
Support activity cost allocation
Jake’s Gems mines and produces diamonds, rubies, and other gems. The gems are produced by way of the Mining and Cutting activities. These production activities are supported by the Maintenance and Security activities. Security costs are allocated to the production activities based on asset value. Maintenance costs are normally allocated based on machine hours. However, Maintenance costs typically correlate more with the number of service calls. Information regarding the activities is provided in the following table:
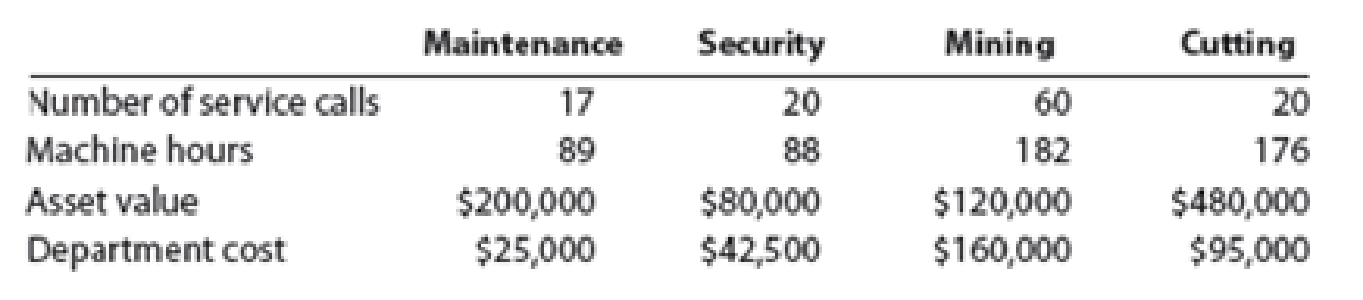
Instructions
1. Should Maintenance costs continue to be allocated based on machine hours? Why would a different driver be more appropriate?
2. Based on your response to part (1), determine the total costs allocated from each support activity to the other activities using the reciprocal services method and the most appropriate cost driver for Maintenance.
3. Jake’s Gems is considering cutting costs by switching to a simpler support activity cost allocation method. Using the information provided and given your response to part (2), determine if switching to the direct method would significantly alter the production activity costs.
a.
Identify the cost driver to allocate maintenance costs and whether or not to use the machine hours as the cost driver.
Explanation of Solution
Cost Driver: The cost driver refers to the all the activities on which the money is spent to produce the product or the service. It has a cause-effect relationship with the resources utilized in production. The cost drivers are used to form the activity cost pools.
The support department costs in the production are the indirect costs that difficult to identify and be associated to the concerned cost drivers. Hence, it is difficult to apply support department costs to the products.
Machine hours are not an accurate cost driver and must not be used. Service calls must be used as it a more appropriate cost driver as maintenance department is associated more with the service calls rather than the machine hours.
b.
Compute the total cost of each production department after allocating all support costs to the production departments using the cost driver chosen in part a.
Explanation of Solution
Maintenance Department Cost to be allocated:
The total Maintenance Department costs include 25% of the Security department costs as,
Therefore, the Security Department cost is,
Security Department Cost to be allocated:
The total Security Department costs include 20% of the Maintenance department costs as,
Therefore, the Security Department cost is,
Substitute the equation for M into the S equation:
Substitute the value of S into the M equation:
Maintenance Department Cost Allocation:
Compute the allocation of costs from Maintenance Department to Security Department:
The cost allocated from Maintenance Department to Security Department is $7,500.
Compute the allocation of costs from Maintenance Department to Cutting Department:
The cost allocated from Maintenance Department to Cutting Department is $7,500.
Compute the allocation of costs from Maintenance Department to Mining Department:
The cost allocated from Maintenance Department to Mining Department is $22,500.
Security Department Cost Allocation:
Compute the allocation of costs from Security Department to Maintenance Department:
The cost allocated from Security Department to Maintenance Department is $12,500.
Compute the allocation of costs from Security Department to Cutting Department:
The cost allocated from Security Department to Cutting Department is $30,000.
Compute the allocation of costs from Security Department to Mining Department:
The cost allocated from Security Department to Mining Department is $7,500.
Total Costs of Production Departments:
Compute the total cost of the Cutting Department:
The total costs of the Cutting department are $132,500.
Compute the total cost of the Mining Department:
The total costs of the Pruning department are $190,000.
c.
Identify the impact on the costs if company switches to simpler cost allocation method than the one used in part (b).
Explanation of Solution
Maintenance Department Cost Allocation:
Compute the allocation of costs from Maintenance Department to Cutting Department:
The cost from Maintenance Department that should be allocated to Cutting department is $6,250.
