
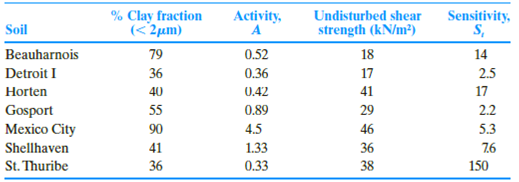
The properties of seven different clayey soils are shown below (Skempton and Northey, 1952). Investigate the relationship between the strength and plasticity characteristics by performing the following tasks:
a. Estimate the plasticity index for each soil using Skempton’s definition of activity [Eq. (4.28)].
b. Estimate the probable mineral composition of the clay soils based on PI and A (use Table 4.3)
c. Sensitivity (St) refers to the loss of strength when the soil is remolded or disturbed. It is defined as the ratio of the undisturbed strength (τf-undisturbed) to the remolded strength (τf-remolded)) at the same moisture content [Eq. (12.49)]. From the given data, estimate τf-remolded for the clay soils.
d. Plot the variations of undisturbed and remolded shear strengths with the activity, A, and explain the observed behavior.
(a)
Find the plasticity index for each soil using Skempton’s definition of activity.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the plasticity index of the Beauharnais soil using the relation.
Here, A is an activity.
Substitute 0.52 for A and 79 for % of clay–size fraction, by weight.
Similarly, calculate the plasticity index for the remaining soils.
Determine the remolded shear strength of the Beauharnais soil using the relation.
Here,
Substitute
Similarly, calculate the remolded shear strength of the remaining soils.
Summarize the calculated values of plasticity index and the remolded shear strength as in Table 1.
| Soil | % Clay fraction | Activity A | Plasticity Index |
| Beauharnois | 79 | 0.52 | 41.08 |
| Detroit I | 36 | 0.36 | 12.96 |
| Horten | 40 | 0.42 | 16.80 |
| Gosport | 55 | 0.89 | 48.95 |
| Mexico City | 90 | 4.5 | 405 |
| Shell haven | 41 | 1.33 | 54.53 |
| St.Thuribe | 36 | 0.33 | 11.88 |
(b)
Find the probable mineral composition of the clay soils based on PI and A.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the probable mineral composition of the clay soils based on PI and A.
Refer Table 4.3, “Typical values of liquid limit, plastic limit, and activity of some clay minerals” in the textbook.
Take the mineral composition of the Beauharnois soil as Illite for the activity value of 0.52 and the plasticity index value of 41.08.
Therefore, the mineral composition of Beauharnois soil is Illite.
Similarly, calculate the probable mineral composition of the remaining soils.
Summarize the calculated values of mineral composition as in Table (2).
| Soil | Activity A | Plasticity Index | Mineral composition |
| Beauharnois | 0.52 | 41.08 | Illite |
| Detroit I | 0.36 | 12.96 | Kaolinite |
| Horten | 0.42 | 16.80 | Kaolinite |
| Gosport | 0.89 | 48.95 | Illite |
| Mexico City | 4.5 | 405 | Montmorillonite |
| Shell haven | 1.33 | 54.53 | Montmorillonite |
| St.Thuribe | 0.33 | 11.88 | Kaolinite |
(c)
Find the remoulded shear strength of the clay soil.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the remoulded shear strength of the Beauharnais soil using the relation.
Here,
Substitute
Similarly, calculate the remolded shear strength of the remaining soils.
Summarize the calculated values of remolded shear strength as in Table 3.
| Soil | Activity A | Undisturbed Shear strength | Sensitivity |
Remoulded Shear strength |
| Beauharnois | 0.52 | 18 | 14 | 1.3 |
| Detroit I | 0.36 | 17 | 2.5 | 6.8 |
| Horten | 0.42 | 41 | 17 | 2.4 |
| Gosport | 0.89 | 29 | 2.2 | 13.2 |
| Mexico City | 4.5 | 46 | 5.3 | 8.7 |
| Shell haven | 1.33 | 36 | 7.6 | 4.7 |
| St.Thuribe | 0.33 | 38 | 150 | 0.3 |
(d)
Plot the variations of undisturbed and remolded shear strengths with the activity A.
Explanation of Solution
Refer Table 3.
Plot the graph between the undisturbed, remolded shear strengths with the activity A as in Figure 1.
