
Concept explainers
A golfer tees off from a location precisely at ϕi = 35.0° north latitude. He hits the ball due south, with range 285 m. The ball’s initial velocity is at 48.0° above the horizontal. Suppose air resistance is negligible for the golf ball. (a) For how long is the ball in flight? The cup is due south of the golfer’s location, and the golfer would have a hole-in-one if the Earth were not rotating. The Earth’s rotation makes the tee move in a circle of radius RE cos ϕi = (6.37 × 106 m) cos 35.0° as shown in Figure P6.47. The tee completes one revolution each day. (b) Find the eastward speed of the tee relative to the stars. The hole is also moving cast, but it is 285 m farther south and thus at a slightly lower latitude ϕf. Because the hole moves in a slightly larger circle, its speed must he greater than that of the tee. (c) By how much does the hole’s speed exceed that of the tee? During the time interval the ball is in flight, it moves upward and downward as well as southward with the projectile motion you studied in Chapter 4, but it also moves eastward with the speed you found in part (b). The hole moves to the east at a faster speed, however, pulling ahead of the ball with the relative speed you found in part (c). (d) How far to the west of the hole does the ball land?
Figure P6.47
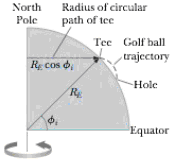
(a)
The time of flight of the ball.
Answer to Problem 47CP
The time for which the ball be in flight is
Explanation of Solution
The range of the motion after hitting the ball is
The range of the parabolic motion
Here,
Write the expression for the equation for parabolic motion
As initial and final distance is equal,
Rearrange the above expression for
Substitute
Rearrange the above expression for
Substitute
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the time for which the ball be in flight is
(b)
The relative eastward speed of the tee with respect to the stars.
Answer to Problem 47CP
The relative eastward speed of the tee with respect to the stars is
Explanation of Solution
Write the formula to calculate the eastward speed of the tee relative to the stars
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the relative eastward speed of the tee with respect to the stars is
(c)
The value by which the hole's speed exceed that of the tee.
Answer to Problem 47CP
The value by which the hole's speed exceed that of the tee is
Explanation of Solution
Write the formula to calculate the length of the arc
Rearrange the above expression for
Substitute
Write the formula to calculate the speed of the hole
Here,
Substitute
Calculate the difference between the speed of tee and the speed of hole.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the value by which the hole's speed exceed that of the tee is
(d)
The distance to the west of the hole from the position where the ball lands.
Answer to Problem 47CP
The distance to the west of the hole from the position where the ball land is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the distance to west of the hole
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the distance to the west of the hole from the position where the ball land is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Bundle: Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Volume 2, Loose-leaf Version, 10th + WebAssign Printed Access Card for Serway/Jewett's Physics for Scientists and Engineers, 10th, Multi-Term
- A sniper atop a building 150m high fired a bullet parallel to the horizontal with a speed of 1800km/h. Assuming that the bullet will hit its target, what would be the resulting range?arrow_forwardA daredevil drove his motorcycle up an incline at 30 degree angle with the horizontal and got air borne at the end of the incline at 20 m/s, 11 m above the ground. How far horizontally did he land with his motorcycle on the ground, on a safety net?arrow_forwardA plane that is capable of travelling at 140 m/s wishes to travel due north from City A to City B, 500 km away, but encounters a constant crosswind that blows 25 m/s due west. What must the plane’s heading be in order to reach its destination? Suppose the pilot has no navigational expertise and decides to aim straight for City B. How far west of City B will the plane end up?arrow_forward
- In the figure, a ball is launched with a velocity of magnitude 7.00 m/s, at an angle of 41.0° to the horizontal. The launch point is at the base of a ramp of horizontal length d1 = 6.00 m and height d2 = 3.60 m. A plateau is located at the top of the ramp. Does the ball land on the ramp or the plateau? When it lands, what are the magnitude and angle of its displacement from the launch point?arrow_forwardIn the figure, a ball is launched with a velocity of magnitude 6.00 m/s, at an angle of 44.0° to the horizontal. The launch point is at the base of a ramp of horizontal length d1 = 6.00 m and height d2 = 3.60 m. A plateau is located at the top of the ramp. (a) Does the ball land on the ramp or the plateau? When it lands, what are the (b) magnitude and (c) angle of its displacement from the launch point?arrow_forwarda projectile is fired from the ground with an initial velocity of 250m/s at an angle of 60 degrees above the horizontalarrow_forward
- An enemy ship is on the east side of a mountain island, as shown in the figure. The enemy ship has maneuvered to within d1 = 2077 m of the h = 1940 m high mountain peak and can shoot projectiles with an initial speed of vi = 244 m/s. If the western shoreline is horizontally d2 = 273 m from the peak, what are the distances from the western shore at which a ship can be safe from the bombardment of the enemy ship?arrow_forwardA tennis ball is struck with an initial velocity of 30 m/s, 28 degrees above the horizontal.How long will it take to travel 25 feet, horizontally, independent of its vertical motion?arrow_forwardAn NFL quarterback throws a pass, for which the launch angle is 29 degrees above horizontal, with an initial speed of 13.9 m/s, and the ball is caught at the same height at which is was released. How far horizontally does the ball travel, in meters, while it is in flight?arrow_forward
- A football game begins with a kickoff in which the ball travels a horizontal distance of 37 m(approximately 40 yd) and lands at the same level from which it was kicked. If the ball waskicked at an angle of 44 ° above the horizontal, what was its initial speed?arrow_forwardA projectile is fired from the edge of a 180-m cliff with an initial velocity of 150 m/s at an angle of 30° with the horizontal. Neglecting air resistance, find the horizontal distance from the gun to the point where the projectile strikes the ground. 3100 m 2260 m 3160 m 2200 marrow_forwardA cannon launches a cannonball from level ground with an initial speed of 80 m/s at an angle of 280 above the horizontal. What horizontal distance does the cannonball travel when the cannonball returns to the ground? Given the same initial velocity of launch, at what other angle above the ground can the cannonball be fired and achieve the same horizontal range as before? (Assume that g = 9.81 m/s2.) a. Range = 540 m, and angle = 420 above the horizontal b. Range = 600 m, and angle = 620 above the horizontal c. Range = 270 m, and angle = 620 above the horizontal d. Range = 540 m, and angle = 620 above the horizontal e. Range = 270 m, angle = 420 above the horizontalarrow_forward
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
