
Concept explainers
The range of the values of the mass m2 so that the two connected blocks resting on two inclined planes are in equilibrium.
Answer to Problem 83QAP
The mass m2 can have values between 3.51 kg and 52.64 kg for the system of masses to be in equilibrium.
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
Formula used:
From the diagram given, if the value of m2 falls below a certain value, it would slide up the plane and the block of mass m1 would slide down. This gives the value of the minimum mass of m2.
If the value of m2 increases beyond a certain value, the block would slide down the plane and the block of mass m1 would slide up.
By drawing the free body diagrams for each case, and applying the force equations for each case, the range of the values of m2 can be determined.
Explanation and Calculation:
Case 1:
Consider the case when the block 1slides down the plane and the block 2 slides up the plane.
The free body diagram for m1 is shown below:
The block rests on an incline which makes an angle
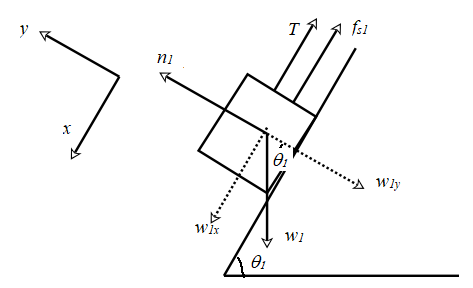
The weight
Resolve the weight w1 into components along the +x and −y directions as shown. The magnitudes of the components are given by,
Write the force equation along the +y direction.
Since the block is in equilibrium,
Therefore,
The force of friction is given by,
The system is in equilibrium along the x direction too. Therefore,
Using equations (1) and (2), in the above equation,
In a similar manner, construct a free body diagram for the block 2.
The block rests on an incline which makes an angle
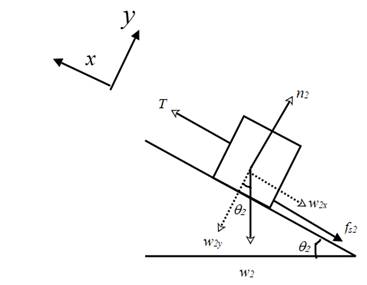
The weight
Resolve the weight w2 into components along the −x and −y directions as shown. The magnitudes of the components are given by,
Write the force equation along the +y direction and apply the condition for equilibrium.
Therefore,
The force of friction is given by,
The system is in equilibrium along the x direction too. Therefore,
Using equations (4) and (6), in the above equation,
Add equations (3) and (7) and write an expression for m2.
Substitute the known values of the variables in the expression and calculate the value of m2.
The minimum value of m2 for which the system is in equilibrium is 3.51 kg.
Case 2:
Consider the case when the block 1slides up the plane and the block 2 slides down the plane.
The free body diagram for m1 is shown below:
Assume the +x direction up the incline and the +y direction perpendicular to the plane. The weight
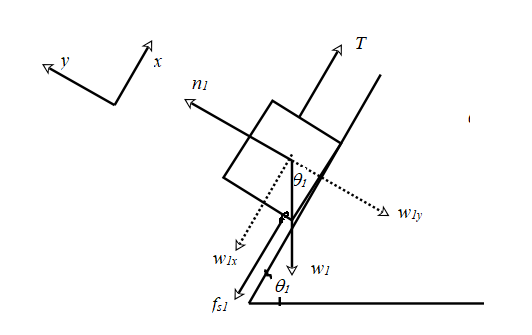
The equations (1) and (2) are applied to this free body diagram too.
Write the condition for equilibrium along the x direction.
Use equations (1) and (2) in the expression.
In a similar manner, construct a free body diagram for the block 2.
. Assume a coordinate system which has the +x direction pointing down the plane and the +y direction perpendicular to the plane away from it. The weight
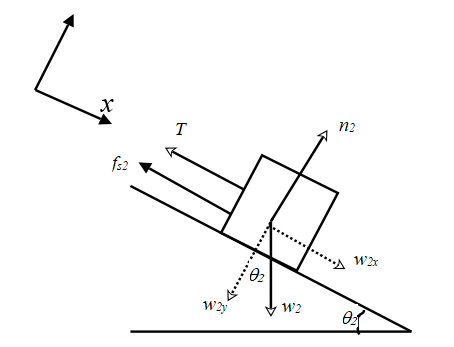
The equations (4), (5) and (6) are valid for this case too.
Write the equation for equilibrium along the x direction.
Using equations (4) and (6) in the expression,
Add equations (8) and (9) and write an expression for m2.
Substitute the known values of the variables in the expression.
The maximum value of m2 for the system to be in equilibrium is 52.64 kg.
Conclusion:
Thus, the mass m2 can have values between 3.51 kg and 52.64 kg for the system of masses to be in equilibrium.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
COLLEGE PHYSICS-ACHIEVE AC (1-TERM)
- A block of mass 3.00 kg is pushed up against a wall by a force P that makes an angle of = 50.0 with the horizontal as shown in Figure P5.12. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the wall is 0.250. (a) Determine the possible values for the magnitude of P that allow the block to remain stationary. (b) Describe what happens if P has a larger value and what happens if it is smaller. (c) Repeat parts (a) and (b), assuming the force makes an angle of = 13.0 with the horizontal. Figure P5.12arrow_forwardA block of mass 3.00 kg is pushed up against a wall by a force P that makes an angle of = 50.0 with the horizontal as shown in Figure P5.34. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the wall is 0.250. (a) Determine the possible values for the magnitude of P that allow the block to remain stationary. (b) Describe what happens if P has a larger value and what happens if it is smaller. (c) Repeal parts (a) and (b), assuming the force makes an angle of = 13.0 with the horizontal. Figure P5.34arrow_forwarda 0.5-kg block resting on a table is pulled by a constant horizontal force that causes it to accelerate at a rate of 2.5 m/s2. a) Calculate the magnitude of the applied force if friction between the surface is negligible. b) Calculate the magnitude of the applied force if friction between the surface is 2 N.arrow_forward
- A 12-kg crate rests on a horizontal surface and a boy pulls on it with a force that is 30◦ belowthe horizontal. If the coefficient of static friction is 0.40, the minimum magnitude force heneeds to start the crate moving is: Choices: 54N 47N 71N 44N 56N Show complete solution and free body diagramarrow_forwardThe citizen's car is a 1700-kg Mercedes-Benz 300SL. The citizen manages to park his car next to the express on a highway that rises 15* above the horizontal. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the tires of the car and the road is 0.14. (a) Calculate the magnitudes of the normal forces and the static friction force exerted by the soil on the tires. (b) If at the moment the brakes that hold the car at rest give way and the car begins to move downhill, determine the acceleration and average force with which the car reaches the end of the hill.arrow_forward4. A 28.0 kg crate is being push across a horizontal floor with a force F = 155 N that makes an angle θ = 28.0° with the horizontal as illustrated in the figure below. Find the magnitude of the acceleration of the crate, given that the coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the floor is 0.13.arrow_forward
- In laboratory experiment, a 0.5-kg block resting on a table is pulled by a constant horizontal force that causes it to accelerate at a rate of 2.5 m/s2. a) Calculate the magnitude of the applied force if friction between the surface is negligible. b) Calculate the magnitude of the applied force if friction between the surface is 2 N.arrow_forwardOne 3.6-kgkg paint bucket is hanging by a massless cord from another 3.6-kgkg paint bucket, also hanging by a massless cord. a) If the two buckets are pulled upward with an acceleration of 1.25 m/s^2 by the upper cord, calculate the tension in the top cord. b) If the two buckets are pulled upward with an acceleration of 1.25 m/s^2 by the upper cord, calculate the tension in the bottom cord.arrow_forward1. A crate is lying on a plane inclined at an angle ɵ. What is the angle between the weight of the crate and the force exerted by the plane on the crate? a) θ - 180° b) θ c) 180° - θ d) 180° 2. An object is being acted upon by an unbalanced force if a) it is speeding up b) it is slowing down c) it changes its direction d) all of the abovearrow_forward
- A box is pushed to the right at an angleof30° above the horizontal with a force of 200 N. The mass of the box is m = 20.0 kg and is moving on a flat horizontal surface for which the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.40 Draw the free-body diagram of the box. Calculate the magnitude of the normal force Calculate the magnitude of the acceleration of the box.arrow_forwardA car is driving in a horizontal circle within the surface of a cone as shown in Fig. 2(a). The car has mass M and is driving with constant velocity. Assume that there is no friction acting on the car. The horizontal circle is held at a height H above the vertex of the cone. The angle between the axis of the cone and its side is θ. (a) Draw the free-body diagram with the forces acting on the car and indicate the direction ofacceleration. (b) Given the quantities given and the gravity g, find the normal acting on the car and and its velocity. Hint: If physics, trigonometry, and algebra are developed correctly your velocity will be independentof θ.arrow_forwardAn adventurous archaeologist crosses between two rock cliffs, with a raging river far below, by slowly going hand-over-hand along a rope stretched between the cliffs. He stops to rest at the middle of the rope. The rope will break if the tension in it exceeds 3.00 x 104 N, and our hero’s mass is 81.6 kg. a. If the angle that the rope makes with the cliff is 75o, find the tension in the rope. b. What is the smallest value the angle can have if the rope is not to break?arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning


