
a.
Prepare the journal entries made by the parent to record the sale of the equipment to the subsidiary; and by the subsidiary to record the purchase and the [I] entries for the year of sale.
a.
Explanation of Solution
An acquisition of assets is the purchase of a corporation by purchasing its assets rather than its stock. An acquisition is when one company acquires most or all of the shares of another company to gain control over that company. An investment in equity is money which is invested in a company by buying that company's shares in the stock market. Typically, those shares are traded in a stock exchange.
The required
| Date | Account title and Explanation | Post Ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash | ||||
| Equipment | ||||
| Gain on sale of Equipment | ||||
|
(To record the sale of equipment) |
Table (1)
The required journal entry recorded by the subsidiary is as follows:
| Date | Account title and Explanation | Post Ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Equipment | ||||
| Cash | ||||
|
(To record the purchase of equipment) | ||||
| [Igain] Gain on sale of equipment | ||||
| Equipment | ||||
| Accumulated depreciation | ||||
| (To adjust Gain, Equipment, and Accumulated Depreciation on the date of the intercompany transfer of equipment) | ||||
| [Idep] Accumulated Depreciation | ||||
| Depreciation Expense | ||||
| (To eliminate the excess depreciation expense recorded by the subsidiary, and to adjust accumulated depreciation from the BOY amount to the EOY amount) |
Table (2)
Working notes:
In January of 2014, the parent sold Equipment to the subsidiary for a cash price of $128,700. The subsidiary retained the depreciation policy of the parent and depreciates the equipment over its remaining 10-year useful life.
Depreciation charged by the subsidiary on equipment is $128,700/10 i.e., $12,870
The parent had acquired the equipment at a cost of $124,800 and depreciated the equipment over its 12-year useful life using the straight-line method.
Depreciation charged by the parent on equipment is $124,800/12 i.e., $10,400
Calculate excess depreciation:
b.
Compute the remaining portion of the deferred gain on January 1, 2016.
b.
Explanation of Solution
In January of 2014, the parent sold Equipment to the subsidiary for a cash price of $128,700. The subsidiary retained the
Depreciation charged by the subsidiary on equipment is $128,700/10 i.e., $12,870
The parent had acquired the equipment at a cost of $124,800 and depreciated the equipment over its 12-year useful life using the straight-line method.
Depreciation charged by the parent on equipment is $124,800/12 i.e., $10,400
Calculate excess depreciation:
Operating expenses of the subsidiary is
Gain on the sale of equipment is
Through the BOY, two years have passed, so the deferred gain at the start of the current year is as follows:
Hence, the remaining portion of the deferred gain on Jan 1, 2016 is
c.
Compute the amount of netincome (loss) from subsidiary reported by the parent company for the year ended Dec 31,2016 assuming that the parent applied the equity method.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Equity income is money generated from stock dividends that investors can access by buying dividend-declared stocks or by buying funds that invest in dividend-declared stocks.
Subsidiary net income is
AAP Depreciation is
Deferred gain on intercompany sale is
The computation to yield the income (loss) from subsidiary reported by the parent company during2016is as follows:
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Subsidiary net income | |
| AAP Depreciation | |
| Deferred gain on intercompany sale | |
| Income (loss) from subsidiary |
Table (3)
Hence, the income (loss) from subsidiary is
d.
Compute the equity investment account balanceon Dec 31, 2016.
d.
Explanation of Solution
An investment in equity is money which is invested in a company by buying that company's shares in the stock market. Typically, those shares are traded in a stock exchange.
EOY
EOY Common stock of subsidiary is
Calculate EOY Unamortized AAP assets:
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Dep./Amort. | Amount |
| PPE, net | |||
| Patent | |||
| Goodwill | |||
| EOY AAP assets |
Table (4)
The computation to yield the Equity Investment balance on Dec 31, 2016 is as follows:
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
|
EOY subsidiary retained earnings | |
| EOY subsidiary common stock | |
| Add: Unamortized AAP @ EOY | |
| Less: Unconfirmed gain @ EOY | |
| EOY Equity investment balance |
Table (5)
Hence, the equity investment balance as on Dec 31, 2016is
e.
Prepare the consolidation entries for the year ended Dec 31, 2016.
e.
Explanation of Solution
Consolidated financial statements are a group of entities financial statements that are presented as those of a single economic entity. They are the financial statements of a group in which the parent company and its subsidiaries introduce their assets, liabilities, equity, revenue, expenses and cash flows as those of a single business organization.
