
a.
Organize the transaction data in accounts under an
a.
Explanation of Solution
Percentage of sales method: Credit sales are recorded by debiting (increasing)
It is a method of estimating the bad debts (expected loss on extending credit), by multiplying the expected percentage of uncollectible with the total amount of net credit sale (or total sales) for a specific period. Under percentage of sales method, estimated bad debts would be treated as a bad debt expense of the particular period.
Horizontal statements model: The model that represents all the financial statements, balance sheet, income statement, and statement of cash flows in one table in a horizontal form, is referred to as, horizontal statements model.
Organize the transaction data in accounts under an
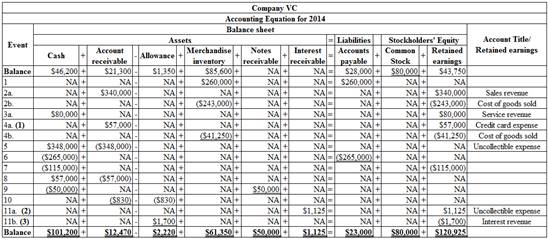
Table (1)
Working note 1: Calculate the amount of credit card sales made to customers:
The merchandise sold to credit card customers for $60,000 and the company charges a fee of 5% on sales. So, the credit card expense is
Working note 2: Calculate the amount of interest receivable:
Given: The loan amount is $50,000 and the rate of interest is 9%. So the total interest income is calculated as follows:
Working note 3: Calculate the amount for uncollectible accounts expense:
b.
Prepare an income statement, statement of changes in
b.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement: The financial statement which reports revenues and expenses from business operations and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period is referred to as income statement.
Prepare the income statement.
| Company VC | ||
| Income statement | ||
| For the year ended December 31, 2014 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Revenue | ||
| Sales revenue | $400,000 | |
| Service revenue | $80,000 | |
| Total revenue | $480,000 | |
| Less: Cost of goods sold | ($284,250) | |
| Gross profit | $195,750 | |
| Less: Operating Expenses | ||
| Credit card expenses | $3,000 | |
| Selling and administrative expenses | $115,000 | |
| Uncollectible accounts expense | $1,700 | |
| Total operating income | ($119,700) | |
| Operating income | $76,050 | |
| Add: Non-operating items | ||
| Interest revenue | $1,125 | |
| Net income | $77,175 | |
Table (2)
Statement of changes in the stockholders’ equity: This statement reflects whether the components of stockholders’ equity have increased or decreased during the period.
Prepare the statement of changes in stockholders’ equity.
| Company VC | ||
| Statement of changes in stockholders’ equity | ||
| For the year ended December 31, 2014 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Beginning common stock | $80,000 | |
| Add: Common stocks issued | $0 | |
| Ending common stock | $80,000 | |
| Beginning | $43,750 | |
| Add: Net income | $77,175 | |
| Ending retained earnings | $120,925 | |
| Total stockholders’ equity | $200,925 | |
Table (3)
Balance sheet: Balance Sheet is one of the financial statements that summarize the assets, the liabilities, and the Shareholder’s equity of a company at a given date. It is also known as the statement of financial status of the business.
Prepare the balance sheet.
| Company VC | ||
| Balance sheet | ||
| As of December 31, 2014 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Assets | ||
| Cash | $101,200 | |
| Accounts receivable | $12,470 | |
| Less: Allowance for doubtful accounts | ($2,220) | $10,250 |
| Merchandise inventory | $61,350 | |
| Interest receivable | $1,125 | |
| Notes receivable | $50,000 | |
| Total assets | $223,925 | |
| Liabilities | ||
| Accounts payable | $23,000 | |
| Total liabilities | $23,000 | |
| Stockholders’ equity | ||
| Common stock | $80,000 | |
| Retained earnings | $120,925 | |
| Total stockholders' equity | $200,925 | |
| Total liabilities and stockholders' equity | $223,925 | |
Table (4)
Statement of cash flows: This statement reports all the cash transactions involves for inflow and outflow of cash, and the result of these transactions is reported as an ending balance of cash at the end of reported period.
Prepare the statement of cash flows.
| Company VC | ||
| Statement of cash flow | ||
| For the year December 31, 2014 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Cash flow from operating activities: | ||
| Inflow from customers (4) | $485,000 | |
| Outflow for inventory | ($265,000) | |
| Outflow for expenses | ($115,000) | |
| Net cash flow from operating activities | $105,000 | |
| Cash flow from investing activities | ||
| Outflow for notes receivable | ($50,000) | |
| Net cash flow from investing activities | ($50,000) | |
| Cash flow from financing activities | $0 | |
| Net change in cash | $55,000 | |
| Add: Beginning cash balance | $46,200 | |
| Ending cash balance | $101,200 | |
Table (5)
Working note 4: Calculate the amount of total
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
SURVEY OF ACCOUNTING-ACCESS

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





