
Concept explainers
(a)
The reading on the scale in an elevator when elevator accelerates at
Answer to Problem 87QAP
The reading on the scale is
Explanation of Solution
Givendata:
Formula Used:
Newton's second law:
Calculation:
We are interested in calculating the reading on the scale for accelerationof the elevator, at
together as one object.
The reading on the scale is equal in magnitude to the normalforce acting on the dog. Gravity also acts on the dog.
We can use Newton's second law tocalculate N as a function of the acceleration.
We'll define up to be positive y throughout ourcalculation.
Free-body diagram of the dog:
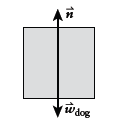
Conclusion:
Thus, we have the reading on the scale in an elevator when elevator accelerates at
(b)
The reading on the scale in an elevator when elevator cruises down at a steady speed.
Answer to Problem 87QAP
The reading on the scale is
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Formula Used:
Newton's second law:
Calculation:
We are interested in calculating the reading on the scale for elevator cruises down at a steady speed., which is equal to the acceleration of the scale and dog since they traveltogether as one object.
The reading on the scale is equal in magnitude to the normal force acting on the dog. Gravity also acts on the dog.
We can use Newton's second law to calculate N as a function of the acceleration.
We'll define up to be positive y throughout our calculation.
Free-body diagram of the dog:
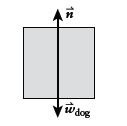
Conclusion:
Thus, we have the reading on the scale in an elevator
(c)
The reading on the scale in an elevator when elevator accelerates at
Answer to Problem 87QAP
The reading on the scale is
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Formula Used:
Newton's second law:
Calculation:
We are interested in calculating the reading on the scale for acceleration as
of the elevator, which are equal to the accelerations of the scale and dog since they travel
together as one object.
The reading on the scale is equal in magnitude to the normal force acting on the dog. Gravity also acts on the dog.
We can use Newton's second law to calculate N as a function of the acceleration.
We'll define up to be positive y throughout our calculation.
Free-body diagram of the dog:
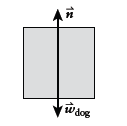
Conclusion:
The reading on the scale in an elevator when elevator accelerates at
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
COLLEGE PHYSICS LL W/ 6 MONTH ACCESS
- As a fish jumps vertically out of the water, assume that only two significant forces act on it: an upward force F exerted by the tail fin and the downward force due to gravity. A record Chinook salmon has a length of 1.50 m and a mass of 61.0 kg. If this fish is moving upward at 3.00 m/s as its head first breaks the surface and has an upward speed of 6.00 m/s after two-thirds of its length has left the surface, assume constant acceleration and determine (a) the salmons acceleration and (b) the magnitude of the force F during this interval.arrow_forwardThe coefficient of static friction between a persons shoe and the ground is 0.80. Determine the maximum magnitude of acceleration of a 60 kg person, if he starts running on a horizontal surface from rest.arrow_forwardThe Top Thrill Dragster stratacoaster at Cedar Point Amusement Park in Ohio uses a hydraulic launching system to accelerate riders from 0 to 54 m/s (120 mi/hr) in 3.8 seconds before climbing a completely vertical 420-foot hill . Determine the net force required to accelerate an 86-kg man.arrow_forward
- The parameters of instantaneous speed, altitude, net engine thrust and wind speed are given for the above 5000 kg aircraft, which accelerates and moves at a fixed altitude, while leaving a load of 150 kg. In case the air friction is neglected, calculate the distance between the load and the aircraft while falling to the ground.arrow_forward3.- A truck tows a 400 kg log from a ditch by means of a winch attached to its rear part. Knowing that the winch applies a constant force F and the coefficient of kinetic friction between the ground and the log is 0.5, determine the force F if the log reaches a speed of 0.5 m / s in 1.8 s. Visual representation (Make drawings or diagrams, clearly indicate the vectors and variables involved in the problem, it can be on the drawing)arrow_forwardA 27.0-kg block is initially at rest on a horizontal surface. A horizontal force of 74.0 N is required to set the block in motion, after which a horizontal force of 61.0 N is required to keep the block moving with constant speed. (a) Find the coefficient of static friction between the block and the surface.(b) Find the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the surface.arrow_forward
- In 1991, a lobster with a mass of 20.0 kg was caught off the coast of Nova Scotia, Canada.Imagine this lobster involved in a friendly tug of war with several smaller lobsters on ahorizontal plane at the bottom of the sea. Suppose the smaller lobsters are able to drag thelarge lobster, so that after the large lobster has been moved 1.55 m its speed is 0.550 m/s. Ifthe lobster is initially at rest, what is the magnitude of the net force applied to it by thesmaller lobsters? Assume that friction and resistance due to moving through water arenegligiblearrow_forwardAs a fish jumps vertically out of the water, assume that only two significant forces act on it: an upward force F exerted by a tail fin and the downward force due to gravity. A record Chinook salmon has a length of 1.50 m and a mass of 48.5 kg. if this fish is moving upward at 3.00 m/s as its head first breaks the surface and has an upward speed of 5.80 m/s after two-thirds of its length has left the surface. what is the magnitude of the force F during the intervalarrow_forwardThe coefficient of friction between the wheels of Dave's 1985 Ford coupe and the dry pavement is 0.85. Determine the acceleration which the 1300 kg coupe experiences while skipping to a stoparrow_forward
- 3. A 25.0-kg block is initially at rest on a horizontal surface. A horizontal force of 75.0 N is required to set the block in motion, after which a horizontal force of 60.0 N is required to keep the block moving with constant speed. Find the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the surface.arrow_forwardAn object experiences a net zero external unbalanced force. Is it possible for the object to be travelling with a non-zero velocity? If yes,then state an example.arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning



