
The revenue recognition principle:
The revenue recognition principle refers to the revenue that should be recognized in the time period, when the performance obligation (sales or services) of the company is completed.
Revenue recognized point of long term contract:
A long-term contract qualifies for revenue recognition over time. The seller can recognize the revenue as per percentage of the completion of the project, which is recognized as revenue minus cost of completion until date.
If a contract does not meet the performance obligation norm, then the seller cannot recognize the revenue till the project is complete.
To determine: The amount of gross profit or loss to be recognized under various situations.
Explanation of Solution
The amount of gross profit or loss to be recognized under various situations is as follows:
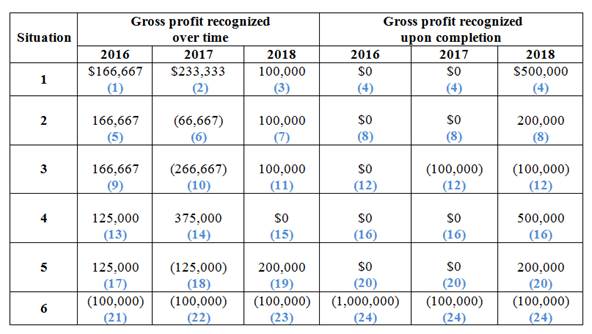
(Figure 1)
Working note:
Situation – 1
1. Compute the value of gross profit or loss recognized over time
Here,
| Particulars | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 |
| Contract price (A) | $5,000,000 | $5,000,000 | $5,000,000 |
| Actual costs to date | 1,500,000 | 3,600,000 | 4,500,000 |
| Estimated costs to complete | 3,000,000 | 900,000 | 0 |
| Total estimated costs (B) | 4,500,000 | 4,500,000 | 4,500,000 |
| Estimated gross profit(actual in 2018)
|
$500,000 | $500,000 | $500,000 |
Table (1)
In the year 2016:
In the year 2017:
In the year 2018:
2. Compute the value of gross profit or loss recognized upon completion
| Year | Gross profit recognized |
| 2016 | 0 |
| 2017 | 0 |
| 2018 | $500,000 |
| Total gross profit | $500,000 |
Table (2)
(4)
Situation – 2
1. Compute the value of gross profit or loss recognized over time
Here,
| Particulars | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 |
| Contract price (A) | $5,000,000 | $5,000,000 | $5,000,000 |
| Actual costs to date | 1,500,000 | 2,400,000 | 4,800,000 |
| Estimated costs to complete | 3,000,000 | 2,400,000 | 0 |
| Total estimated costs (B) | 4,500,000 | 4,800,000 | 4,800,000 |
| Estimated gross profit(actual in 2018)
|
$500,000 | $200,000 | $200,000 |
Table (3)
In the year 2016:
In the year 2017:
In the year 2018:
2. Compute the value of gross profit or loss recognized upon completion
| Year | Gross profit recognized |
| 2016 | 0 |
| 2017 | 0 |
| 2018 | $200,000 |
| Total gross profit | $200,000 |
Table (4)
(8)
Situation – 3
1. Compute the value of gross profit or loss recognized over time
Here,
| Particulars | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 |
| Contract price (A) | $5,000,000 | $5,000,000 | $5,000,000 |
| Actual costs to date | 1,500,000 | 3,600,000 | 5,200,000 |
| Estimated costs to complete | 3,000,000 | 1,500,000 | 0 |
| Total estimated costs (B) | 4,500,000 | 5,100,000 | 5,200,000 |
| Estimated gross profit(actual in 2018)
|
$500,000 | $(100,000) | $(200,000) |
Table (5)
In the year 2016:
In the year 2017:
In the year 2018:
2. Compute the value of gross profit or loss recognized upon completion
| Year | Gross profit recognized |
| 2016 | 0 |
| 2017 | $(100,000) |
| 2018 | $(100,000) |
| Total gross profit | $(200,000) |
Table (6)
(12)
Situation – 4
1. Compute the value of gross profit or loss recognized over time
Here,
| Particulars | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 |
| Contract price (A) | $5,000,000 | $5,000,000 | $5,000,000 |
| Actual costs to date | 500,000 | 3,500,000 | 4,500,000 |
| Estimated costs to complete | 3,500,000 | 875,000 | 0 |
| Total estimated costs (B) | 4,000,000 | 4,375,000 | 4,500,000 |
| Estimated gross profit(actual in 2018)
|
$1,000,000 | $625,000 | $500,000 |
Table (7)
In the year 2016:
In the year 2017:
In the year 2018:
2. Compute the value of gross profit or loss recognized upon completion
| Year | Gross profit recognized |
| 2016 | 0 |
| 2017 | 0 |
| 2018 | $500,000 |
| Total gross profit | $500,000 |
Table (8)
(16)
Situation – 5
1. Compute the value of gross profit or loss recognized over time
Here,
| Particulars | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 |
| Contract price (A) | $5,000,000 | $5,000,000 | $5,000,000 |
| Actual costs to date | 500,000 | 3,500,000 | 4,800,000 |
| Estimated costs to complete | 3,500,000 | 1,500,000 | 0 |
| Total estimated costs (B) | 4,000,000 | 5,000,000 | 4,800,000 |
| Estimated gross profit(actual in 2018)
|
$1,000,000 | $0 | $200,000 |
Table (9)
In the year 2016:
In the year 2017:
In the year 2018:
2. Compute the value of gross profit or loss recognized upon completion
| Year | Gross profit recognized |
| 2016 | 0 |
| 2017 | 0 |
| 2018 | $200,000 |
| Total gross profit | $200,000 |
Table (10)
(20)
Situation – 6
1. Compute the value of gross profit or loss recognized over time
Here,
| Particulars | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 |
| Contract price (A) | $5,000,000 | $5,000,000 | $5,000,000 |
| Actual costs to date | 500,000 | 3,500,000 | 5,300,000 |
| Estimated costs to complete | 4,600,000 | 1,700,000 | 0 |
| Total estimated costs (B) | 5,100,000 | 5,200,000 | 5,300,000 |
| Estimated gross profit(actual in 2018)
|
$(100,000) | $(200,000) | $(300,000) |
Table (11)
In the year 2016:
In the year 2017:
In the year 2018:
2. Compute the value of gross profit or loss recognized upon completion
| Year | Gross profit recognized |
| 2016 | $(100,000) |
| 2017 | (100,000) |
| 2018 | (100,000) |
| Total gross profit | $(300,000) |
Table (12)
(24)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
INTERMEDIATE ACCOUNTING WITH AIR FRANCE-KLM 2013 ANNUAL REPORT

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





