
Concept explainers
To review:
The observed relationship between increased forest fragmentation and increased incidence of Lyme disease.
Introduction:
Forest fragmentation is the process of division of large habitats into smaller, divided, and isolated fragmented areas. It lowers the quality of the forest. This results in the decline in the species richness in the fragments. The white-footed mice occupy a broad ecological niche, while opossums are absent from low-quality forest fragment.
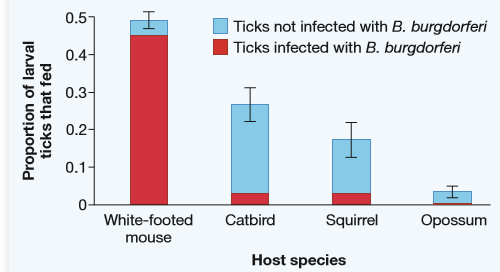
Hypothesis proposed: B. burgdorferi is the bacterium that is transferred into the body of humans by the ticks. The bacterium is an endoparasite that lives inside the human body and causes Lyme disease. The newly hatched ticks do not harbor B. burgdorferi bacterium as they are killed by the host when they crawl onto the host organism, and if they are successful in harvesting the blood from their host, then they are generally not infected by B. burgdorferi. A bar diagram showing the proportion of larval ticks that fed and caused infection versus host species is given below:
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 52 Solutions
Biological Science (6th Edition)
- The unicellular cyanobacterium Prochlorococcus sp. is the most abundant photosynthetic microbe in tropical and subtropical oceans. At least two ecotypes exist: one is adapted to high light and the other to lower light intensities. How does the presence of these two ecotypes contribute to their physiological success and their numerical success? How would you determine the amount of fixed carbon they contribute to these open-ocean ecosystems?arrow_forwardWhy do you think high nitrogen rates resulted in an increased incidence of rice diseases in general? How do you think it is related to the increase of insect populations?arrow_forwardCreate a two-part figure showing the effects of forest fragmentation on the community of small mammals relevant to Lyme disease in eastern forests. Figure A should depict the interaction network of a large forestpatch with higher species diversity. Figure B should illustrate how the interaction network and transmission of Borrelia burgdorferi are different in a small forest fragment with low species diversity than they are in largeforest patches with greater diverisity. Eastern forests are diverse communities in which many species interact with one another. Your figure will be asimplified interaction network showing some of the most important species related to the ecology of Lyme disease. Remember that your goal is to illustrate how increasing fragmentation affects forest mammal communities in a way that increases Lyme disease risk.• Choose from the following species for your figure: black-legged tick, white-footed mouse, raccoon, eastern chipmunk, gray squirrel, white-tailed deer,…arrow_forward
- a.Briefly describe the roles of Rhizobium, Nitrosomonas, Nitrobacter and Pseudomonasbacteria in the nitrogen cycle (about 200 words). b. Provide one example for each of the following from the sulfur cycle: a biotic flux a natural abiotic flux an anthropogenic flux..arrow_forwarda- Removing live acorn barnacles stimulated the growth of macroalgae b- macroalgae dominated the occupation of the surface of rocks after four years and their success was greatly increased relative to controls when both barnacle species were removed. c- acorn barnacle shells facilitate algal density on rocks d- acorn barnacles increase there coverage of rocks when little brown barnacles reach their highest density and seem to replace little brown barnacles on the rock during 1985arrow_forwardCompare parasitism and mutualism for the two factors (A and B) below. A) What distinguishes these two strategies from the other strategies for interaction? B) What is the long-term benefit to the micro-symbiont as far as access to a new host? C) What is the cost (e.g. DNA that needs to be maintained)?arrow_forward
- 4.1 Attine ants cultivate a garden of Leucocoprini fungus for its nourishment, while the fungus receives all its requirements for growth from the ants. The ants also promote the growth of an actinomycete, Pseudonocardia, which produces an antimicrobial compound that inhibits the growth of another fungus, Escovopsis which is a parasite of Leucocoprini. Check all the applicable interactions observed in this multi-species interaction from the choices givenarrow_forwardExplain in no more than one paragraph, the importance of ammonification in the nitrogen cycle to the biotic and abiotic ecosystemarrow_forwardWhat is the relationship between an increase in fossil fuel consumption and increased carbon in terrestrial plants? How might this change flora populations? What impact could twenty years at this level of consumption have on flora? What is the relationship between an increase in total carbon concentration (the smokestack) and increased carbon in the ocean surface? How might this change marine life populations? What impact could fifty years at this level of emissions have on marine fauna? On marine flora? In addition to circulating through the carbon cycle, where else might excess carbon be found? In fifty years, where would you be most likely to see excess carbon? Which areas are most highly (and quickly) affected by an increase in carbon emissions (and increase in fossil fuel consumption)? How would these effects manifest themselves? What are the dangers/benefits to these areas?arrow_forward
- Pesticides vary in terms of their persistence in soils. Give three possible reasons for the existence of such variation.arrow_forwardBiologically, what conditions are necessary for stable coexistence of competitors? Describe the major ways that species can adapt to enhance the probability of stable coexistence.arrow_forwardWhat is the primary source of anthropogenic sulfur dioxide and why do you think that in the Philippines there are so much problem related to sulfur dioxide emission?arrow_forward