Compute the allocation of costs from Maintenance Department to Mining Department:
The cost allocated from Maintenance Department to Pruning department is $18,750.
Security Department Cost Allocation:
Compute the allocation of costs from Security Department to Cutting Department:
The cost allocated from Security Department to Cutting department is $34,000.
Compute the allocation of costs from Security Department to Pruning Department:
The cost allocated from Security Department to Pruning department is $8,500.
Total Costs of Production Departments:
Compute the total cost of the Cutting Department:
The total costs of the Cutting department are $135,250.
Compute the total cost of the Mining Department:
The total costs of the Pruning department are $187,250.
The switch from the existing method to the direct method would ensure the reduction of cost also there is a very little change in the costs being allocated amongst the two methods.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Managerial Accounting
- Support department cost allocation Blue Mountain Masterpieces produces pictures, paintings, and other home decor. The Printing and Framing production departments are supported by the Janitorial and Security departments. Janitorial costs are allocated to the production departments based on square feet, and security costs are allocated based on asset value. Information about these departments is detailed in the following table: Management has experimented with different support department cost allocation methods in the past. The different allocation methods did not yield large differences of cost allocation to the production departments. Instructions 1. Determine which support department cost allocation method Blue Mountain Masterpieces would most likely use to allocate its support department costs to the production departments. 2. Determine the total costs allocated from each support department to each production department using the method you determined in part (1). 3. Without doing calculations, consider and answer the following: If Blue Mountain Masterpieces decided to use square feet instead of asset value as the cost driver for security services, how would this change the allocation of Security Department costs?arrow_forwardFlowchart of accounts related to service and processing departments Alcoa Inc. (AA) is the worlds largest producer of aluminum products. One product that Alcoa manufactures is aluminum sheet products for the aerospace industry. The entire output of the Smelting Department is transferred to the Rolling Department. Part of the fully processed goods from the Rolling Department are sold as rolled sheet, and the remainder of the goods are transferred to the Converting Department for further processing into sheared sheet. Prepare a chart of the flow of costs from the processing department accounts into the finished goods accounts and then into the cost of goods sold account. The relevant accounts are as follows:arrow_forwardSupport activity cost allocation Jake’s Gems mines and produces diamonds, rubies, and other gems. The gems are produced by way of the Mining and Cutting activities. These production activities are supported by the Maintenance and Security activities. Security costs are allocated to the production activities based on asset value. Maintenance costs are normally allocated based on machine hours. However, Maintenance costs typically correlate more with the number of service calls. Information regarding the activities is provided in the following table: Maintenance Security Mining Cutting Number of service calls 17 20 60 20 Machine hours 89 88 182 176 Asset value $200,000 $80,000 $300,000 $300,000 Department cost $25,000 $42,500 $160,000 $95,000 1. Is the process of allocating maintenance costs based on machine hours correct? Identify the measure than can possibly…arrow_forward
- Support activity cost allocation Jake’s Gems mines and produces diamonds, rubies, and other gems. The gems are produced by way of the Mining and Cutting activities. These production activities are supported by the Maintenance and Security activities. Security costs are allocated to the production activities based on asset value. Maintenance costs are normally allocated based on machine hours. However, Maintenance costs typically correlate more with the number of service calls. Information regarding the activities is provided in the following table: Maintenance Security Mining Cutting Number of service calls 17 20 60 20 Machine hours 89 88 182 176 Asset value $200,000 $80,000 $300,000 $300,000 Department cost $25,000 $42,500 $160,000 $95,000 1. Is the process of allocating maintenance costs based on machine hours correct? Identify the measure than can possibly…arrow_forwardSupport activity cost allocationJake’s Gems mines and produces diamonds, rubies, and other gems. The gems are produced by way of the Mining and Cutting activities. These production activities are supported by the Maintenance and Security activities. Security costs are allocated to the production activities based on asset value. Maintenance costs are normally allocated based on machine hours. However, Maintenance costs typically correlate more with the number of service calls. Information regarding the activities is provided in the following table:MaintenanceSecurityMiningCuttingNumber of service calls17 20 60 20 Machine hours89 88 182 176 Asset value$200,000 $80,000 $300,000 $300,000 Department cost$25,000 $42,500 $160,000 $95,000 1. Is the process of allocating maintenance costs based on machine hours correct? Identify the measure than can possibly be used to allocate the maintenance costs.No Measures that can possibly be used to allocate the maintenance costs.a. Number of service…arrow_forward***ONLY NEED HELP WITH BOLD PART OF QUESTION*** Support activity cost allocation Jake’s Gems mines and produces diamonds, rubies, and other gems. The gems are produced by way of the Mining and Cutting activities. These production activities are supported by the Maintenance and Security activities. Security costs are allocated to the production activities based on asset value. Maintenance costs are normally allocated based on machine hours. However, Maintenance costs typically correlate more with the number of service calls. Information regarding the activities is provided in the following table: Maintenance Security Mining Cutting Number of service calls 17 20 60 20 Machine hours 89 88 182 176 Asset value $200,000 $80,000 $300,000 $300,000 Department cost $25,000 $42,500 $160,000 $95,000 Is the process of allocating maintenance costs based on machine hours correct? Identify the measure than can possibly be used to…arrow_forward
