Analysis:
Ratio is used to compare two arithmetical figures. In case of the ratio analysis of the company, the financial ratios are calculated. The financial ratios examine the performance of the company and is used in comparing with other same business. It indicates relationship of two or more parts of financial statements.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
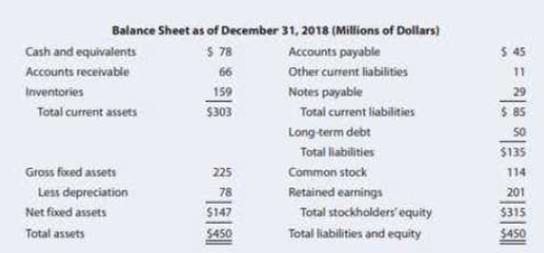
Current assets are $303.
Current liabilities are $85.
The formula to calculate current ratio is as follows:
Substitute $303 for current assets and $85 for current liabilities.
Thus, current ratio is 3.56 times.
Fixed Assets Turnover Ratio:
It reflects the efficiency of the company to utilize fixed asset to increase sale.
Given information:
Sales are $795.
Net fixed assets are $147.
The formula to calculate fixed assets turnover is as follows:
Substitute $795 for total sales and $`147 for fixed assets in above formula.
Thus, fixed assets turnover is 5.40 times.
Debt-to-Capital Ratio:
It is percentage of total capital that is financed by the borrowed fund. Borrowed fund includes short and long-term debts. Operating debt like account payable, accrual are not considered.
Given information:
Total debt is $79 (working note).
Equity is $315 (working note).
The formula of Debt-to-capital ratio is as follows:
Substitute $79 for total debt and $315 for equity in above formula.
Thus, debt-to-capital ratio is 20.05%.
Working notes:
Compute total debt.
Given information:
Long-term debt is $50.
Notes payable is $29.
Calculation of total debt of the company is as follows:
Thus, total debt is $79.
Compute the total value of the common equity is as follows:
Given information:
Common stock is $114.
Retained earnings are $201.
Formula to calculate common equity is as follows:
Substitute $114 for common stock and $201 for retained earnings.
Thus, common equity is $315.
Total Assets Turnover Ratio:
It indicates how effectively the asset of a company is utilized. Total asset is the sum of current assets and fixed assets.
Given,
Total sales is $795
Total assets are $450.
Formula to calculate total assets turnover is,
Substitute $795 for total sales and $450 for total assets.
Thus, total assets turnover is 1.76 times.
Times-Interest Earned Ratio:
It is the type of solvency ratio that indicates the capability of business to repay interest and provide debt related services.
Given,
Earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) are $49.5.
Interest expense is $4.5.
Formula to calculate times interest earned is as follows:
Substitute $49.5 for EBIT and $4.5 for interest expense.
Thus, the times interest earned ratio is 11%.
Profit Margin
Profit margin is the ratio net income of the company and total sales. It is one of the profitability ratios.
Given information:
Net income is $27.
Sales are $795.
Formula to calculate profit ratio is as follows:
Substitute $27 for net income and $795 for sales in above formula.
Thus, profit ratio is 3.40%.
Return on Assets:
It is a profitability ratio. This ratio shows profit earning capability on per dollar of assets. It shows the percentage of net income on total assets. Higher the return on assets better the profitability. Total assets include fixed as well as current assets.
Given information
Net income is$27.
Total asset is $450.
Formula to calculate return on assets is,
Substitute $27 for net income and $450 for total value of assets.
Thus, return on assets is 6%.
Inventory Turnover Ratio:
Inventory turnover ratio reflects the number of times average inventory is converted into sales during the period under consideration. It is used to measures the efficiency of business operations.
Given information:
Total sales are $795.
Total inventory is $159.
Formula to calculate inventory turnover ratio is as follows:
Substitute $795 for total sales and $159 for total inventory.
Thus, inventory turnover ratio is 5 times.
Return on Equity:
Return on equity is the return earned from the capital invested in equity. It is the ratio of net income and shareholders’ equity. This ratio measures the performance of the company and tells how well the company is performing. This ratio is used to compare own firm with competitors.
Given information:
Net income is $27.
Common equity is $315 [Equation (2)].
Formula to calculate return on equity is as follows:
Substitute $27 for net income and $315 for common equity.
Thus, return on equity is 8.57%.
Days Sales Outstanding
Days sales outstanding is used to measure days that a business usually requires to collects its receivable in average. It indicates account receivable of the firm and firm’s efficiency in collecting the account receivable.
Given information
Receivables are $66.
Annual sale is $795.
Formula to calculate day’s sales outstanding is as follows:
Substitute $66 for account receivables and $795 for annual sales.
Thus, day’s sales outstanding is 30.30 days.
Return on Invested Capital:
It represent the amount of return earned by all investors and can be calculated by dividing total earnings available for investors to total invested capital.
Given information:
Earnings before interest and tax (EBIT) are $49.5.
Tax rate is 40%.
Total debt is $79 [equation (1)]
Total equity is $315[equation (2)]
Substitute $49.5 for EBIT, $79 for debt, 40% for the tax rate and $315for equity.
Thus, return on invested capital is 7.53%.
b.
To determine: DuPont equation and comparison of company’s ratio with industry average ratio.
Du Pont Equation:
Among all ratios, return on equity is very common. It shows the value of the firm. Improvement in the ROE is considered as valued addition to the firm. ROE can be linked with other ratios. Analysis of such ratios will indicate proper reason for change in ROE. The combination is known as Du Pont equation, which is shown below.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Return on equity (ROE) is 8.57%.
Net income of the company is$27.
Sales of the company are $795.
Total assets are $450.
Total common equity is $315.
The Du point relation of the company’s ratios is shown below,
Substitute $27 for net income, $795 for sales, $450 for total assets and $315 for common equity
Thus DuPont equation is
Comparison:
| Profit Margin | Total Assets Turnover | Equity Multiplier | ROE | |
| Firm | 3.40% | 1.76 times | 1.429 times | 8.57% |
| Industry | 3% | 3 times | 1.249times | 12.86% |
Table (1)
- After analyzing the Du sPont, equation total asset turnover of the firm is lower than industry’s average. Probably firm is carrying more assets than required to carry to support its sales. The firm should increase it sales.
- The return on equity is lower than industry average but the profit margin is higher than industry’s average.
Working notes:
Calculate Industry’s equity multiplier.
Given information:
Industry’s ROE is 12.86%.
Total assets turnover is 3 times.
Profit margin is 3%.
The formula to calculate ROE is as follows:
Substitute 12.86% for ROE, 3% for the profit margin and 3 times for total assets turnover.
Thus, equity multiplier is 1.429 times.
Therefore, DuPont equation has been constructed and the company’s ratios are compared with industry average ratios.
c.
To identify: The balance sheet accounts or income statement figures are primarily responsible for the low profits or not.
Answer to Problem 24P
- Net income is calculated from the income statement so it can be said the income statement figures are accountable for low profits.
- If the firm has not enough cash and other resources and has, too much debt it will results in low sales and funds to get necessary resources. Thus, the items of balance sheet are also responsible for the low profits.
Explanation of Solution
- The figures of income statement like sales, operating expenses affect the profit. If the sale is high, the net income is also high and sales decreases it will decrease profit of the firm. Similarly if there is an increase or decrease in the operating expenses the profit will be affected directly. Therefore, it can be said the income statement items are responsible for low profit.
- The items of balance sheet accounts like cash, inventory debt and capital affect the profit of the firm. If the level of inventory is too high or the debt is too high it can results in low profit. Thus, it can be said the balance sheet items are somehow responsible for lower profit.
Therefore, the balance sheet accounts and income statement figures are responsible for low profit.
d.
To identify: The specific accounts seems to be most out of line comparative to other companies in the same industry.
Answer to Problem 24P
The specific account, which seems to be most out of line relative to the other firms in the same industry, is given below:
- Fixed assets turnover
- Inventory turnover ratio
- Total assets turnover
- Return on assets
- Return on equity
- Return on invested capital(ROIC)
Explanation of Solution
- The fixed asset turnover of the firm is 5.40 times while the industry average is 6 times. It can be said that the ratio is low in comparison to that of the other firm in industry.
