
Concept explainers
(a)
Calculate
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Straight-line method: Under the straight-line method of depreciation, the same amount of depreciation is allocated every year over the estimated useful life of an asset. The following is the formula to calculate the depreciation.
Determine depreciation expense, accumulated depreciation, and book value at the end of sixth year under straight line depreciation method.
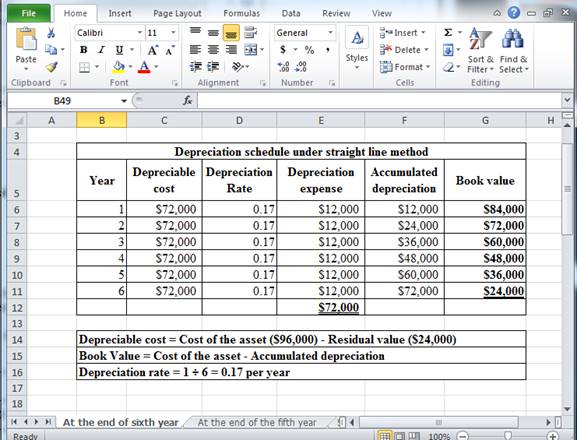
Table (1)
Hence, the depreciation expense, accumulated depreciation, and book value at the end of the sixth year, under straight line method are $12,000, $72,000 and $24,000 respectively.
Record the adjusting entry for depreciation expense at the end of the third year under straight line depreciation method.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Depreciation expense – Equipment (Refer table (1)) | 12,000 | |||
| Accumulated depreciation -Equipment | 12,000 | |||
| (To record the depreciation expense) |
Table (2)
To record the adjusting entry for depreciation expense at the end of the third year:
- Depreciation expense is an expense (decreases the
stockholders’ equity ) and it is increased by $12,000. Therefore, debit depreciation account with $12,000. - Accumulated depreciation is a contra-asset. Increase in the accumulated depreciation account decreases the related asset account. Therefore, credit accumulated depreciation account with $12,000.
Working Note:
The above calculation is computed using spreadsheet as follows:
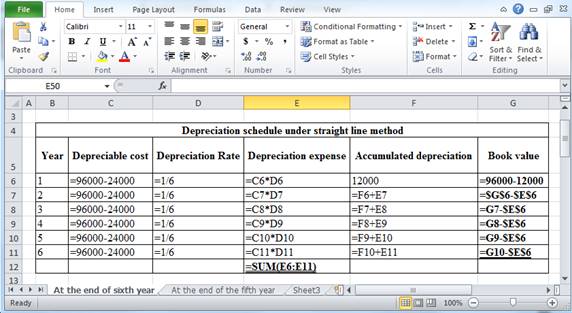
Table (3)
(b)
Calculate depreciation expense, accumulated depreciation, and book value for each of the six years using double-declining-balance method and record the adjusting entry for depreciation expense at the end of the third year under each method.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Double-declining-balance method: The depreciation method which assumes that the consumption of economic benefits of long-term asset is high in the early years but gradually declines towards the end of its useful life is referred to as double-declining-balance method.
Determine depreciation expense, accumulated depreciation, and book value at the end of sixth year under double declining balance method.
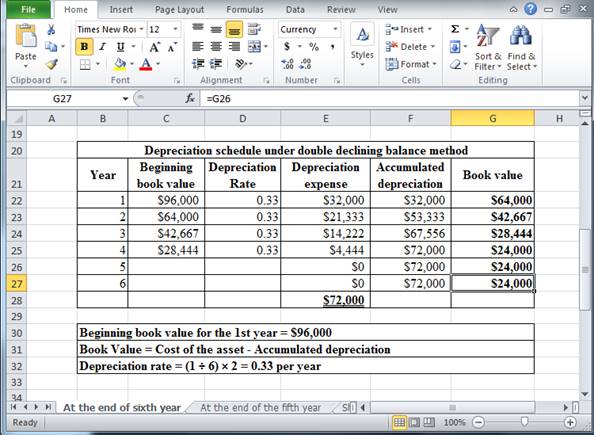
Table (4)
Hence, the depreciation expense, accumulated depreciation, and book value at the end of the sixth year, under double declining balance method are $0, $72,000 and $24,000 respectively.
Record the adjusting entry for depreciation expense at the end of the third year under double declining balance method.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Depreciation expense – Equipment (Refer table (4)) | 14,222 | |||
| Accumulated depreciation -Equipment | 14,222 | |||
| (To record the depreciation expense) |
Table (5)
To record the adjusting entry for depreciation expense at the end of the third year:
- Depreciation expense is an expense (decreases the stockholders’ equity) and it is increased by $14,222. Therefore, debit depreciation account with $14,222.
- Accumulated depreciation is a contra-asset. Increase in the accumulated depreciation account decreases the related asset account. Therefore, credit accumulated depreciation account with $14,222.
Working Note:
The above calculation is computed using spreadsheet as follows:
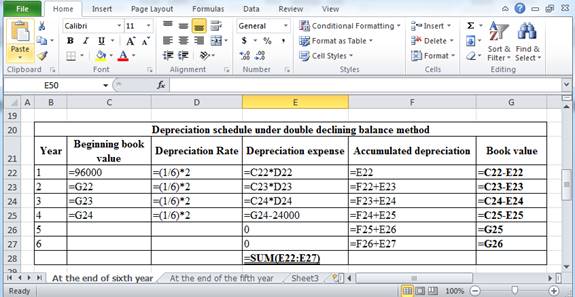
Table (6)
(c)
Calculate depreciation expense, accumulated depreciation, and book value for each of the six years using activity-based method and record the adjusting entry for depreciation expense at the end of the third year under each method.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Activity based method: In this method of depreciation, the amount of depreciation is charged based on the units of production each year.
Determine depreciation expense, accumulated depreciation, and book value at the end of sixth year under activity based method.
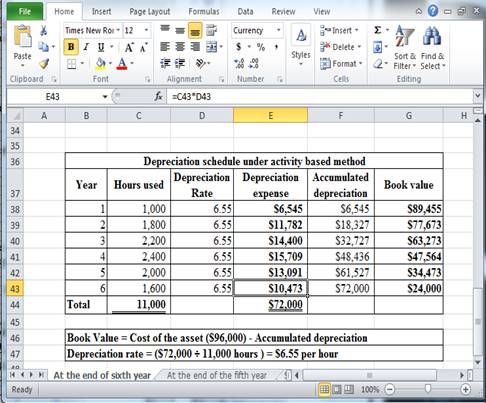
Table (7)
Hence, the depreciation expense, accumulated depreciation, and book value at the end of the sixth year, under activity based method are $10,473, $72,000 and $24,000 respectively.
Record the adjusting entry for depreciation expense at the end of the third year under activity based method.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Depreciation expense – Equipment (Refer table (7)) | 14,400 | |||
| Accumulated depreciation -Equipment | 14,400 | |||
| (To record the depreciation expense) |
Table (8)
To record the adjusting entry for depreciation expense at the end of the third year:
- Depreciation expense is an expense (decreases the stockholders’ equity) and it is increased by $14,400. Therefore, debit depreciation account with $14,400.
- Accumulated depreciation is a contra-asset. Increase in the accumulated depreciation account decreases the related asset account. Therefore, credit accumulated depreciation account with $14,400.
Working Note:
The above calculation is computed using spreadsheet as follows:
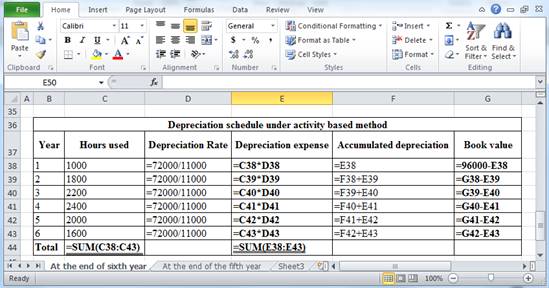
Table (9)
Calculate depreciation expense, accumulated depreciation, and book value for each of the fifth years using (a) straight-Line, (b) double-declining-balance, and (c) activity-based if the company had initially estimated the residual value to be $16,000 and the useful life to be five years.
Explanation of Solution
(a)
Straight-line method: Under the straight-line method of depreciation, the same amount of depreciation is allocated every year over the estimated useful life of an asset. The following is the formula to calculate the depreciation.
Determine depreciation expense, accumulated depreciation, and book value at the end of sixth year under straight line depreciation method.
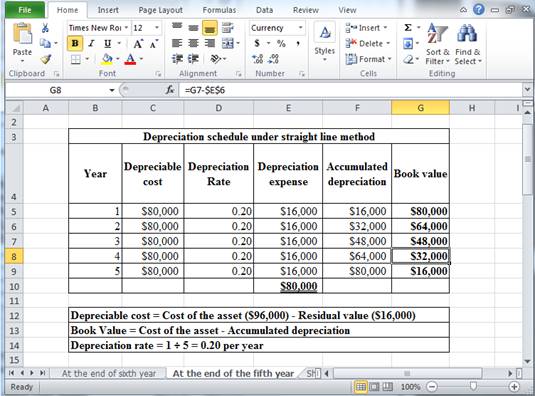
Table (10)
Hence, the depreciation expense, accumulated depreciation, and book value at the end of the sixth year, under straight line method are $16,000, $80,000 and $16,000 respectively.
Record the adjusting entry for depreciation expense at the end of the third year under straight line depreciation method.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Depreciation expense – Equipment (Refer table (10)) | 16,000 | |||
| Accumulated depreciation -Equipment | 16,000 | |||
| (To record the depreciation expense) |
Table (11)
To record the adjusting entry for depreciation expense at the end of the third year:
- Depreciation expense is an expense (decreases the stockholders’ equity) and it is increased by $16,000. Therefore, debit depreciation account with $16,000.
- Accumulated depreciation is a contra-asset. Increase in the accumulated depreciation account decreases the related asset account. Therefore, credit accumulated depreciation account with $16,000.
Working Note:
The above calculation is computed using spreadsheet as follows:
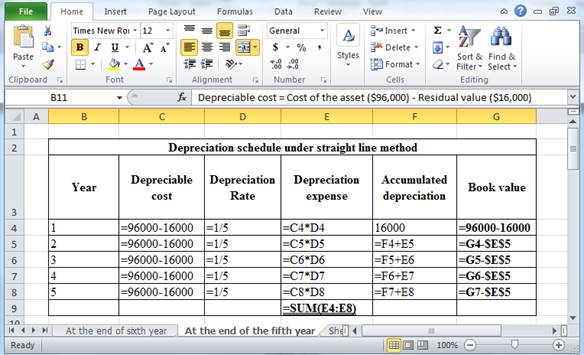
Table (12)
(b)
Double-declining-balance method: The depreciation method which assumes that the consumption of economic benefits of long-term asset is high in the early years but gradually declines towards the end of its useful life is referred to as double-declining-balance method.
Determine depreciation expense, accumulated depreciation, and book value at the end of sixth year under double declining balance method.
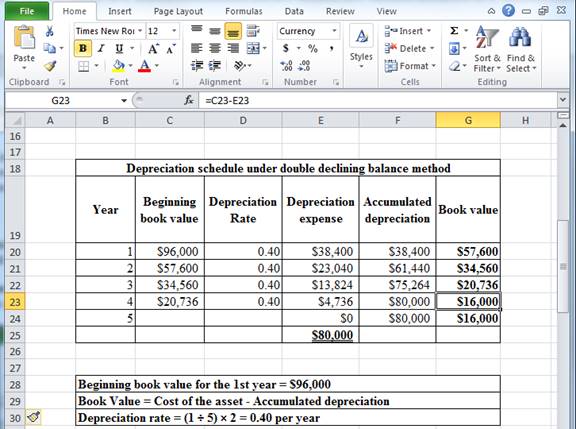
Table (13)
Hence, the depreciation expense, accumulated depreciation, and book value at the end of the fifth year, under s double declining balance method are $0, $80,000 and $16,000 respectively.
Record the adjusting entry for depreciation expense at the end of the third year under double declining balance method.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Depreciation expense – Equipment (Refer table (13)) | 13,824 | |||
| Accumulated depreciation -Equipment | 13,824 | |||
| (To record the depreciation expense) |
Table (14)
To record the adjusting entry for depreciation expense at the end of the third year:
- Depreciation expense is an expense (decreases the stockholders’ equity) and it is increased by $13,824. Therefore, debit depreciation account with $13,824.
- Accumulated depreciation is a contra-asset. Increase in the accumulated depreciation account decreases the related asset account. Therefore, credit accumulated depreciation account with $13,824.
Working Note:
The above calculation is computed using spreadsheet as follows:
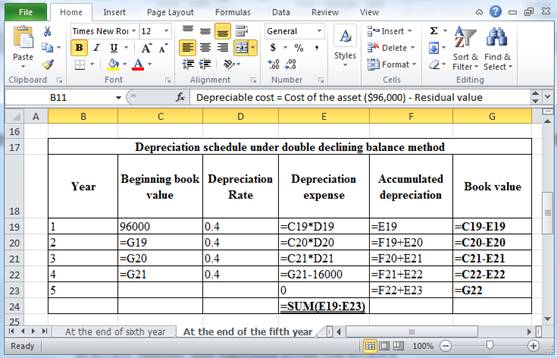
Table (15)
(c)
Activity based method: In this method of depreciation, the amount of depreciation is charged based on the units of production each year.
Determine depreciation expense, accumulated depreciation, and book value at the end of sixth year under activity based method.
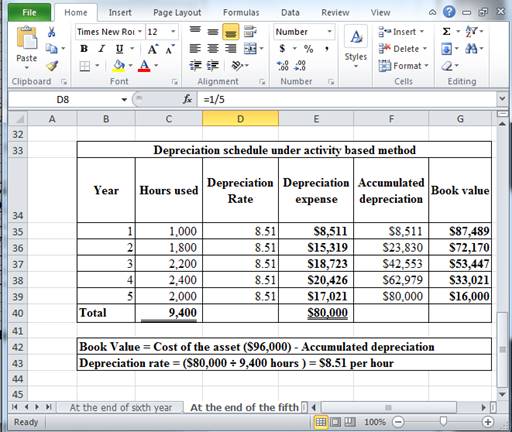
Table (16)
Hence, the depreciation expense, accumulated depreciation, and book value at the end of the fifth year, under activity based method are $17,021, $80,000 and $16,000 respectively.
Record the adjusting entry for depreciation expense at the end of the third year under activity based method.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Depreciation expense – Equipment (Refer table (16)) | 18,723 | |||
| Accumulated depreciation -Equipment | 18,723 | |||
| (To record the depreciation expense) |
Table (17)
To record the adjusting entry for depreciation expense at the end of the third year:
- Depreciation expense is an expense (decreases the stockholders’ equity) and it is increased by $18,723. Therefore, debit depreciation account with $18,723.
- Accumulated depreciation is a contra-asset. Increase in the accumulated depreciation account decreases the related asset account. Therefore, credit accumulated depreciation account with $18,723.
Working Note:
The above calculation is computed using spreadsheet as follows:
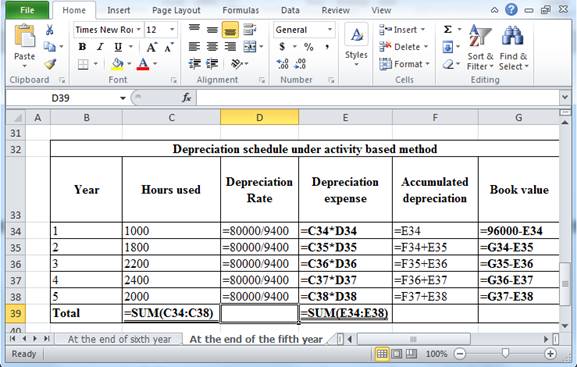
Table (18)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Financial Accounting (Connect NOT Included)

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





