
Concept explainers
Calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold for four inventory methods (LO6–3)
PROBLEMS: SET B
Jimmie’s Fishing Hole has the following transactions related to its top-selling Shimano fishing reel for the month of June:
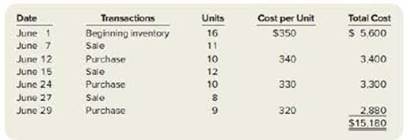
Requited:
1. Calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at June 30, using the specific identification method The June 7 sale consists of fishing reels from beginning inventory, the June 15 sale consists of three fishing reels from beginning inventory and nine fishing reels from the June 12 purchase, and the June 27 sale consists of one fishing reel from beginning inventory and seven fishing reels from the June 21 purchase.
2. Using FIFO, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at June 30.
3. Using LIFO, calculate ending inventory arid cost of goods sold at June 30.
4. Using weighted average cost, calculate ending inventory and cost of goods sold at June 30.
1.
To Compute: The ending inventory and cost of goods sold using the specific identification method.
Explanation of Solution
Specific identification method:
Specific identification method is a method in which the company records each item of the inventory at its original cost. Under this method, when the goods are sold, the company can easily identify the original costs at which they were purchased for. This method helps in arriving at the accurate cost of goods sold, and ending inventory.
Calculate the units of ending inventory.
|
Calculation of Ending Inventory | |||
| Details | Number of Units | Rate Per Unit ($) | Total Cost ($) |
| Beginning balance | 16 | ||
| Less: Sales – June 7 | (11) | ||
| Less: sales– June 15 | (3) | ||
| Less: Sales –June 27 | (1) | ||
| Balance | 1 | 350 | 350 |
| Purchases: | |||
| June 12 | 10 | ||
| Less: Sales – June 15 | (9) | ||
| Balance | 1 | 340 | 340 |
| Purchases: | |||
| June 24 | 10 | ||
| Less: October 28 | (7) | - | |
|
Balance |
3 |
330 | 990 |
|
June 29 |
9 |
320 |
2,880 |
|
Ending Inventory |
14 | 45,650 | |
Table (1)
Therefore, the cost of Ending Inventory in specific identification method is $45,650.
Calculate the cost of goods sold:
| Calculation of Cost of Goods Sold | |||
| Details | Number of Units | Rate Per Unit ($) | Total Cost ($) |
| June 1: Beginning balance | 11 | 350 | 3,850 |
| June 1: Beginning balance | 3 | 350 | 1,050 |
| June 12: Purchase | 9 | 340 | 3,060 |
| June 1: Beginning balance | 1 | 350 | 350 |
| June 24: Purchase | 7 | 330 | 2,310 |
| Cost of Goods Sold | 31 | 10,620 | |
Table (2)
Therefore, the Cost of Goods Sold in specific identification method is $10,620.
2.
To Compute: The ending inventory and cost of goods sold using the FIFO method.
Explanation of Solution
First-in-First-Out:
In First-in-First-Out method, the costs of the initially purchased items are considered as cost of goods sold, for the items which are sold first. The value of the ending inventory consists of the recent purchased items.
Calculate the total Cost and units of Goods Available for Sales.
| Calculation of Goods Available for Sales | |||
| Details | Number of Units | Rate per unit ($) | Total Cost ($) |
| Beginning balance | 16 | 350 | 5,600 |
| Add: Purchases | |||
| June 12 | 10 | 340 | 3,400 |
| June 24 | 10 | 330 | 3,300 |
| June 29 | 9 | 320 | 2,880 |
|
Total Goods available for Sale |
45 |
15,180 | |
Table (3)
Calculate the units of ending inventory.
| Calculation of Ending Inventory (Units) | ||
| Details | Number of Units | Number of Units |
| Beginning balance | 16 | |
| Add: Purchases | ||
| June 12 | 10 | |
| June 24 | 10 | |
| June 29 | 9 | |
| Total Goods available for Sale | 45 | |
| Less: Sales | ||
| June 7 | 11 | |
| June 15 | 12 | |
| June 27 | 8 | |
| Total Sales | (31) | |
| Ending Inventory | 14 | |
Table (4)
Calculate the cost of ending inventory.
The ending inventory is 14 units.
| Calculation of Cost of Ending Inventory | |||
| Details | Number of Units | Rate per Unit ($) | Total Cost ($) |
| June 24 | 5 | 330 | 1,650 |
| June 29 | 9 | 320 | 2,880 |
| Ending Inventory | 14 | 4,530 | |
Table (5)
In FIFO method the ending inventory comprises of the inventory purchased last, because the inventory purchased first were sold first.
Therefore, the cost of Ending Inventory in the FIFO is $4,530.
Cost of Goods Sold.
31 units are sold.
| Calculation of Cost of Goods Sold | |||
| Details | Number of Units | Rate per Unit ($) | Total Cost ($) |
| Beginning Inventory | 16 | 350 | 5,600 |
| June 12 | 10 | 340 | 3,400 |
| June 24 | 5 | 330 | 1,650 |
| Cost of Goods Sold |
31 |
10,650 | |
Table (6)
As it is FIFO method the earlier purchased items will sell first.
Therefore, the Cost of Goods Sold in the FIFO Method is $10,650.
3.
To Compute: The ending inventory and cost of goods sold using the LIFO method.
Explanation of Solution
Last-in-Last-Out:
In Last-in-First-Out method, the costs of last purchased items are considered as the cost of goods sold, for the items which are sold first. The value of the closing stock consists of the initial purchased items.
Ending Inventory:
Calculate the cost of ending inventory.
| Calculation of Cost of Ending Inventory | |||
| Details | Number of Units | Rate per Unit ($) | Total Cost ($) |
| Beginning Inventory | 14 | 350 | 4,900 |
| Ending Inventory | 14 | 350 | 4,900 |
Table (7)
- The ending inventory is 14 units (Refer to Table 4).
- In LIFO method, the ending inventory comprises of the inventory purchased first, because the inventory purchased last were sold first.
- Therefore, the ending inventory of 8 units is from the beginning inventory.
Therefore, the cost of Ending Inventory in the LIFO method is $4,900.
Cost of Goods Sold:
| Details | Number of Units | Rate per unit ($) | Total Cost ($) |
| Beginning Inventory | 2 | 350 | 700 |
| June 12 Purchase | 10 | 340 | 3,400 |
| June 24 Purchase | 10 | 330 | 3,300 |
| June 29 Purchase | 9 | 320 | 2,880 |
| Cost of Goods Sold |
31 |
10,280 |
Table (8)
- 31 units are sold (Refer to Table 4).
- As it is LIFO method the recent purchased items will sell first.
- Hence, the cost of goods sold will be the recent purchased items.
Therefore, the Cost of Goods Sold in the LIFO Method is $10,280.
4.
To Compute: The ending inventory and cost of goods sold using the Weighted-average method.
Explanation of Solution
Weighted-average cost method:
Under Weighted average cost method, the company calculates a new average cost after every purchase is made. It is determined by dividing the cost of goods available for sale by the units on hand.
Calculate the Weighted-average cost.
Total cost of goods available for sale = $15,180 (Refer to table - 3)
Total units of goods available for sale = 45 units (Refer to table - 3)
Calculate the amount of Ending Inventory.
Weighted- average cost per unit = $337.3333 (1)
Number of units in ending inventory = 14 units (Refer to table - 4)
Therefore, the cost of Ending Inventory in the Weighted-average-cost Method is $4,722.6.
Calculate the Cost of Goods Sold.
Weighted- average cost per unit= $337.3333 (1)
Units sold = 31 units
Therefore, the Cost of goods sold in the Weighted-average-cost Method is $10,457.33.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
FINANCIAL ACCT LL W/ACCESS
- Refer to the information in E22-13. Required: Prepare the correcting journal entries if the company discovers each error 2 years after it is made and it has closed the books for the second year. Ignore income taxes. E22-13: The following are independent errors made by a company that uses the periodic inventory system: a. Goods in transit, purchased on credit and shipped FOB destination, 10,000, were included in purchases but not in the physical count of ending inventory. b. Purchase of a machine for 2,000 was expensed. The machine has a 4-vear life, no residual value, and straight-line depreciation is used. c. Wages payable of 2,000 were not accrued. d. Payment of next years rent, 4,000, was recorded as rent expense. e. Allowance for doubtful accounts of 5,000 was not recorded. The company normally uses the aging method. f. Equipment with a book value of 70,000 and a fair value of 100,000 was sold at the beginning of the year. A 2-year, non-interest-bearing note for 129,960 was received and recorded at its face value, and a gain of 59,960 was recognized. No interest revenue was recorded and 14% is a fair rate of interest.arrow_forwardRefer to the information for Morgan Inc. above. If Morgan uses a perpetual inventory system, what is the cost of ending inventory under FIFO at April 30? a. $32,500 b. $38,400 c. $63,600 d. $69,500arrow_forwardCompany Edgar reported the following cost of goods sold but later realized that an error had been made in ending inventory for year 2021. The correct inventory amount for 2021 was 12,000. Once the error is corrected, (a) how much is the restated cost of goods sold for 2021? and (b) how much is the restated cost of goods sold for 2022?arrow_forward
- Company Elmira reported the following cost of goods sold but later realized that an error had been made in ending inventory for year 2021. The correct inventory amount for 2021 was 32,000. Once the error is corrected, (a) how much is the restated cost of goods sold for 2021? and (b) how much is the restated cost of goods sold for 2022?arrow_forward( Appendix 6B) Refer to the information for Morgan Inc. above. If Morgan uses a periodic inventory system, what is the cost of ending inventory under LIFO at April 30? a. $32,800 b. $38,400 c. $63,600 d. $69,200arrow_forwardRE7-8 Johnson Company uses a perpetual inventory system. On October 23, Johnson purchased 100,000 of inventory on credit with payment terms of 1/15, net 45. Using the net price method, prepare journal entries to record Johnsons purchases on October 23 and the subsequent payment on October 31. Using the information from RE7-8, prepare journal entries to record Johnsons purchase on October 23 and the subsequent payment on November 30.arrow_forward
- The following are independent errors made by a company that uses the periodic inventory system: a. Goods in transit, purchased on credit and shipped FOB destination, 10,000, were included in purchases but not in the physical count of ending inventory. b. Purchase of a machine for 2,000 was expensed. The machine has a 4-year life, no residual value, and straight-line depreciation is used. c. Wages payable of 2,000 were not accrued. d. Payment of next years rent, 4,000, was recorded as rent expense. e. Allowance for doubtful accounts of 5,000 was not recorded. The company normally uses the aging method. f. Equipment with a book value of 70,000 and a fair value of 100,000 was sold at the beginning of the year. A 2-year, non-interest-bearing note for 129,960 was received and recorded at its face value, and a gain of 59,960 was recognized. No interest revenue was recorded and 14% is a fair rate of interest. Required: 1. Next Level Indicate the effect of each of the preceding errors on the companys assets, liabilities, shareholders equity, and net income in the year in which the error occurs. State whether the error causes an overstatement (+), an understatement (), or no effect (NE). 2. Prepare the correcting journal entry or entries required at the beginning of the year for each of the preceding errors, assuming the company discovers the error in the year after it was made. Ignore income taxes.arrow_forwardInventory by three cost flow methods Details regarding the inventory of appliances on January 1, 20Y7, purchases invoices during the year, and the inventory count on December 31. 2O’7. of Amsterdam Appliances are summarized as follows: Instructions Discuss which method (FIFO or LIFO) would be preferred for income tax purposes in periods of (a) rising prices and (b) declining prices.arrow_forwardWebster Company adopted do liar-value LIFO on January 1, 2019. Webster produces three products: X, Y, and Z. Websters beginning inventory consisted of the following: During 2019, Webster had the following purchases and sales: Required: 1. Compute the LIFO cost of the ending inventory assuming Webster uses a single inventory pool. Round cost index to 4 decimal places. 2. Compute the LIFO cost of the ending inventory assuming Webster uses three inventory pools. Round cost indexes to 4 decimal places.arrow_forward
- louie company sells Astro's photocards for P30 each. the following was taken from the inventory records during march: date photocard units cost march 03 purchase 500 P15 march10 sale 300 17 purchase 1000 P17 20 sale 600 23 sale 300 30 purchase 1000 P20 1. Determine the cost of sales and cost of ending inventory using First-in-First-out Method (Periodic) 2.Determine the cost of sales and cost of ending inventory using Weighted Average Method 3. Determine the cost of sales and cost of ending inventory using Moving Average Methodarrow_forwardE5-4 On June 10, Diaz Company purchased $8,000 of merchandise from Taylor Company, FOB shipping point, terms 2/10, n/30. Diaz pays the freight costs of $400 on June 11. Dam- aged goods totaling $300 are returned to Taylor for credit on June 12. The fair value of these goods is $70. On June 19, Diaz pays Taylor Company in full, less the purchase dis- count. Both companies use a perpetual inventory system. Instructions (a) Prepare separate entries for each transaction on the books of Diaz Company. (b) Prepare separate entries for each transaction for Taylor Company. The merchandise purchased by Diaz on June 10 had cost Taylor $4,800. E5-5 Presented below are transactions related to R. Humphrey Company. 1. On December 3, R. Humphrey Company sold $570,000 of merchandise to Frazier Co., terms 1/10, n/30, FOB destination. R. Humphrey paid $400 for freight charges. The cost of the merchandise sold was $350,000. 2. On December 8, Frazier Co. was granted an allowance of $20,000 for merchandise…arrow_forward
 Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Survey of Accounting (Accounting I)AccountingISBN:9781305961883Author:Carl WarrenPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College