Consolidated accounting is used to club a parent company's financial information and one or more subsidiaries. The parent prepares consolidated financial statements through
The computation ofBOY [ADJ] for 2016 consolidation is as follows:
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
|
Change in retained earnings (S) thru BOY | |
| Cumulative AAP amort thru BOY | |
| Less: BOY Downstream Unconfirmed Asset | |
| ADJ Amount |
Table (6)
The required consolidation journal entries are as follows:
| Date | Account title and Explanation | Post Ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| [ADJ] BOY Equity Investment | ||||
| BOY Retained Earnings (P) | ||||
| [C] Income (loss) from subsidiary | ||||
| Dividends | ||||
| [E] Common Stock (S) @ BOY | ||||
| Retained Earnings (S) @BOY | ||||
| Equity Investment | ||||
| [A] PPE, net | ||||
| Patent | ||||
| Goodwill | ||||
| Equity Investment@ BOY | ||||
| [D Depreciation and Amort. expenses | ||||
| PPE, net | ||||
| Patent | ||||
|
(To record depreciation and amortization expense for the [A] assets) | ||||
| [Igain] Equity investment @BOY | ||||
| PPE, net | ||||
| [Idep] PPE, net | ||||
| Depreciation Expense |
Table (7)
f.
Prepare the consolidation spreadsheet for the year ended December 31, 2016.
f.
Explanation of Solution
Consolidated financial statements are a group of entities financial statements that are presented as those of a single economic entity. They are the financial statements of a group in which the parent company and its subsidiaries introduce their assets, liabilities, equity, revenue, expenses and cash flows as those of a single business organization.
A consolidated balance sheet provides a parent company's assets and liabilities and all of its subsidiaries in a legal document, without any differentiation on which items pertain to which companies.
Consolidation worksheet is an instrument used to prepare a parent's consolidated financial statements and their subsidiaries. It demonstrates the individual book values of companies, the adjustments and eliminations necessary, and the consolidated final values.
The consolidated spreadsheet for the year ended December 31, 2016 is shown below:
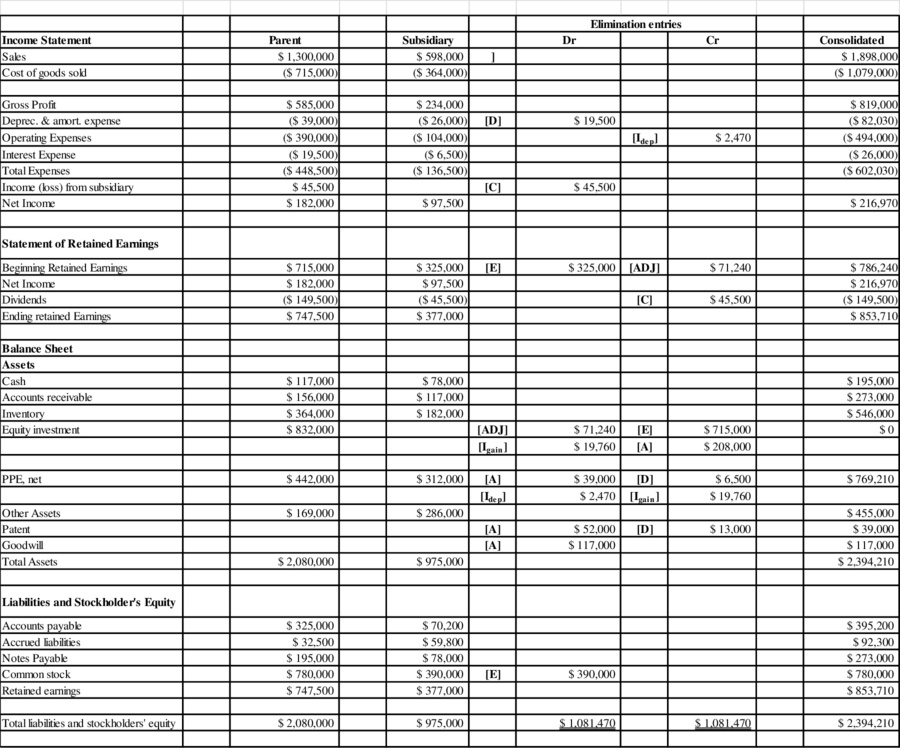
Table (8)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
ADVANCED ACCOUNTING

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