- Jake’s Gems mines and produces diamonds, rubies, and other gems. The gems are produced by way of the Mining and Cutting activities. These production activities are supported by the Maintenance and Security activities. Security costs are allocated to the production activities based on asset value. Maintenance costs are normally allocated based on machine hours. However, Maintenance costs typically correlate more with the number of service calls. Information regarding the activities is provided in the following table: Maintenance Security Mining Cutting Number of service calls 17 20 60 20 Machine hours 89 88 182 176 Asset value $200,000 $80,000 $300,000 $300,000 Department cost $25,000 $42,500 $160,000 $95,000 1. Is the process of allocating maintenance costs based on machine hours correct? Identify the measure than can possibly be used to allocate the…arrow_forwardSupport Activity Cost Allocation Kizzle’s Crepes Co. produces world famous crepes. The company’s crepes are produced via its Mixing and Cooking activities, which both rely on the Janitorial and Maintenance activities. Kizzle’s management knows the most practical driver of Janitorial costs is square feet, but is uncertain whether to allocate Maintenance costs based on asset value of production equipment, number of service calls, or machine hours. Kizzle’s management estimates that the Cooking and Mixing activities each require about twice as much space as the Maintenance activity. 1. Identify the base for choosing the cost driver. a. The company needs to choose a driver that can be measured practically. b. The company needs to choose the driver that matches the department activity. c. The company needs to choose the driver that matches the support department function. d. All the above. Identify the driver which cannot be used as cost driver for maintenance cost. a. Square feet. b.…arrow_forwardSupport department cost allocation—reciprocal services method Davis Snowflake & Co. produces Christmas stockings in its Cutting and Sewing departments. The Maintenance and Security departments support the production of the stockings. Costs from the Maintenance Department are allocated based on machine hours, and costs from the Security Department are allocated based on asset value. Information about each department is provided in the following table: MaintenanceDepartment SecurityDepartment CuttingDepartment SewingDepartment Machine hours 800 2,000 7,200 10,800 Asset value $2,000 $1,670 $2,500 $5,500 Department cost $36,000 $16,000 $64,000 $82,000 Determine the total cost of each production department after allocating all support department costs to the production departments using the reciprocal services method. CuttingDepartment SewingDepartment Production departmentsʼ total costs…arrow_forward
- Product Costs using Activity Rates Hercules Inc. manufactures elliptical exercise machines and treadmills. The products are produced in its Fabrication and Assembly production departments. In addition to production activities, several other activities are required to produce the two products. These activities and their associated activity rates are as follows:arrow_forwardSupport department cost allocation—reciprocal services method Davis Snowflake & Co. produces Christmas stockings in its Cutting and Sewing departments. The Maintenance and Security departments support the production of the stockings. Costs from the Maintenance Department are allocated based on machine hours, and costs from the Security Department are allocated based on asset value. Information about each department is provided in the following table: MaintenanceDepartment SecurityDepartment CuttingDepartment SewingDepartment Machine hours 800 2,000 7,600 10,400 Asset value $2,000 $1,380 $1,500 $6,500 Department cost $43,200 $19,200 $62,000 $84,000 Determine the total cost of each production department after allocating all support department costs to the production departments using the reciprocal services method. CuttingDepartment SewingDepartment Production departmentsʼ total costs…arrow_forwardSupport department cost allocation—reciprocal services method Davis Snowflake & Co. produces Christmas stockings in its Cutting and Sewing departments. The Maintenance and Security departments support the production of the stockings. Costs from the Maintenance Department are allocated based on machine hours, and costs from the Security Department are allocated based on asset value. Information about each department is provided in the following table: MaintenanceDepartment SecurityDepartment CuttingDepartment SewingDepartment Machine hours 800 2,000 7,600 10,400 Asset value $2,000 $1,470 $2,500 $5,500 Department cost $41,760 $18,560 $68,000 $78,000 Determine the total cost of each production department after allocating all support department costs to the production departments using the reciprocal services method.arrow_forward
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,

