
(a)
Record the acceptance of the note on March 1, when the note had interest of 6%.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Note receivable: Note receivable refers to a written promise for the amounts to be received within a stipulated period of time. This written promise is issued by a debtor or borrower to lender or creditor. Notes receivable is an asset of a business.
Prepare
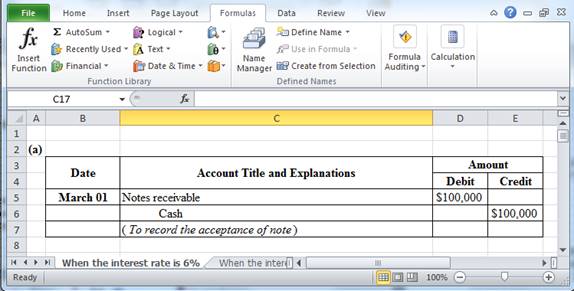
Table (1)
March 01: To record the acceptance of note.
- Notes receivable is an asset. Lending of cash increases notes receivable balance. Thus, notes receivable is debited with $100,000.
- Cash is an asset. Lending of cash decreases the cash balance. Thus, it is credited with $100,000.
(b)
Calculate the amount of interest revenue to recognize in each year until the note is settled, when the note had interest of 6%.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Interest revenue: Interest revenue is the amount charged on the principal value of notes receivable for the privilege of borrowing money. Interest is to be paid by the borrower and to be received by the lender. Interest revenue is calculated as follows:
Calculate the amount of interest revenue to recognize in each year until the note is settled, when the note had interest of 6%.
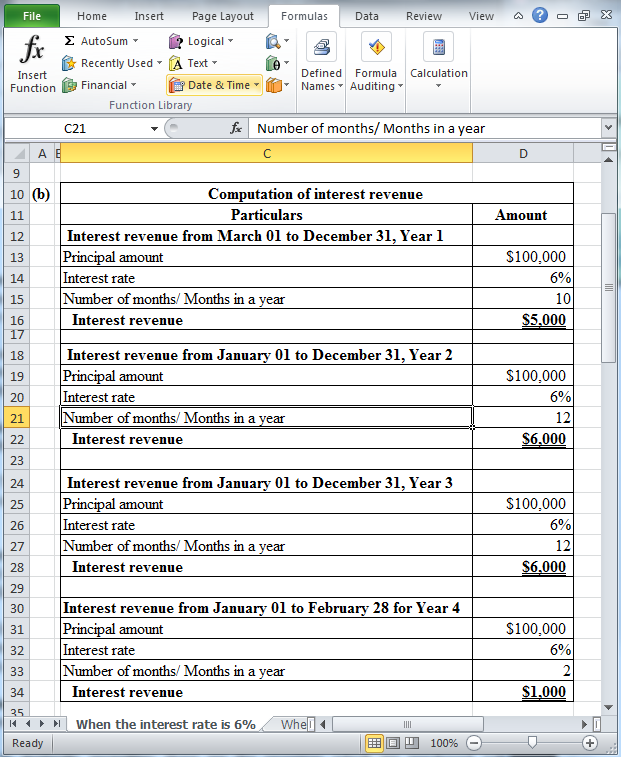
Table (2)
Hence, the interest revenue for Year 1 (for 10 months), Year 2, Year 3 and Year 4 (for 2 months) are $5,000, $6,000, $6,000 and $1,000 respectively.
Working note:
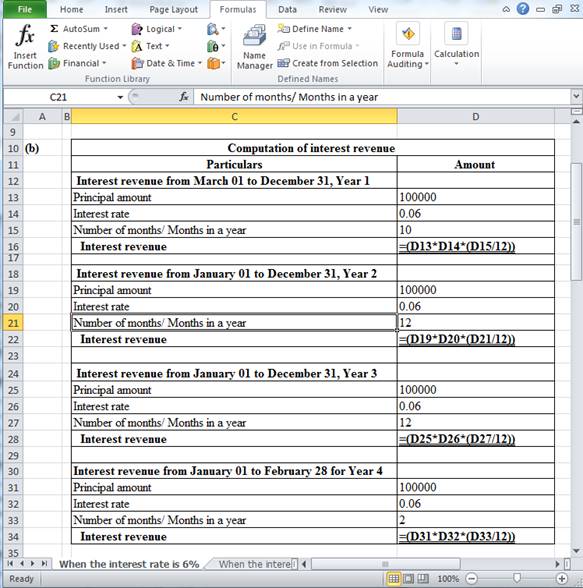
Table (3)
(c)
Record the entry to accrue interest revenue on December 31 in each year, when the note had interest of 6%.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Interest revenue: Interest revenue is the amount charged on the principal value of notes receivable for the privilege of borrowing money. Interest is to be paid by the borrower and to be received by the lender. Interest revenue is calculated as follows:
Record the entry to accrue interest revenue on December 31 in each year.
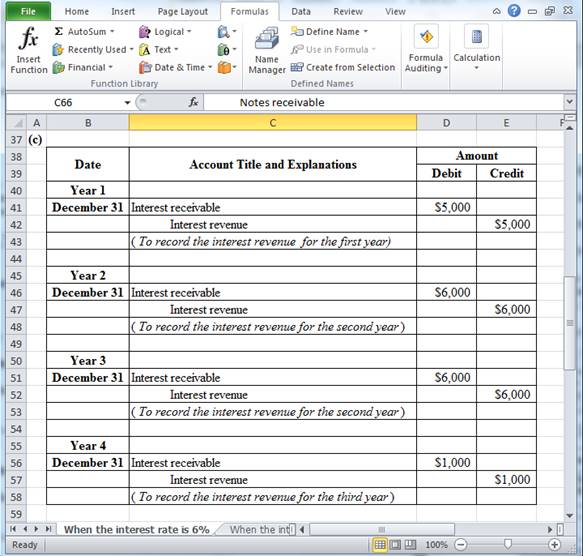
Table (4)
December 31: To record the interest revenue for the first year.
- Interest receivable is an asset. It increases the assets receivables balance. Thus, interest receivable is debited with $5,000.
- Interest revenue is a component of
retained earnings . It increases the retained earnings. Thus, interest revenue is credited with $5,000.
December 31: To record the interest revenue for the second year.
- Interest receivable is an asset. It increases the assets receivables balance. Thus, interest receivable is debited with $6,000.
- Interest revenue is a component of retained earnings. It increases the retained earnings. Thus, interest revenue is credited with $6,000.
December 31: To record the interest revenue for the third year.
- Interest receivable is an asset. It increases the assets receivables balance. Thus, interest receivable is debited with $1,000.
- Interest revenue is a component of retained earnings. It increases the retained earnings. Thus, interest revenue is credited with $1,000.
(d)
Record the entry for cash received at maturity, when the note had interest of 6%.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Notes receivable: Note receivable refers to a written promise for the amounts to be received within a stipulated period of time. This written promise is issued by a debtor or borrower to lender or creditor. Notes receivable is an asset of a business.
Record the entry for cash received at maturity, when the note had interest of 6%.
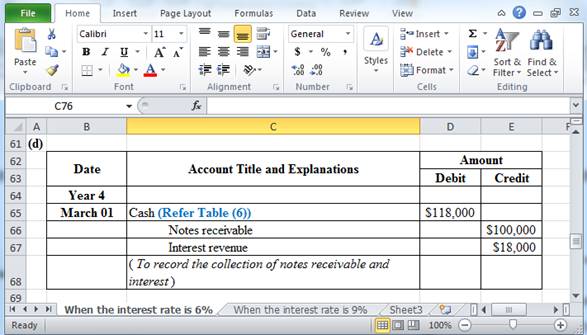
Table (5)
Hence, the total amount to be paid at the time of maturity is $118,000.
Working Note:
Determine the total amount to be paid at the time of maturity.
