
Concept explainers
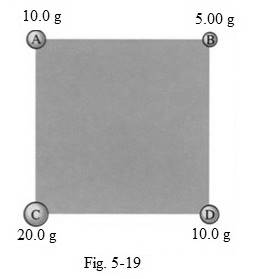
The center of mass of the particles which are positioned at the corners of a square with length of sides measuring
Answer to Problem 30P
Position of center of mass
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
Mass of particle A
Mass of particle B
Mass of particle C
Mass of particle D
Length of side of square
Formula used:
The x and y coordinates, of the center of mass of particles of a system in a two dimensional plane is calculated by the following formula:
Wherein
Similarly the y coordinates are given by the following formula:
Wherein
The position of center of mass of a particle having x and y coordinate is given by the formula:
Wherein r is the position of center of mass of the particle, while
Calculation:
As per figure 5-19, the x and y coordinates of position of mass at A is
Similarly the x and y coordinates for the position of mass at B, C and D respectively are
Substituting the various values of masses of particles at points A, B, C and D and also its horizontal distances from origin in the equation:
Similarly substituting the various values of masses of particles at points A, B, C and D and also its vertical distances from origin in the equation:
The position of center of mass is given by the formula:
Substituting
Conclusion:
The x and y coordinates of the particles are
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Physics Fundamentals
- Three skydivers are plummeting earthward. They are initially holding onto each other, but then push apart. Two skydivers of mass 70 and 80 kg gain horizontal velocities of 1.2 m/s north and 1.4 m/s southeast, respectively. What is the horizontal velocity of the third skydiver, whose mass is 55 kg?arrow_forwardWhere is the center of mass of a semicircular wire of radius R that is centered on the origin, begins and ends on the x axis, and lies in the x, y plane?arrow_forwardFind the center of mass of a cone of uniform density that has a radius R at the base, height h, and mass M. Let the origin be at the center of the base of the cone and have +z going through the cone vertex.arrow_forward
- If 1 of the Earth’s mass were transferred to the Moon, how far would the center of mass of the Earth-Moon-population system move? The mass of the Earth is 5.971024kg and that of the Moon is 7.341022kg . The radius of the Moon’s orbit is about 3.84105m .arrow_forwardFind the center of mass of a rectangular block of length a and width b that has a nonuniform density such that when the rectangle is placed in the x, y-plane with one corner at the origin and the block placed in the first quadrant with the two edges along the x- and y-axes, the density is given by (x,y)=0x , where 0 is a constant.arrow_forwardFind the center of mass of a semicircular plate of radius r .arrow_forward
- a person in kayak atarts padding, and it accelarates from 0 to 0.474 m/s in a distance of 0.584 m. if the combined mass of the person and the kayak is 69.9kg, what is the magnitude of the net force acting on the kayak?arrow_forwardGive the location of the centre of mass of a (i) sphere, (ii) cylinder, (iii) ring, and (iv) cube, each of uniform mass density. Does the centre of mass of a body necessarily lie inside the body ?arrow_forwardWhere is the center of mass of a semicircular wire of radius R that is centered on the origin, begins and ends on the x axis, and lies in the x,y plane?arrow_forward
- find the mass M and center of mass x of the linearwire covering the given interval and having the given density δ(x). 1 ≤ x ≤ 4, δ(x) = √xarrow_forwardAccording to legend, Galileo Galilei dropped two balls of different mass from the top of the leaning tower of Pisa in 1589. Whether or not this public experiment ever took place, Galileo was able to demonstrate that, contrary to Aristotle’s teaching, all bodies fall at the same rate regardless of mass, assuming that one is not so tenuous that it is slowed by air resistance. In this experiment, an equation is presented relating the acceleration of gravity at Earth’s surface, g, to the height that an object falls from, h, and the time it takes the object to reach the ground, t. Gravity acceleration at Earth’s surface has been measured many times. In British Imperial Units, Small Metric Units, and Large Metric Units, the standard values of g are: g = 32 feet per second-squared (ft/s2) g = 980 centimeters per second-squared (cm/s2) g = 9.8 meters per second-squared (m/s2). Theory Newton succeeded in explaining gravitational acceleration using his Laws of…arrow_forwardFind the center of mass of the half disk of radius 5 in the x-positive half planearrow_forward
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
