
Concept explainers
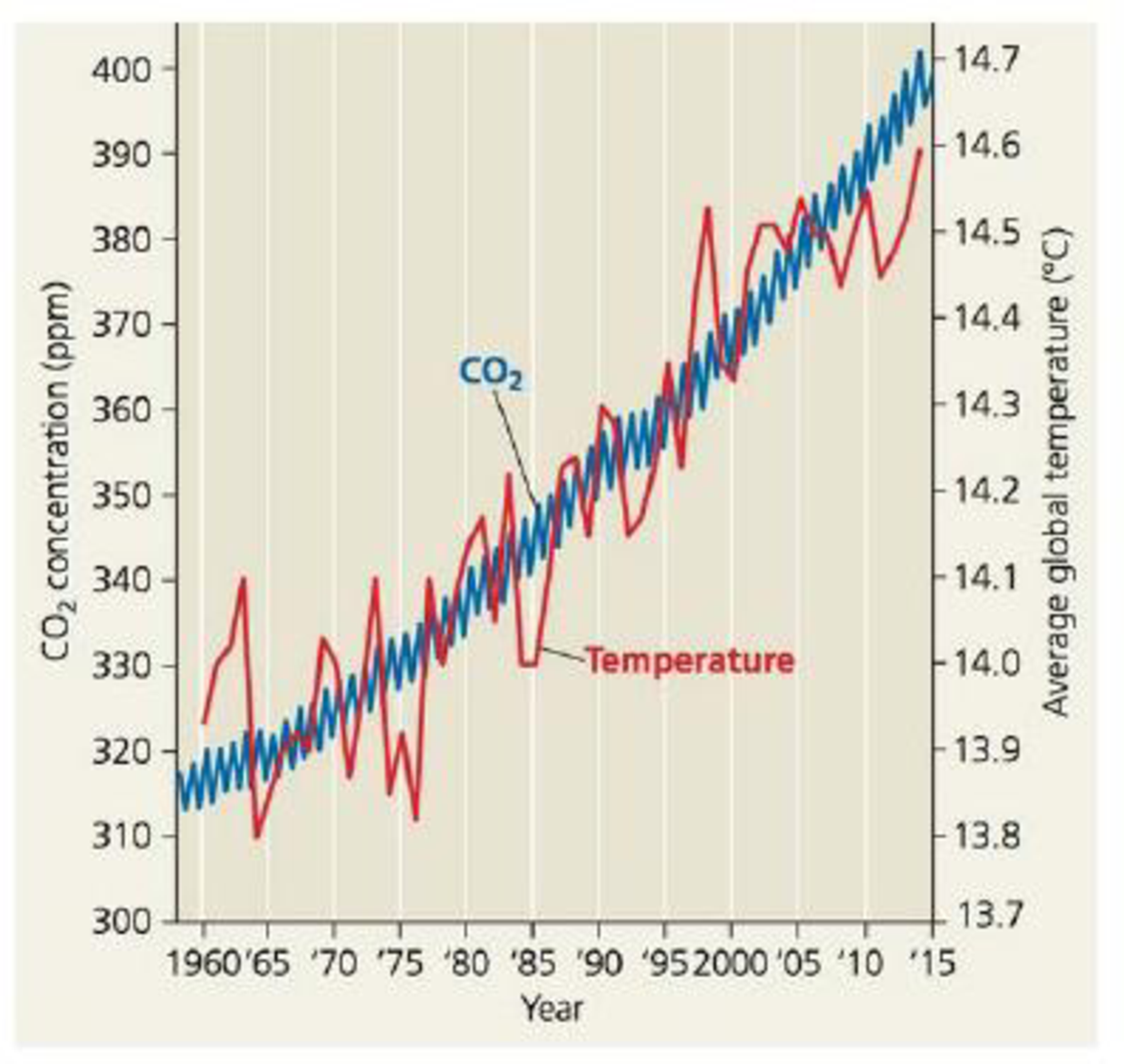
SCIENTIFIC INQUIRY (a) Estimate the average CO2. concentration in 1975 and in 2012 using data provided in Figure 56.28. (b) On average, how rapidly did CO2 concentration increase (ppm/yr) from 1975 to 2012? (c) Estimate the approximate CO2 concentration in 2100, assuming that the C02 concentration continues to rise as fast as it did from 1975 to 2012. (d) Draw a graph of average C02 concentration from 1975 to 2012 and then use a dashed line to extend the graph to the year 2100. (e) Identify the ecological factors and human decisions that might influence the actual rise in CO2. concentration. (e) Discuss how additional scientific data could help societies predict this value.
Figure 56.28 Increase in atmospheric carbon dioxide concentration at Mauna Loa, Hawaii, and average global temperatures. Aside from normal seasonal fluctuations, the CO2 concentration (blue curve) increased steadily from 1958 to 2015. Though average global temperatures (red curve) fluctuated a great deal over the same period, there is a clear warming trend.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 56 Solutions
Bio 121 Campbell Biology Truman College
- The main cause of the increase in the amount of CO2 in Earth’satmosphere over the past 150 years is(A) increased worldwide primary production.(B) increased worldwide standing crop.(C) an increase in the amount of infrared radiation absorbedby the atmosphere.(D) the burning of larger amounts of wood and fossil fuelsarrow_forward1.What is the most common source of CO2 emissions? 2.How do ice cores provide CO2 level data that is thousands of years old? 3.lf CO2 levels have changed over the past 400,000 years, what evidence do we have that shows human impacts are changing CO2 levels currently? 4.How are CO2 levels and temperature linked? 5.What is the Keeling curve? 6.Is the Keeling curve controversial? Why or why not? 7.Within the past four years, how have CO2 levels changed?arrow_forwardaccording to the chart pie 1)what percentage of energy is produced by fossil fuel? 2)what percentage of energy is produced by energy technologies? 3) how much energy is produced by all alternative energy combined? U.S. energy consumption by energy source, 2017 Total 97.7 quadrillion British thermal units (Btu) Total = 11.0 quadrillion Btu geothermal 2 % solar 6% petroleum 37% - wind 21% biomass waste 4% biofuels 21% renewable energy 11% nuclear electric power 9% biomass 45% natural gas 29% wood 19% coal 14% hydroelectric 25%arrow_forward
- global CO2 levels in the past million years were at or higher concentration that they are today (i.e. over 407 ppm). True or Falsearrow_forwardWIII save this response. Question 10 Which correctly describes the atmospheric cycle of CO2 concentrations in various places in the world? O the global CO2 concentration remain stable throughout the year the CO2 concentration in the southern and northern hemisphere cycle at the same time of the year O the CO2 concentration has larger annual fluctuations in the southern hemisphere because of the larger ocean area O the CO, concentration has larger annual fluctuations in the northern hemisphere because of the larger land area A Moving to another question will save this response.arrow_forwardWhat is the trend of CO2 cons in recent years?arrow_forward
- Part B) Paul Ehrlich prediction the carrying capacity of the global human population to be around 5.8 billion people. This is an: a)underestimation of the actual carrying capacityb)overestimationC)He was exactly right Part c) Amazingly, a water bear -microscopic invertebrates- can adjust its metabolism to zero and “hibernate” when the habitat dries. Then, presto-add water and it springs back to life. This is an example of ___ to a ____stress.a. acclimation, temperatureb acclimation, waterc adaptation, energyd adaptation, nutrientsPart D) The long-leaf pine forest ecosystem once extended across 95 million acres of the southeastern US. However only 5 million acres now remain. This refers to a large reduction ina. the species rangeb a metapopulationc a mega populationarrow_forwardThis is the Keeling Curve, the record of atmospheric CO2 as measured at Mauna Loa, Hawaii, over the last several decades. What do the small oscillations in this curve reflect? November 18, 2021 Carbon dioxide concentration at Mauna Loa Observatory 420 410 Full Record ending November 18, 2021 400 390 380 370 360 350 340 8 330 320 310 1960 2000 1965 1970 1975 1980 1985 1990 1995 2005 2010 2015 2020 O a. The change in the direction of ocean breezes over Hawaii b. Annual cycles, driven by the seasonal pattern of photosynthesis in the Northern Hemisphere O c. The episodic outgassing of the Mauna Loa volcano where the observatory is located d. Annual cycles, driven by CO2 incorporation into glaciers in winter Co, Concentration (ppm)arrow_forward400 2016 350 300 1900 (D 1800 250 200 150 800,000 600,000 400,000 200,000 Years before present What is the major reason for the change in the carbon dioxide concentrations seen in the last 150 years? tv Aa MacBook Air 吕0 888 DII DD F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 F10 # $ & 3 4 6 7 081 9. E R Y H J K LL CO2 concentration (parts per million)arrow_forward
- 400 2016 350 300 1900 O 1800 250 200 150 800,000 600,000 400,000 200,000 Years before present What is the major reason for the change in the carbon dioxide concentrations seen in the last 150 years? 15 étv Aa MacBook Air 80 888 DD F3" F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 F10 23 2$ & * ) 4 9. 8 E R Y F H J K CO, concentration (parts per million)arrow_forwardThe three images below are snapshots of the atmospheric CO2 concentration in May, July, and September of a year. To interpret the CO2 concentration: blue/green/yellow indicates lower to medium CO2 concentrations and red/maroon/pink indicates medium-high to highest CO2 concentrations. Question: Which of the phenomena described below best explains why CO2 concentrations are lowest in the summer when compared to the spring or fallI/winter? 2006 / 05 / 09 NASA 2006 / 07 / 12 Canon Den ano n n Cat C m e NASA Global Medeling and Assinilten Offoe Cate ae 2006 / 11 / 13 Gobal Modeling and Assimiation Ofice NASA O Higher rates of plant and algae growth in summer lead to higher photosynthesis rates O Less fossil fuels are emitted by humans in the summer O More cars are driven by humans in the summer O Lower rates of plant and algae growth in summer lead to decreased rates of photosynthesisarrow_forwardThe term BOD (Biological Oxygen Demand): Group of answer choices is a measure of the organic matter and other oxygen-demanding wastes in a)a lake or stream. b)is the highest after a person eats a candy bar c)is defined as the amount of oxygen needed by fish to survive. d)is defined as the number of organisms that need oxygen in a stream. Nextarrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