- Inventory turnover of 5 times while industry has 10 times. The firm ratio seems out of line to the other firms in the same industry.
- Total assets turnover of firm is 1.76 times is too low in comparison to industry average that is 3 times. It seems out of the line to other firms in the same industry.
- Return on asset of firm is 6% and industry average is 9%, which indicates the firm has lower ratio than other firm in same industry.
- Return on common equity of the firm is 8.57% and average of the industry is 12.86%. The firm got lower ratio than the other firms did which makes firm out of line to the other firm in the same industry.
- Return on invested capital of the firm is 7.53% while the industry average is 11.50%. It shows the firm ratio somehow out of line relative to the other firm.
Therefore, Fixed Assets turnover, inventory turnover ratio, total assets turnover, return on asset, return on equity, and return on invested capital (ROIC)seems to be most out of line comparative to other firms in the same industry.
(e)
To identify: The validity of the ratio analysis if the firm had marked seasonal sales pattern or if the sales grew rapidly during the year and the way of correcting potential problems.
Answer to Problem 24P
- If the sales of the company grew rapidly many ratios such related to cash, receivables, inventories and current liabilities might be distorted. Similarly ratios which are based on sales, profit, and common equity could be influenced.
- This type of problem can be corrected by using average figure instead of ending figures.
Explanation of Solution
The increase in sale affects the ratios which are calculated being based on the sales. The increases in sales increases the cash balance, receivables and it also affect the net income of the company. The ratio will get influenced from such increase.
Therefore, if the firm had pronounced seasonal sales and if the sales grew quickly during the year the ratios will get distorted and such problem can be solved by taking average figure rather than end period figures.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Bundle: Fundamentals of Financial Management, Loose-leaf Version, 15th + MindTap Finance, 1 term (6 months) Printed Access Card
- Refer to RE22-2. Assume Heller Company had sales revenue of 510,000 in 2019 and 650,000 in 2020. Prepare Hellers partial income statements (through gross profit) for 2019 and 2020. RE22-2 Heller Company began operations in 2019 and used the LIFO method to compute its 300,000 cost of goods sold for that year. At the beginning of 2020, Heller changed to the FIFO method. Heller determined that its cost of goods sold under FIFO would have been 250,000 in 2019. For 2020, Hellers cost of goods sold under FIFO was 360,000, while it would have been 410,000 under LIFO. Heller is subject to a 21% income tax rate. Compute the cumulative effect of the retrospective adjustment on prior years income (net of taxes) that Heller would report on its retained earnings statement for 2020.arrow_forwardThe following information is available for Cooke Company for the current year: The gross margin is 40% of net sales. What is the cost of goods available for sale? a. 5840,000 b. 960,000 c. 1,200,000 d. 1,220,000arrow_forwardCost of goods sold and related items The following data were extracted from the accounting records of Harkins Company for the year ended April 30, 20Y8: Estimated returns of current year sales 11,600 Inventory, May 1, 20Y7 380,000 Inventory, April 30, 20Y8 415,000 Purchases 3,800,000 Purchases returns and allowances 150,000 Purchases discounts 80,000 Sales 5,850,000 Freight in 16,600 a. Prepare the Cost of goods sold section of the income statement for the year ended April 30, 20Y8, using the periodic inventory system. b. Determine the gross profit to be reported on the income statement for the year ended April 30, 20Y8. c. Would gross profit be different if the perpetual inventory system was used instead of the periodic inventory system?arrow_forward
- The following selected information is taken from the financial statements of Arnn Company for its most recent year of operations: During the year, Arnn had net sales of 2.45 million. The cost of goods sold was 1.3 million. Required: Note: Round all answers to two decimal places. 1. Compute the current ratio. 2. Compute the quick or acid-test ratio. 3. Compute the accounts receivable turnover ratio. 4. Compute the accounts receivable turnover in days. 5. Compute the inventory turnover ratio. 6. Compute the inventory turnover in days.arrow_forwardOn January 1, Pope Enterprises inventory was 625,000. Pope made 950,000 of net purchases during the year. On its year-end income statement, Pope reported cost of goods sold of 1,025,000. Calculate Popes December 31 ending inventory.arrow_forward
 Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning