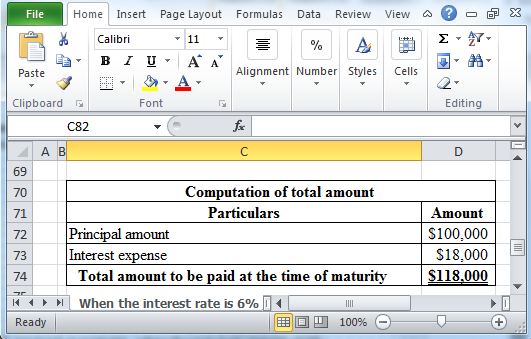
Table (6)
(a) Record the acceptance of the note on March 1, if the note had interest of 9%.
(b) Calculate the amount of interest revenue to recognize in each year until the note is settled, if the note had interest of 9%.
(c) Record the entry to accrue interest revenue on December 31 in each year, if the note had interest of 9%.
(d) Record the entry for cash received at maturity, if the note had interest of 9%.
Explanation of Solution
(a) Record the acceptance of the note on March 1, if the note had interest of 9%.
Notes receivable: Notes receivable refers to a written promise for the amounts to be received within a stipulated period of time. This written promise is issued by a debtor or borrower to lender or creditor. Notes receivable is an asset of a business.
Prepare journal entry.
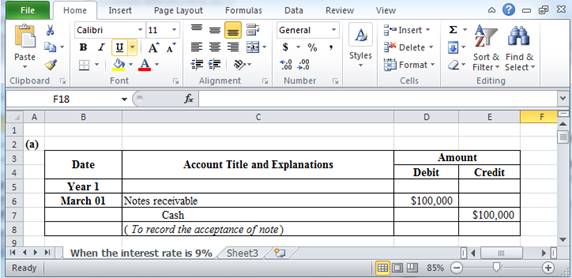
Table (7)
March 01: To record the acceptance of note.
- Notes receivable is an asset. Issuance of notes increases the notes receivables balance. Thus, notes receivable is debited with $100,000.
- Cash is an asset. Lending of cash decreases the cash balance. Thus, it is credited with $100,000.
(b) Calculate the amount of interest revenue to recognize in each year until the note is settled, if the note had interest of 9%.
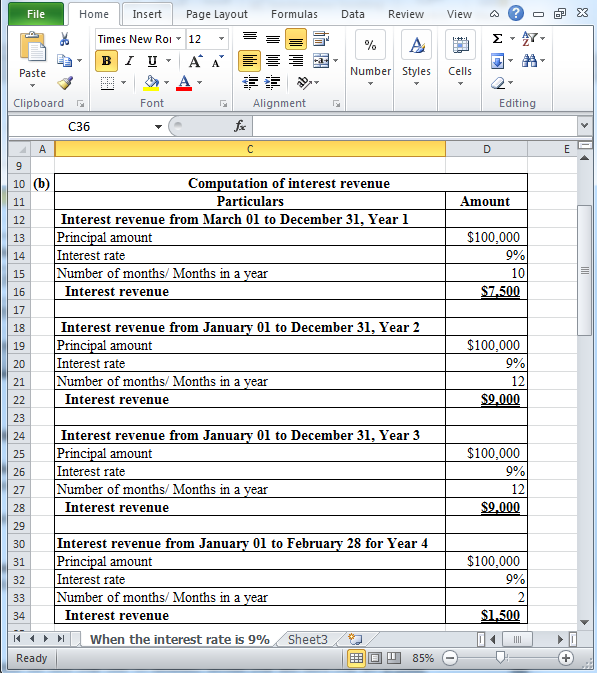
Table (8)
Hence, the interest revenue for Year 1 (for 10 months), Year 2, Year 3 and Year 4 (for 2 months) are $7,500, $9,000, $9,000 and $1,500 respectively.
Working note:
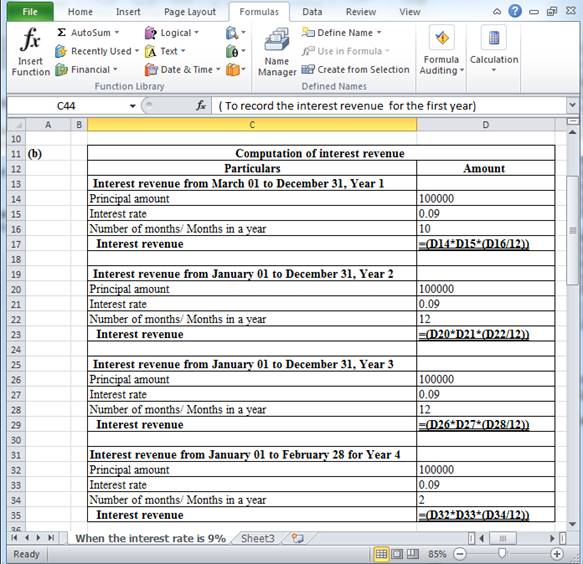
Table (9)
(c) Record the entry to accrue interest revenue on December 31 in each year, if the note had interest of 9%.
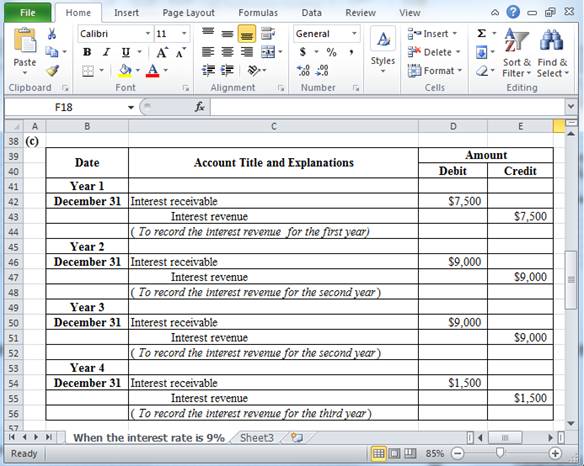
Table (10)
December 31: To record the interest revenue for the first year.
- Interest receivable is an asset. It increases the assets receivables balance. Thus, interest receivable is debited with $7,500.
- Interest revenue is a component of retained earnings. It increases the retained earnings. Thus, interest revenue is credited with $7,500.
December 31: To record the interest revenue for the second year.
- Interest receivable is an asset. It increases the assets receivables balance. Thus, interest receivable is debited with $9,000.
- Interest revenue is a component of retained earnings. It increases the retained earnings. Thus, interest revenue is credited with $9,000.
December 31: To record the interest revenue for the third year.
- Interest receivable is an asset. It increases the assets receivables balance. Thus, interest receivable is debited with $1,500.
- Interest revenue is a component of retained earnings. It increases the retained earnings. Thus, interest revenue is credited with $1,500.
(d) Record the entry for cash received at maturity, if the note had interest of 9%.
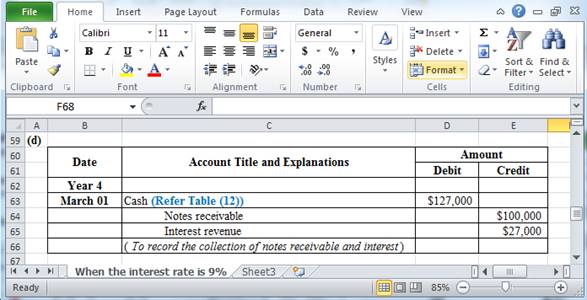
Table (11)
Hence, the total amount to be paid at the time of maturity is $127,000.
Working Note:
Determine the total amount to be paid at the time of maturity.
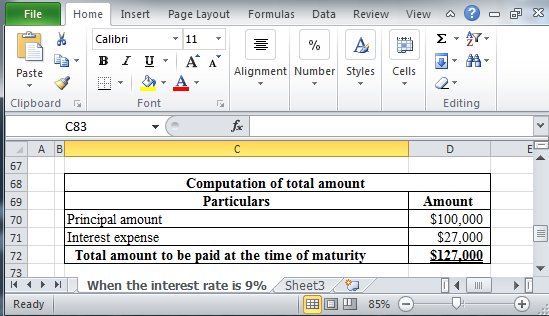
Table (12)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
FIN ACC W/ CONNECT & PROCTORIO >BI<

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