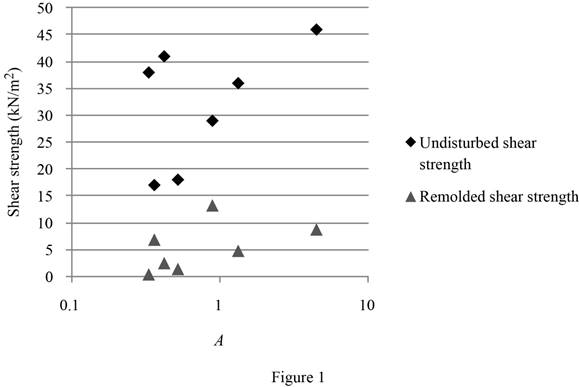
The shear strength of the clay obtains from two components, one is cohesion, which is the cementing force between particles, and second one is frictional resistance, which is mainly due to the particle movement of one particle over another. The cohesion contribution is greater to the shear strength, when the clay activity is greater. Although no reliable correlation can be developed from Figure 1, both the undisturbed and remolded shear strengths certainly show increasing trends as the activity increases.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
PRIN.OF GEOTECH.ENGR. (LL) - W/MINDTAP
- Refer to the soil in Problem 4.5. Using the Casagrande plasticity chart, graphically estimate the shrinkage limit of the soil as shown in Figure 4.22. 4.5 The following data were obtained by conducting liquid limit and plastic limit tests on a soil collected from the site. Liquid limit tests: Plastic limit test: PL = 19.3% a. Draw the flow curve and determine the liquid limit. b. Using the Casagrande plasticity chart (Figure 4.21), determine the soil type.arrow_forwardRepeat Problem 2.11 with the following data. 2.11 The grain-size characteristics of a soil are given in the following table. a. Draw the grain-size distribution curve. b. Determine the percentages of gravel, sand, silt, and clay according to the MIT system. c. Repeat Part b using the USDA system. d. Repeat Part b using the AASHTO system.arrow_forwardA soil profile is shown in Figure P3.3 along with the standardpenetration numbers in the clay layer. Use Eqs. (3.8b)and (3.9) to determine the variation of cu and OCR withdepth. What is the average value of cu and OCR?arrow_forward
- Determine the volume of water flowing through the sample shown in the figure per hour. There are 3 different soil layers and each is 200mm in length and diameter is 150mm. A constant head of 470mm is maintained across the soil sample. The porosity for Soil I is 0.5 and the value of k is 5*10^-3 cm/s. The porosity for Soil II is 0.55 and the value of k is 4.2*10^-2 cm/s. The porosity for Soil III is 0.35 and the value of k is 3.69*10^-4 cm/s. The hydraulic conductivities are measured in the direction of the flow.arrow_forwardA soil sample presents the physical indices presented in Table 2. Determining the classificationof the soil sample, according to the Unified Classification System (SUCS), diagram in Figure 1.arrow_forwardFollowing are the results of a field unit weight determination test on a soil using the Sand Cone Method. Determine the field unit weight of the soil. FEEDBACK GUARANTEEDarrow_forward
- Answer the following: a) What is the difference between the U-line and the A-line on a plasticity chart? b) What is the dividing point between silts and clays on a plasticity chart? c) What is the dividing point between low, medium, and high plasticity on a plasticity chart? d) An inorganic soil has a Liquid Limit of 55 and a Plastic Limit of 30. Using the plasticity chart determine the relative classification for this soil.arrow_forwardFigure 2 shows the dry density versus water content relationship for a fine-grained soilcompacted using two different levels of energy. Three points are identified on thesecompaction curves and labeled as A, B and C. Describe and compare the soil structure of A and B.arrow_forwardA sieve analysis of a soil sample of weight (400 g) was performed and the results were as follows. Required 1-Find the% passing and plot the gradient gradient. 2-Find the regularity coefficient and the Cu gradientarrow_forward
- b) Determine D10, D30 and D60 for each soil. c) Calculate the uniformity coefficient and coefficient of gradation Cu and Ccrespectively.arrow_forwardin a partially saturated soil e (void ratio) = 1.2; w = 30%; Ss = 2.66; calculate the γm(specific gravity of soil mass) and γd (dry specific weight of sample) of said soil. complete the diagram show in the image. I WILL RATE IT.arrow_forwardA 1-ft3 sample of undisturbed soil is found to have a dry weight of 107 lb. If the specific gravity of soil solids is 2.70, what is the void ratio of the sample? What is the porosity?arrow_forward
 Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning


