
Concept explainers
SCIENTIFIC INQUIRY Jens Clausen and colleagues, at the Carnegie Institution of Washington, studied how the size of yarrow plants (Achillea lmmlosa) growing on the slopes of the Sierra Nevada varied with elevation. They found that plants from low elevations were generally taller than plants from high elevations, as shown in the diagram.
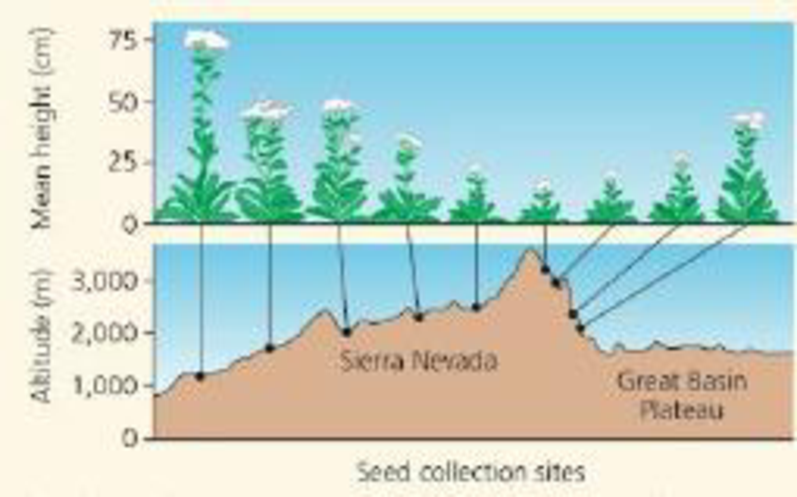
Data from J. Clausen et al., Experimental studies on the nature of species III. Environmental responses of climatic races of Achillea, Carnegie Institution of Washington Publication No 581 (1948)
Clausen and colleagues proposed two hypo theses to explain this variation within a species: (1) ·There are genetic differences between populations of plants found at different elevations. (2) The species has developmental flexibility and can assume tall or short growth forms, depending on local abiotic factors. If you had seeds from yarrow plants found at low and high elevations, how would you test these hypotheses?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 52 Solutions
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY CUSTOM W/MASTERING
- Many rare and endangered species are specialist. Explain what this term means. As an environment changes, should we worry about losing specialist? Why or why not?arrow_forwardMicrofauna alone decomposed leaf litter most rapidly mesofauna and microfauna together could not decompose any leaf little macrofauna alone provided the slowest decomposition faunal groups of all sizes together provided the most rapid decoposition soil fauna plays no role in leaf littler decompositionarrow_forwardpart A) When researchers removed its competitor (Chthamalus), ___________ still only occupied deep waters. Clinostomus Geospiza Balanus none of the options are correct Hirundo Part B) Brown et al. (2020) used _________ to test whether there was an association between salmon density and how green trees were near rivers and streams. none of the options are correct satellite images genomic techniques soil samples volunteersarrow_forward
- SCIENTIFIC INQUIRY An ecologist studying desert plantsperformed the following experiment. She staked out twoidentical plots, containing sagebrush plants and small annualwildflowers. She found the same five wildflower species inroughly equal numbers on both plots. She then enclosed oneplot with a fence to keep out kangaroo rats, the most commongrain-eaters of the area. After two years, four of the wildflowerspecies were no longer present in the fenced plot, but onespecies had become much more abundant. The control plothad not changed in species diversity. Using the principles ofcommunity ecology, propose a hypothesis to explain her results.What additional evidence would support your hypothesis?arrow_forwardHello, I notice you only answer 3 questions su i cut it. 1. Research on the ethnobotany of Cacao and be able to know the influence of man on its dispersal. 2. Enumerate some economically important species belonging to the families studied in this exercise. (EUDICOTS: (1)MALPIGHIALES, (2)MALVALES AND (3) MYRTALES)arrow_forwardA hypothetical community on a barren mid-Atlantic island consists of two fish-eating seabirds (the booby and the noddy), the fungi and microorganisms that live on the birds' dung, a tick that feeds on these two birds, a cactus, a moth that feeds on cast-off feathers, a beetle that lives on dung organisms, and spiders that eat the other arthropods. There are no other plants and no lichens. Which of the following choices incorrectly pairs a member of this assemblage with its position in the trophic structure? Group of answer choices: cactus, producer spiders, secondary consumer moths, detritivores fungi, detritivores booby and noddy birds, primary consumersarrow_forward
- Did any of these species increase in number and what could account for this increase? (Everything is in there, there is no missing information, it is based on the data)arrow_forwardThe blue-green bacteria (also called cyanobacteria) in some lichens are capable of nitrogen fixation. Why would this be especially advantageous in early stages of ecological succession?arrow_forwardAustralian researchers removed a parasitic plant called mistletoe froma forest and observed the consequences. During the 3-yearexperiment, over 30% of the insect and bird species disappeared fromthe mistletoe-free forest. Another forest in which no mistletoe wasremoved saw no change in species diversity. What might the biologistsconclude from these data?arrow_forward
- ex. Locate any woodland or forest area close to your home. Create a 10 x 10 m quadrat once you've identified a suitable location. Markings can be made with a straw or a rope. List and count any fauna found at the locations (either inside or outside the quadrats). 1. How far should you record and observe any fauna encountered outside the quadrat? Why do you think it is not necessary to note the distance for faunal observation outside the quadrat?arrow_forwardWRITE ABOUT A THEME: INTERACTIONS Organisms interactwith each other and the physical environment. In a shortessay (100–150 words), explain how the response of diatompopulations to a drop in nutrient availability can affect bothother organisms and aspects of the physical environment(such as carbon dioxide concentrations).arrow_forwardAerobic organisms are dependent on autotrophs. One reason for this dependency is that most autotrophs provide the aerobic organisms with oxygen. nitrogen gas. carbon dioxide. hydrogen. Two different species in a particular ecosystem share the same niche. What is most likely true about these two species? They are the result of an allopatric speciation event They compete intensely One is a predator, the other its prey They are the result of a sympatric speciation eventarrow_forward
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781337408332Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781337408332Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap...BiologyISBN:9781305073951Author:Cecie Starr, Ralph Taggart, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning



