
Concept explainers
(a)
The distance travelled by Carlos and Shannon when Shannon catches up to Carlos.
(a)
Answer to Problem 70P
The distance travelled by Carlos and Shannon when Shannon catches up to Carlos is
Explanation of Solution
The free body diagram of the given situation is shown in the Figure 1.
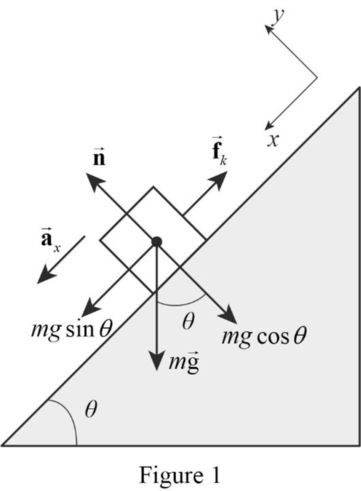
Let the positive x direction be down the slope and the positive y direction is in the direction of normal force.
Since there is no force in the vertical direction, the net force in the vertical direction is zero.
Here,
From the free body diagram, write the expression for net force in the horizontal direction.
Here,
Use
Write the kinematic equation to find the Carole’s velocity after travelling the
Here,
Write the kinematic equation to find the distance travelled by Carlos at the beginning pf the time interval.
Here,
Write the kinematic equation to find the distance travelled by Carlos at the beginning of the time interval.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute,
Substitute,
Substitute,
Substitute,
Substitute,
The distance travelled by the Shannon and Carlos are same.
Equate equation (VII) and (VIII), and solve for
Substitute,
Therefore, the distance travelled by Carlos and Shannon when Shannon catches up to Carlos is
(b)
The speed of the Shannon with respect to Carlos.
(b)
Answer to Problem 70P
The speed of the Shannon with respect to Carlos is
Explanation of Solution
Write the
Conclusion:
Substitute,
Substitute,
Since Carlos is moving in the same direction as Shannon, the relative speed of Shannon with respect to Carlos can be calculated as follows,
Therefore, the speed of the Shannon with respect to Carlos is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
College Physics
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





