
Concept explainers
a)
Organize the transactions in accounts under an
a)
Explanation of Solution
Organize the transactions in accounts under an accounting equation:
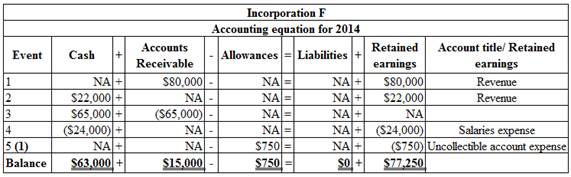
Table (1)
Working Note 1: Calculate the bad debt expense:
b)
Prepare the income statement, statement of changes in stockholders’ equity,
b)
Explanation of Solution
Income statement:
It is one of the financial statements, which reports revenues and expenses from business operations and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period.
Prepare the income statement for 2014.
| Incorporation F | ||
| Income statement | ||
| For the year ended December 31, 2014 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Service Revenue | $102,000 | |
| Operating Expenses: | ||
| Salaries Expense | $24,000 | |
| Uncollectible Accounts Expense | $750 | |
| Total Operating Expenses | ($24,750) | |
| Net Income | $77,250 | |
Table (2)
Statement of stockholder's equity: This statement reports the beginning stockholder's equity and all the changes which led to ending stockholder's equity. Additional capital, net income from income statement is added to and dividends are deducted from beginning stockholder's equity to arrive at the end result, closing balance of stockholder's equity.
Prepare the statement of changes in the
| Incorporation F | ||
| Statement of changes in the Stockholders Equity | ||
| For the year ended December 31, 2014 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Beginning | $0 | |
| Add: Net Income | $77,250 | |
| Ending Retained Earnings | $77,250 | |
| Total Stockholders’ Equity | $77,250 | |
Table (3)
Balance Sheet: Balance Sheet summarizes the assets, the liabilities, and the Shareholder’s equity of a company at a given date. It is also known as the statement of financial status of the business.
Prepare the balance sheet as on December 31, 2014:
| Incorporation F | ||
| Balance sheet | ||
| As on December 31, 2014 | ||
| Assets | ||
| Cash | $63,000 | |
| Accounts Receivable | $15,000 | |
| Less: Allowance for Doubtful Accounts | ($750) | $14,250 |
| Total Assets | $77,250 | |
| Liabilities | $0 | |
| Stockholders’ Equity | ||
| Common Stock | $0 | |
| Retained Earnings | $77,250 | |
| Total Stockholders’ Equity | $77,250 | |
| Total Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity | $77,250 | |
Table (4)
Statement of cash flows:
It is one of the financial statements which reports the source and application of cash between two balance sheet dates. It shows how the cash is sourced and used for the company’s operating, investing, and financing activities.
Prepare the statement of cash flows for 2014:
| Incorporation F | ||
| Statement of cash flows | ||
| For the year ended December 31, 2014 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Cash Flows From Operating Activities: | ||
| Cash collection from Customers | $87,000 | |
| Cash paid for Expenses | ($24,000) | |
| Net Cash Flow from Operating Activities | $63,000 | |
| Cash Flows From Investing Activities | $0 | |
| Cash Flows From Financing Activities | $0 | |
| Net Change in Cash | $63,000 | |
| Add: Beginning Cash Balance | $0 | |
| Ending Cash Balance | $63,000 | |
Table (5)
c)
Calculate the net realizable value of the accounts receivable at December 31, 2014.
c)
Explanation of Solution
Cash realizable value (net realizable value): Cash realizable value is the net amount of receivables which a business expects to collect from its debtors. Accounts receivable less allowance for doubtful accounts is represented as cash realizable value.
Calculate the net realizable value of the accounts receivable at December 31, 2014.
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Accounts receivable balance at December 31, 2014 | $15,000 |
| Less: Allowance for Doubtful Accounts, December 31, 2014 | ($750) |
| Net realizable value of the accounts receivable at December 31, 2014 | $14,250 |
Table (6)
Therefore, the net realizable value of the accounts receivable at December 31, 2014 is $14,250.
d. (a)
Organize the transactions in accounts under an accounting equation.
d. (a)
Explanation of Solution
Accounting equation: Accounting equation is an accounting tool expressed in the form of equation, by creating a relation between resources or assets of a business and claims on the resources by the creditors, and the owners.
Organize the transactions in accounts under an accounting equation:
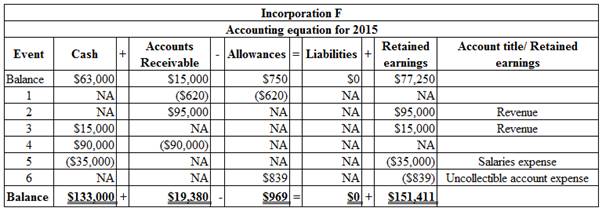
Table (7)
Working Note 2: Calculate the bad debt expense
Bad debts are estimated 5% of the ending accounts receivables balance. Ending accounts receivable for the year 2015 are $19,380.
d (b)
Prepare the income statement, statement of changes in stockholders’ equity, balance sheet, and statement of cash flows for 2015.
d (b)
Explanation of Solution
Income statement: It is one of the financial statements, which reports revenues and expenses from business operations and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period.
Prepare the income statement for 2014:
| Incorporation F | ||
| Income statement | ||
| For the year ended December 31, 2015 | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Service Revenue | $110,000 | |
| Operating Expenses: | ||
| Salaries Expense | $35,000 | |
| Uncollectible Accounts Expense | $839 | |
| Total Operating Expenses | ($35,839) | |
| Net Income | $74,161 | |
Table (8)
Statement of stockholder's equity: This statement reports the beginning stockholder's equity and all the changes which led to ending stockholder's equity. Additional capital, net income from income statement is added to and dividends are deducted from beginning stockholder's equity to arrive at the end result, closing balance of stockholder's equity.
Prepare the statement of changes in the stockholders equity for 2014.
| Incorporation F | ||
| Statement of changes in the Stockholders Equity | ||
| For the year ended December 31, 2015 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Beginning Retained Earnings | $77,250 | |
| Add: Net Income | $74,161 | |
| Ending Retained Earnings | $151,411 | |
| Total Stockholders’ Equity | $151,411 | |
Table (9)
Balance Sheet: Balance Sheet summarizes the assets, the liabilities, and the Shareholder’s equity of a company at a given date. It is also known as the statement of financial status of the business.
Prepare the balance sheet as on December 31, 2015:
| Incorporation F | ||
| Balance sheet | ||
| As on December 31, 2015 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Assets | ||
| Cash | $133,000 | |
| Accounts Receivable | $19,380 | |
| Less: Allowance for Doubtful Accounts | ($969) | $18,411 |
| Total Assets | $151,411 | |
| Liabilities | $0 | |
| Stockholders’ Equity | ||
| Retained Earnings | $151,411 | |
| Total Stockholders’ Equity | $151,411 | |
| Total Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity | $151,411 | |
Table (10)
Statement of cash flows:
It is one of the financial statements which reports the source and application of cash between two balance sheet dates. It shows how the cash is sourced and used for the company’s operating, investing, and financing activities.
Prepare the statement of cash flows for 2015:
| Incorporation F | ||
| Statement of Cash Flows | ||
| For the year ended December 31, 2015 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Cash Flows From Operating Activities: | ||
| Cash collcetion from Customers | $105,000 | |
| Cash paid for Expenses | ($35,000) | |
| Net Cash Flow from Operating Activities | $70,000 | |
| Cash Flows From Investing Activities | $0 | |
| Cash Flows From Financing Activities | ||
| Issue of Common Stock | $0 | |
| Net Change in Cash | $70,000 | |
| Add: Beginning Cash Balance | $63,000 | |
| Ending Cash Balance | $133,000 | |
Table (11)
d (c)
Calculate the net realizable value of the accounts receivable at December 31, 2015.
d (c)
Explanation of Solution
Cash realizable value (net realizable value): Cash realizable value is the net amount of receivables which a business expects to collect from its debtors. Accounts receivable less allowance for doubtful accounts is represented as cash realizable value.
Calculate the net realizable value of the accounts receivable at December 31, 2015.
| Particulars | Amount |
| Accounts receivable balance at December 31, 2015 | $19,380 |
| Less: Allowance for Doubtful Accounts, December 31, 2015 | ($969) |
| Net realizable value of the accounts receivable at December 31, 2015 | $18,411 |
Table (12)
Therefore, the net realizable value of the accounts receivable at December 31, 2015 is $18,411.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Loose-Leaf for Survey of Accounting

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





