
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of
Concept Introduction:
There are few steps in
- Find the longest carbon chain in the molecule and name it.
- Number the longest carbon chain in such a way that the halogen atoms get the lowest number.
- If there are multiple halogen atoms from same atom, a prefix as di, tri, tetra is added to denote the number of halogen atoms.
- Different types of halogens are named in alphabetical order.
- Position of the halogen atom is indicated by writing the number of carbon atom it is attached before the name of the parent hydrocarbon.
- The name is ended as a normal
alkane .
(a)
Answer to Problem 31P
1-chloroethane.
Explanation of Solution
(b)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of
Concept Introduction:
There are few steps in IUPAC nomenclature,
- Find the longest carbon chain in the molecule and name it.
- Number the longest carbon chain in such a way that the halogen atoms get the lowest number.
- If there are multiple halogen atoms from same atom, a prefix as di, tri, tetra is added to denote the number of halogen atoms.
- Different types of halogens are named in alphabetical order.
- Position of the halogen atom is indicated by writing the number of carbon atom it is attached before the name of the parent hydrocarbon.
- The name is ended as a normal alkane.
(b)
Answer to Problem 31P
1,2-dibromoethane.
Explanation of Solution
(c)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the following molecule should be determined.
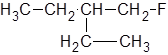
Concept Introduction:
There are few steps in IUPAC nomenclature,
- Find the longest carbon chain in the molecule and name it.
- Number the longest carbon chain in such a way that the halogen atoms get the lowest number.
- If there are multiple halogen atoms from same atom, a prefix as di, tri, tetra is added to denote the number of halogen atoms.
- Different types of halogens are named in alphabetical order.
- Position of the halogen atom is indicated by writing the number of carbon atom it is attached before the name of the parent hydrocarbon.
- The name is ended as a normal alkane.
(c)
Answer to Problem 31P
2-ethyl-1-fluorobutane.
Explanation of Solution
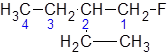
The longest carbon chain giving the halide atom the lowest number has four carbons. So, this is a butane. There is a fluorine atom attached at C-1 and an ethyl group at C-2. Alphabetically, ethyl substituent should be written before, fluoro-. So, the IUPAC name of the compound is 2-ethyl-1-fluorobutane.
(d)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of
Concept Introduction:
There are few steps in IUPAC nomenclature,
- Find the longest carbon chain in the molecule and name it.
- Number the longest carbon chain in such a way that the halogen atoms get the lowest number.
- If there are multiple halogen atoms from same atom, a prefix as di, tri, tetra is added to denote the number of halogen atoms.
- Different types of halogens are named in alphabetical order.
- Position of the halogen atom is indicated by writing the number of carbon atom it is attached before the name of the parent hydrocarbon.
- The name is ended as a normal alkane.
(d)
Answer to Problem 31P
2,2-dimethyl-1-iodopropane.
Explanation of Solution
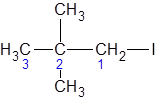
The longest carbon chain giving the halide atom the lowest number has three carbons. So, this is a propane. There is an iodine atom attached at C-1 and two methyl groups at C-2. Alphabetically, iodo- substituent should be written before, methyl. So, the IUPAC name of the compound is 2,2-dimethyl-1-iodopropane.
(e)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of the following molecule should be determined.
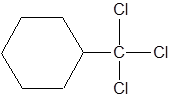
Concept Introduction:
There are few steps in IUPAC nomenclature,
- Find the longest carbon chain in the molecule and name it.
- Number the longest carbon chain in such a way that the halogen atoms get the lowest number.
- If there are multiple halogen atoms from same atom, a prefix as di, tri, tetra is added to denote the number of halogen atoms.
- Different types of halogens are named in alphabetical order.
- Position of the halogen atom is indicated by writing the number of carbon atom it is attached before the name of the parent hydrocarbon.
- The name is ended as a normal alkane.
(e)
Answer to Problem 31P
1-trichloromethylcyclohexane.
Explanation of Solution
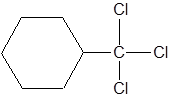
This is a substituted cycloalkane. The cycloalkane has six carbons, so, it is named as cyclohexane. There is a trichloromethyl group attached to C-1 of cyclohexane. So, IUPAC name of this molecule is 1-trichloromethylcyclohexane.
(f)
Interpretation:
The IUPAC name of
Concept Introduction:
There are few steps in IUPAC nomenclature,
- Find the longest carbon chain in the molecule and name it.
- Number the longest carbon chain in such a way that the halogen atoms get the lowest number.
- If there are multiple halogen atoms from same atom, a prefix as di, tri, tetra is added to denote the number of halogen atoms.
- Different types of halogens are named in alphabetical order.
- Position of the halogen atom is indicated by writing the number of carbon atom it is attached before the name of the parent hydrocarbon.
- The name is ended as a normal alkane.
(f)
Answer to Problem 31P
Tribromomethane.
Explanation of Solution
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEM W/SAPLING PACKAGE
- Provide the correct IUPAC name for CaSO₄. and for Provide the correct IUPAC name for Ca(NO₃)₂arrow_forwardWrite the IUPAC name of the following compound:CH3NHCH(CH3)2arrow_forwardName the following compounds according to IUPAC rules K[PtCl3(C2H4)] [Co(NO2)3(NH3)3] [Cr(OH)(H2O)3(NH3)2](NO3)2arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning





