
Concept explainers
a.
To draw: Isoquants at output of 1000 boxes of puffed rice per hour.
a.
Explanation of Solution
The given production function is given by
Where K is the number of puffing guns used and L is the number of workers hired each hour.
When q is 1000, the value of
The isoquant shall be made by joining the points which provide answer to such function, this shall, random numbers can be taken for K, to calculate the value of L.
| Value of K | Calculation | Value of L |
| 10 | 10 | |
| 25 | 4 | |
| 4 | 25 |
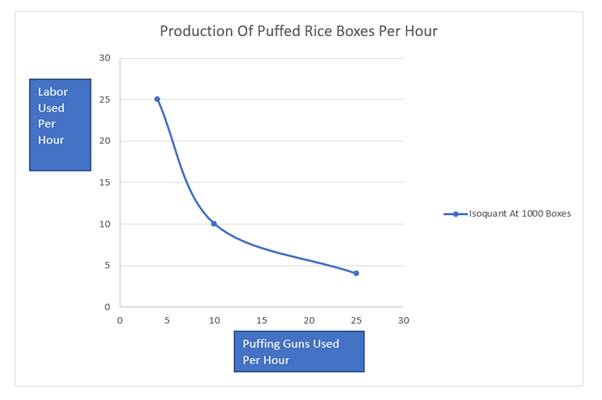
Introduction: Isoquants are
b.
To calculate: Value of L when K is 10 and average labor productivity.
b.
Explanation of Solution
The given production function is given by
Where K is the number of puffing guns used and L is the number of workers hired each hour.
When q is 1000, the value of
Therefore, when the value of K is 10, the value of L must be
In other words, when 10 puffing guns are employed, 10 workers must work each hour to produce 1000 boxes of puffed rice.
Introduction: For any given value of labor (L) or capital (K), one can be calculated from the other by inputting the available value in the production function.
Average productivity refers to the arithmetic mean of total production with total labor input employed.
c.
To state: Impact of technical progress on sub-part (a) and (b).
c.
Explanation of Solution
The new production function is given by
Where K is the number of puffing guns used and L is the number of workers hired each hour.
When q is 1000, the value of
The isoquant shall be made by joining the points which provide answer to such function, this shall, random numbers can be taken for K, to calculate the value of L.
| Value of K | Calculation | Value of L |
| 2 | 12.5 | |
| 5 | 5 | |
| 10 | 2.5 | |
| 12.5 | 2 |
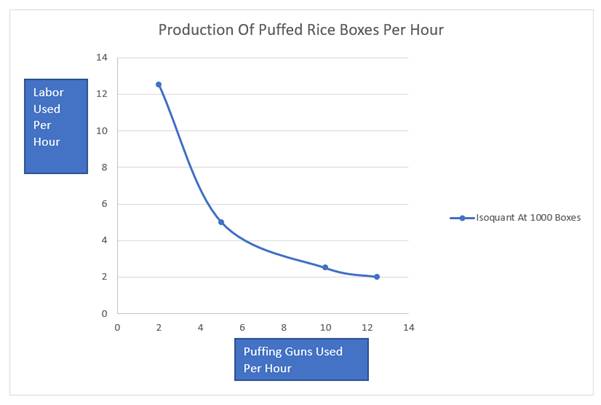
As stated in sub part (b), value of one variable may be calculated by inputting the other in production function, therefore, when the value of K is 10, L shall be
Introduction: Isoquants are curves that represent same level of output at various combination of inputs and are used in determining efficient input mix for lower operational costs.
Average productivity refers to the arithmetic mean of total production with total labor input employed.
d.
To state: Impact of technical progress on sub-part (a) and (b).
d.
Explanation of Solution
The new production function is given by
Where K is the number of puffing guns used and L is the number of workers hired each hour.
The value of
Separate isoquants will be observed every year since the input required to produce the desired output of 1000 boxes would undergo shift.
When q is 1000, the value of
In order to plot the isoquants, arbitrary value of one variable can be taken to find the other variable.
| Year | Required K x L |
| 1 |
|
| 2 |
|
| 3 |
|
The isoquant shall be made by joining the points which provide answer to such function, this shall, random numbers can be taken for K, to calculate the value of L.
Using ‘1’, ‘2’ and ‘3’ to denote the years values for K and L at various levels shall be as follow:
| K1 | L 1 | K2 | L 2 | K3 | L 3 |
| 5.00 | 18.14 | 5.00 | 16.45 | 5.00 | 14.92 |
| 10.00 | 9.07 | 10.00 | 8.23 | 10.00 | 7.46 |
| 15.00 | 6.05 | 15.00 | 5.48 | 15.00 | 4.97 |
Isoquants can be drawn based on the calculated data as:
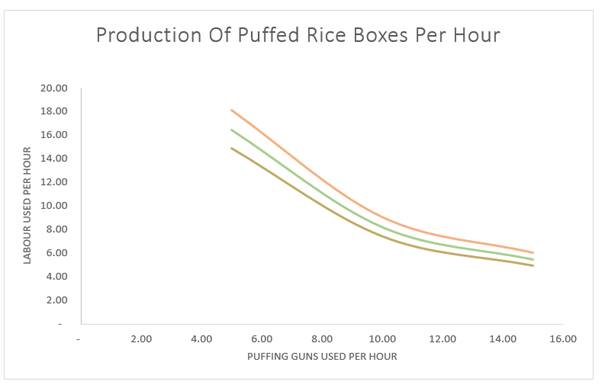
As stated in sub part (b), value of one variable may be calculated by inputting the other in production function, therefore, when the value of K is 10, L shall be
Since technical progress is constant year on year, average productivity per hour will increase year on year as well.
Introduction: Isoquants are curves that represent same level of output at various combination of inputs and are used in determining efficient input mix for lower operational costs.
Average productivity refers to the arithmetic mean of total production with total labor input employed.
Technical progress refers to increase the productivity factor, thereby increasing the production with same available inputs.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
EBK INTERMEDIATE MICROECONOMICS AND ITS
 Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an...EconomicsISBN:9781305506381Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. HarrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: Applications, Strategies an...EconomicsISBN:9781305506381Author:James R. McGuigan, R. Charles Moyer, Frederick H.deB. HarrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Microeconomics: Principles & PolicyEconomicsISBN:9781337794992Author:William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. SolowPublisher:Cengage Learning
Microeconomics: Principles & PolicyEconomicsISBN:9781337794992Author:William J. Baumol, Alan S. Blinder, John L. SolowPublisher:Cengage Learning






