
Income (loss) recognition; Long-term contract; revenue recognition over time vs. upon project completion
• LO5–9
Brady Construction Company contracted to build an apartment complex for a price of $5,000,000. Construction began in 2018 and was completed in 2020. The following is a series of independent situations, numbered 1 through 6, involving differing costs for the project. All costs are stated in thousands of dollars.
Required:
Copy and complete the following table:
The revenue recognition principle
The revenue recognition principle refers to the revenue that should be recognized in the time period, when the performance obligation (sales or services) of the company is completed.
Revenue recognized point of long term contract
A long-term contract qualifies for revenue recognition over time. The seller can recognize the revenue as per percentage of the completion of the project, which is recognized as revenue minus cost of completion until date.
If a contract does not meet the performance obligation norm, then the seller cannot recognize the revenue till the project is complete.
To determine: The amount of gross profit or loss to be recognized under various situations.
Answer to Problem 5.21E
The amount of gross profit or loss to be recognized under various situations is as follows:
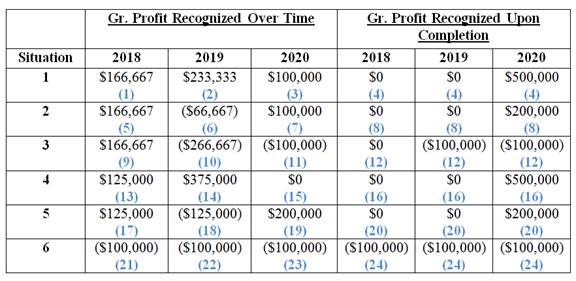
(Figure 1)
Explanation of Solution
Working note:
Situation – 1
1. Compute the value of gross profit or loss recognized over time
Here,
| Particulars | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 |
| Contract price (A) | $5,000,000 | $5,000,000 | $5,000,000 |
| Actual costs to date | 1,500,000 | 3,600,000 | 4,500,000 |
| Estimated costs to complete | 3,000,000 | 900,000 | 0 |
| Total estimated costs (B) | 4,500,000 | 4,500,000 | 4,500,000 |
| Estimated gross profit(actual in 2020)
|
$500,000 | $500,000 | $500,000 |
Table (1)
In the year 2018:
In the year 2019:
In the year 2020:
2. Compute the value of gross profit or loss recognized upon completion
| Year | Gross profit recognized |
| 2018 | 0 |
| 2019 | 0 |
| 2020 | $500,000 |
| Total gross profit | $500,000 |
Table (2)
(4)
Situation – 2
1. Compute the value of gross profit or loss recognized over time
Here,
| Particulars | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 |
| Contract price (A) | $5,000,000 | $5,000,000 | $5,000,000 |
| Actual costs to date | 1,500,000 | 2,400,000 | 4,800,000 |
| Estimated costs to complete | 3,000,000 | 2,400,000 | 0 |
| Total estimated costs (B) | 4,500,000 | 4,800,000 | 4,800,000 |
| Estimated gross profit(actual in 2020)
|
$500,000 | $200,000 | $200,000 |
Table (3)
In the year 2018:
In the year 2019:
In the year 2020:
2. Compute the value of gross profit or loss recognized upon completion
| Year | Gross profit recognized |
| 2018 | 0 |
| 2019 | 0 |
| 2020 | $200,000 |
| Total gross profit | $200,000 |
Table (4)
(8)
Situation – 3
1. Compute the value of gross profit or loss recognized over time
Here,
| Particulars | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 |
| Contract price (A) | $5,000,000 | $5,000,000 | $5,000,000 |
| Actual costs to date | 1,500,000 | 3,600,000 | 5,200,000 |
| Estimated costs to complete | 3,000,000 | 1,500,000 | 0 |
| Total estimated costs (B) | 4,500,000 | 5,100,000 | 5,200,000 |
| Estimated gross profit(actual in 2020)
|
$500,000 | $(100,000) | $(200,000) |
Table (5)
In the year 2018:
In the year 2019:
In the year 2020:
2. Compute the value of gross profit or loss recognized upon completion
| Year | Gross profit recognized |
| 2018 | 0 |
| 2019 | $(100,000) |
| 2020 | $(100,000) |
| Total gross profit | $(200,000) |
Table (6)
(12)
Situation – 4
1. Compute the value of gross profit or loss recognized over time
Here,
| Particulars | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 |
| Contract price (A) | $5,000,000 | $5,000,000 | $5,000,000 |
| Actual costs to date | 500,000 | 3,500,000 | 4,500,000 |
| Estimated costs to complete | 3,500,000 | 875,000 | 0 |
| Total estimated costs (B) | 4,000,000 | 4,375,000 | 4,500,000 |
| Estimated gross profit(actual in 2020)
|
$1,000,000 | $625,000 | $500,000 |
Table (7)
In the year 2018:
In the year 2019:
In the year 2020:
2. Compute the value of gross profit or loss recognized upon completion
| Year | Gross profit recognized |
| 2018 | 0 |
| 2019 | 0 |
| 2020 | $500,000 |
| Total gross profit | $500,000 |
Table (8)
(16)
Situation – 5
1. Compute the value of gross profit or loss recognized over time
Here,
| Particulars | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 |
| Contract price (A) | $5,000,000 | $5,000,000 | $5,000,000 |
| Actual costs to date | 500,000 | 3,500,000 | 4,800,000 |
| Estimated costs to complete | 3,500,000 | 1,500,000 | 0 |
| Total estimated costs (B) | 4,000,000 | 5,000,000 | 4,800,000 |
| Estimated gross profit(actual in 2020)
|
$1,000,000 | $0 | $200,000 |
Table (9)
In the year 2018:
In the year 2019:
In the year 2020:
2. Compute the value of gross profit or loss recognized upon completion
| Year | Gross profit recognized |
| 2018 | 0 |
| 2019 | 0 |
| 2020 | $200,000 |
| Total gross profit | $200,000 |
Table (10)
(20)
Situation – 6
1. Compute the value of gross profit or loss recognized over time
Here,
| Particulars | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 |
| Contract price (A) | $5,000,000 | $5,000,000 | $5,000,000 |
| Actual costs to date | 500,000 | 3,500,000 | 5,300,000 |
| Estimated costs to complete | 4,600,000 | 1,700,000 | 0 |
| Total estimated costs (B) | 5,100,000 | 5,200,000 | 5,300,000 |
| Estimated gross profit(actual in 2020)
|
$(100,000) | $(200,000) | $(300,000) |
Table (11)
In the year 2018:
In the year 2019:
In the year 2020:
2. Compute the value of gross profit or loss recognized upon completion
| Year | Gross profit recognized |
| 2018 | $(100,000) |
| 2019 | (100,000) |
| 2020 | (100,000) |
| Total gross profit | $(300,000) |
Table (12)
(24)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
INTERMEDIATE ACCOUNTING +ACCLL
- 43. On February 20, 2022, ABC Construction Company entered into a fixed-price contract to construct a commercial building for P9,000,000. ABC determined that the performance obligation is satisfied over time. Information relating to the contract is as follows: 2022 2023 Percentage of completion 25% 75% Estimated costs at completion P6,750,000 P7,200,000 How much is the contract costs charged to profit or loss in 2022?arrow_forward41. On February 20, 2022, ABC Construction Company entered into a fixed-price contract to construct a commercial building for P9,000,000. ABC determined that the performance obligation is satisfied over time. Information relating to the contract is as follows: 2022 2023 Percentage of completion 25% 75% Estimated costs at completion P6,750,000 P7,200,000 How much is the gross profit to be recognized in 2023?arrow_forwardQuestion 3What is the proper solution for this problem? B. On August 1, 2021, the board of directors of LL Co. voted to approve the disposal of one of its B division.The sale is expected to occur in June of next year. The B division's revenue and expenses for the period from January 1 to July 31 amounted to P14,000,000 and P10,000,000, respectively. For the period from August 1 to December 31, B Division's revenue amounted to P5,000,000 while expenses totaled P4,500,000. The carrying amount of B Division's net assets on December 31, 2021 was P21,000,000 and the fair value less cost of disposal was P25,000,000. The sale contract requires the company to pay termination cost of affected employees in the amount of P1,200,000 to be paid on September 30, 2022. The income tax rate is 30%. Required:25 – 27. Determine the income (loss) net of tax from discontinued operation.arrow_forward
- 49. ABC Construction Company began work on a contract in 2022 and completed the contract in 2023. The total contact price was P8,500,000. Information related to the construction project are as follows: 2022 2023 Costs incurred during the year P1,200,000 P6,250,000 Estimated costs to complete 4,800,000 - Progress billings during the year 1,450,000 7,050,000 Collections during the year 800,000 6,000,000 How much is the receivable balance as of December 31, 2022?arrow_forwardQ 9 – A company constructs a building for its own use. Construction began on January 1, 2020 and ended on December 31,2020. In 2020, the company made the following expenditures related to this building: January 1, $480,000; March 31, $900,000; June 30, $1,600,000; and October 30, $1,800,000. To help finance construction, the company arranged a 15% construction loan on January 1 for $1,000,000. The company’s other borrowings, outstanding for the whole year, consisted of a $2 million loan and a $4 million note with interest rates of 8% and 6%, respectively. Determine the amount of interest to be capitalized in 2020 in relation to the construction of the building. Q 10 –Eshaq Company’s record of transactions concerning part X for the month of February was as follows.arrow_forwardCA10.3 (LO 2) (Capitalization of Interest) Vania Magazines started construction of a warehouse building for its own use at an estimated cost of $5,000,000 on January 1, 2019, and completed the building on December 31, 2019. During the construction period, Vania has the following debt obligations outstanding. Construction loan—12% interest, payable semiannually, issued December 31, 2018 $2,000,000 Short-term loan—10% interest, payable monthly, and principal payable at maturity, on May 30, 2020 1,400,000 Long-term loan—11% interest, payable on January 1 of each year; principal payable on January 1, 2022 1,000,000 Total cost amounted to $5,200,000, and the weighted average of accumulated expenditures was $3,500,000. Jane Esplanade, the president of the company, has been shown the costs associated with this construction project and capitalized on the balance sheet. She is bothered by the “avoidable interest” included in the cost. She argues that, first, all the…arrow_forward
- 42. ABC, Inc. works on a P5,250,000 contract in 2022 to construct an office building. During 2022, ABC, Inc. uses the cost to cost method. At December 31, 2022, the balances in certain accounts were: Construction in progress – P1,890,000; accounts receivable – P180,000; and billings on construction in process – P900,000; contract retention – P90,000; mobilization fee – P70,000. At December 31,2022, the estimated costs to completion are P2,352,000. How much is the realized gross profit in 2022?arrow_forwardWITH SOLUTION /COMPUTATION 64.On December 31,2019, an entity sold a machine with useful life of 10 years to another entity andsimultaneously leased it back for two years at annual rental of P360,000. Sale price at fair value 3,600,000 Caryingamount 3,300,000 What amount of revenue from sale of the machine should be reported in 2019? 150,000 300,000 360,000 180,000arrow_forwardH5. St. Johns River Shipyards is considering the replacement of an 8-year-old riveting machine with a new one that will increase earnings before depreciation from $24,000 to $44,000 per year. The new machine will cost $82,500, and it will have an estimated life of 8 years and no salvage value. The new riveting machine is eligible for 100% bonus depreciation at the time of purchase. The applicable corporate tax rate is 25%, and the firm's WACC is 12%. The old machine has been fully depreciated and has no salvage value. What is the NPV of the project? Negative value, if any, should be indicated by a minus sign. Round your answer to the nearest cent.arrow_forward
- A6 Purchase the software from ABC Corporation. The agreement with ABC will allow XYZ inc to operate and run the software directly onXYZ’s own internal server. In addition to the cost of the software, XYZ inc anticipates it will incur training and implementation costs for its customer service employees. The purchased software is expected to have a useful life of 3 years. Determine 9-digit FASB codification? and give me your insight and evaluate alternative solution?arrow_forwardson.5 An asset used in a 4-year project falls in the 5-year MACRS class (refer to MACRS table on page 289), for tax purposes. The asset has an acquisition cost of $15,927,647 and will be sold for $5,627,208 at the end of the project. If the tax rate is 0.29, what is the aftertax salvage value of the asset ?arrow_forwardHw.27. Entity A entered into a sale and repurchase agreement for its head office on 1 January 2022, selling the office to Bank B for $78,560,000. On the same date, the head office had a fair value of $97,800,000. Entity A will continue to use the head office for the next 2 years and has the option to buy back the property for $93,765,779, based on an effective interest rate of 9.25% per year over the next 2 years. Property prices are expected to increase over the next 2 years. REQUIRED: Measure the net amount to be shown in the Statement of Profit or Loss for the year ended 31 December 2022. 1. $7,938,979 Expense 2. $19,240,000 Expense 3. $0 4. $7,266,800 Expense 5. None of them.arrow_forward
