
Concept explainers
(a)
If the crate resting on the bed of a decelerating truck would slide during the braking period.
Answer to Problem 77QAP
The crate will not slide, since the acceleration it experiences due to the truck's deceleration is less than the acceleration it experiences due to the force of static friction.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The mass of the crate
Initial velocity of the truck
Final velocity of the truck
Time during which the truck comes to a stop
Coefficient of static friction between the truck and the crate
Formula used:
To find if the crate would slide or not, a free body diagram is drawn for the crate and the force equations for equilibrium and for motion of the crate are determined.
The free body diagram for the crate is shown below:
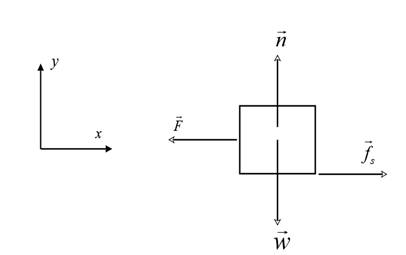
The weight of the block
The block is in equilibrium along the vertical ( y ) direction.
Therefore,
Since,
Therefore,
If
If the force of friction produces an acceleration,
Write an expression for the acceleration due to the force of friction using equations (1) and (2).
The expression for the acceleration produced by the truck is given by,
Calculation:
Calculate the acceleration
Express the initial velocity of the crate in m/s.
Calculate the acceleration a experienced by the crate due to the truck's decoration by substituting the values of the variables in equation (4).
This acceleration acts along the −x direction.
The crate slides if a >af.
Conclusion:
It can be seen that the acceleration in the +x direction is 6.419 m/s2 and that along the −x direction is 1.158 m/s2. Since
(b)
The minimum stopping time for the truck, that prevents the crate from sliding.
Answer to Problem 77QAP
For the crate to not slide on the bed of the truck, the minimum stopping time of the truck is 2.16 s.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Acceleration produced by the
Initial velocity of the truck
Final velocity of the truck
Formula used:
The crate will just remain in equilibrium, if the acceleration acting on it along the −x direction due to the truck's deceleration is equal to the acceleration along the +x direction due to the force of friction.
Calculation:
Rewrite the expression for
Substitute the values of the variables in the equation and solve for
Conclusion:
Thus, for the crate to not slide on the bed of the truck, the minimum stopping time of the truck is 2.16 s.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
COLLEGE PHYSICS
- When you learn to drive, you discover that you need to up slightly on the brake pedal as you come to a stop or the car will stop with a jerk. Explain this in terms of the relationship between static and friction.arrow_forwardDescribe a situation in which the net external force on a system is not zero, yet its speed remains constant.arrow_forwardA box rests on the (horizontal) back of a truck. The coefficient of static friction between the box and the surface on which it rests is 0.24. What maximum distance can the truck travel (starting from rest and moving horizontally with constant acceleration) in 3.0 s without having the box slide?arrow_forward
- When you learn to drive, you discover that you need to let up slightly on the brake pedal as you come to a stop or the car will stop with a jerk. Explain this in terms of the relationship between static and kinetic friction.arrow_forwardA 65-kg ice skater pushes off his partner and accelerates backwards at 1.15 m/s2. If the partner accelerates in the opposite direction at 1.65 m/s2. Find the mass of the other skater assuming that frictional forces are negligible.arrow_forwardThe citizen's car is a 1700-kg Mercedes-Benz 300SL. The citizen manages to park his car next to the express on a highway that rises 15* above the horizontal. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the tires of the car and the road is 0.14. (a) Calculate the magnitudes of the normal forces and the static friction force exerted by the soil on the tires. (b) If at the moment the brakes that hold the car at rest give way and the car begins to move downhill, determine the acceleration and average force with which the car reaches the end of the hill.arrow_forward
- 25- A Hospital bed requires a frictional force Fr to keep it moving with constant velocity across a floor. If the coefficient of friction is μ, then the normal force N is given by: A.μ /Fr B.μ Fr C.Fr /μ D.Fr E.μarrow_forward8 - I. The effect that makes the movement of objects difficult is called friction force.II. The friction force is in the opposite direction to the motion.III. The friction force depends on the characteristics of the friction surface.IV. Friction force is inversely proportional to reaction force.Which of the following are / are the correct statements regarding the friction force? A) I-II-IIIB) II-III-IVC) II-IIID) I-II-III-IVE) I-III-IVarrow_forward1. A truck loaded with sand accelerates along a highway. The driving force on the truck remains constant. What happens to the acceleration of the truck as its trailer leaks sand at a constant rate through a hole on its bottom? a. It decreases at a steady rate b. It remains constant. c. It increases at a steady rate. d. It increases then decreases 2. Which of the following follows the Law of Action and Reaction? a. Falling forward in transport when sudden breaks are applied. b. Object thrown from a certain height. c. kicking hard a stationary ball. d. During swimming, a swimmer moves ahead. answer onlyarrow_forward
- A pickup truck carries cans of paint in the back bed. The coefficient of static friction between the cans and the bed of the truck is 0.30. There is no back gate to the truck. How long should the driver take to accelerate to a speed of 65 mi/h to avoid losing the paint cans out of the rear of the truck?arrow_forwardA 150-N box is being pulled horizontally in a wagon accelerating uniformly at 3.00 m/s2. The box does not move relative to the wagon, the coefficient of static friction between the box and the wagon's surface is 0.600, and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.400. The friction force on this box is closest toarrow_forwardA 10000-kg load sits on the flatbed of a 20000-kg truck moving at 12.0 m/s. Assume that the load is not tied down to the truck, but has a coefficient of static friction of 0.500 and a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.400 with the flatbed of the truck. If the truck needs to stop in 10.0 m with constant acceleration, what is the force of friction between the load and the truck when the brake is first applied?arrow_forward
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning




