
(a)
The forceexerted by the track on the fully loaded roller-coaster at point
(a)
Answer to Problem 16P
The forceexerted by the track on the fully loaded roller-coaster at point
Explanation of Solution
Consider the fully loaded roller-coaster car is moving on a curved path which has a radius of curvature. If the roller-coaster car rotates on a circular path, then it experiences a force acts towards the center of the circle which is known as
The magnitude of centripetal force
- 1. The speed of the roller-coaster car.
- 2. The mass of the roller-coaster car.
- 3. The radius of curvature of the curve path.
The forces act on the fully loaded roller-coaster car when it is at point
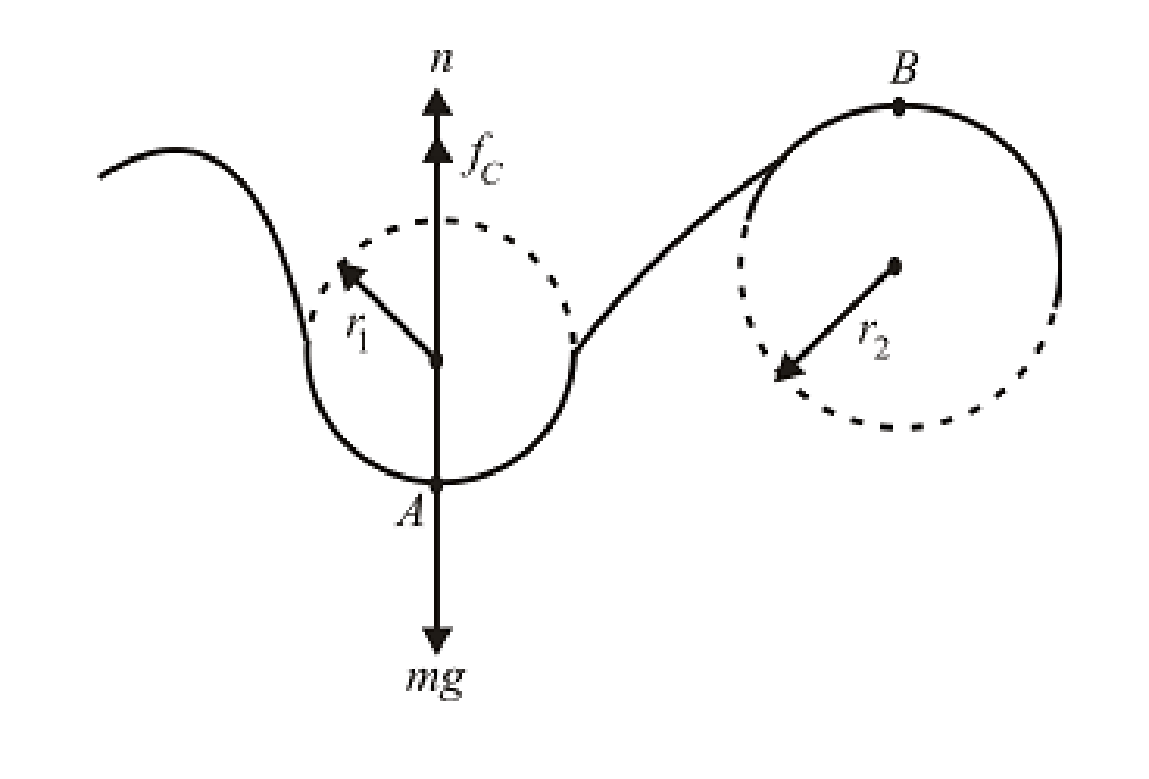
Write the expression for the fully loaded roller-coaster car corresponding to Newton’s second law in
Here,
Write the expression for centripetal acceleration as.
Here,
Substitute
Simplify the above expression for
Conclusion:
Substitute
Thus, the force exerted by the track on the fully loaded roller-coaster at point
(b)
The maximum speed the vehicle can have at point
(b)
Answer to Problem 16P
The maximum speed the vehicle can have at point
Explanation of Solution
The direction of the centrifugal force and the normal force exerted by the track on the fully loaded roller-coaster is in same direction. As the speed of the car increases, the centripetal force increase which results decrease in normal reaction force.
The car keeps on track because of normal force reaction exerted by the track on the car.
At the verge to keep the car on the track, the normal force exerted by the track on the car is equal to zero. If the normal reaction force is equal to zero, then weight of the car will be equal to the centripetal force.
Write the expression for the condition of a car to keep on the track as.
Here,
Write the expression for centrifugal force acts on the car at point
Here,
Substitute
Re-arrange the terms
Simplify the above expression for
Conclusion:
Substitute
Thus, the maximum speed the vehicle can have at point
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics Technology Update
- Two blocks, A and B (with mass 50.0 kg and 1.00 102 kg, respectively), are connected by a string, as shown in Figure P5.86. The pulley is frictionless and of negligible mass. The coefficient of kinetic friction between block A and the incline is k = 0.250. Determine the change in the kinetic energy of block A as it moves from to , a distance of 20.0 m up the incline (and block B drops downward a distance of 20.0 m) if the system starts from rest. Figure P5.86arrow_forwardAn athlete jumping vertically on a trampoline leaves the surface with a velocity of 8.5 m/s upward. What maximum height does she reach? (a) 13 m (b) 2.3 m (c) 3.7 m (d) 0.27 m (e) The answer cant be determined because the mass of the athlete isnt given.arrow_forwardA ball of mass m = 1.80 kg is released from rest at a height h = 65.0 cm above a light vertical spring of force constant k as in Figure P5.64a. The ball strikes the top of the spring and compresses it a distance d = 9.00 cm as in Figure P5.64b. Neglecting any energy losses during the collision, find (a) the speed of the hall just as it touches the spring and (b) the force constant of the spring.arrow_forward
- A 4.0-kg particle moving along the x -axis is acted upon by the force whose functional form appears below. The velocity of the particle at x = 0 is v = 6.0 m/s. Find the particle’s speed at x=(a)2.0m, 2.0 (b)4.0 m. (c) 10.0m, (d) Does the particle turn around at some point and head back toward the origin? (e) Repeat part (d) if v = 2.0 m/s at x = 0.arrow_forwardA 50 g particle that can move along the x-axis experiences the net force Fx=2.0t^2 N where t is in s. The particle is at rest at t = 0 s What is the particle's speed at tt = 2.6 ss? v=________arrow_forwardA nonzero net force acts on an object. Is it possible for any of the following quantities to be constant: the object’s (a) speed; (b) velocity; (c) kinetic energy?arrow_forward
- A box with mass m = 1.5 kg is sliding with a speed of 4.0 m/s on a horizontal surface. When at x = 0, it encounters a rough section where the frictional force varies according to the equation f(x)=−(10+40x)f(x)=−(10+40x) where ff is in newtons and x is in meters. How far does this box slide before stopping?arrow_forwardA small block of mass m=.5kg is fire with an initial speed of v0 = 4m/s alog a horizontal section of frictionless track. The block then moves along the frictionless, smicircular, vertical tracks of radius R= 1.5m a) Determine the force exerted by the track on the block at points A, middle of the semicircle, and B, end of the semicircle. b) The bottom of the track consists of a section (L = .4m) wit friction. Determine the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and that portion of the bottom track if the block just makes it up to the top track on the first trip around.( Hint: If the block makes it to the top track, the force of contact exerted by the track on the block at that point is zero.)arrow_forwardAn Atwood's machine consists of two different masses, both hanging vertically and connected by an ideal string which passes over a pulley. Let the masses be M1 and M2 and M2 = 2M1. Initially, M1 is held fixed a distance y below M2. Find the speed of the blocks when they are the same elevation (that is, the same horizontal position, by then each block has moved y/2).arrow_forward
- A 8.36-kg particle is subject to a net force that varies with position as shown in the figure. The particle starts from rest at x = 0. What is its speed at the following positions? (a) x = 5.00 m m/s(b) x = 10.0 m m/s(c) x = 15.0 m m/sarrow_forwardA net force along the x-axis that has x-component Fx=−12.0N+(0.300N/m^2)x^2 is applied to a 4.60 kg object that is initially at the origin and moving in the −x direction with a speed of 8.60 m/s. A.what is the speed of the object when it reaches the point x=7.90marrow_forwardA freight train consists of two 9.00 ✕ 105 kg engines and 50 cars with average masses of 3.50 ✕ 105 kg. (a) What force (in N) must each engine exert backward on the track to accelerate the train at a rate of 4.00 ✕ 10−2 m/s2 if the force of friction is 7.50 ✕ 105 N, assuming the engines exert identical forces? This is not a large frictional force for such a massive system. Rolling friction for trains is small, and consequently, trains are very energy-efficient transportation systems. (Enter the magnitude.) b) What is the magnitude of the force (in N) in the coupling between the 37th and 38th cars (this is the force each exerts on the other), assuming all cars have the same mass and that friction is evenly distributed among all of the cars and engines? (Assume both engines are at the front of the train.)arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning



