
Concept explainers
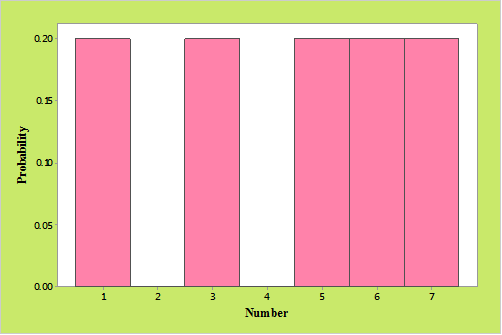
A population consists of
a. Construct a probability histogram for this population.
b. Use the random number table. Table 10 in Appendix I, to select a random sample of size
(HINT: Assign the random digits 0 and 1 to the measurement
c. To simulate the sampling distribution of
a.
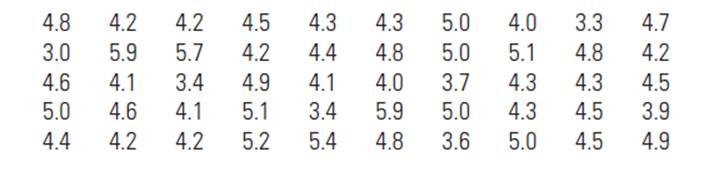
To graph: A probability histogram for the data.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The given population contain
The population mean
Calculation:
Here there are five numbers without repeating therefore the probability of each number to be equal. Hence the probability for a number is
Graph:
In the below histogram height of the bars equal to the probability.
b.
To find: The two sets of samples of size
Answer to Problem 7.17E
The first selected sample is
The second selected sample is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The random digits
Formula used:
where,
Calculation:
If select the first digit of the second column from the Table
Therefore the first selected sample is
Hence the sample mean
If select the second digit of the third column from the Table
Therefore the second selected sample is
Hence the sample mean
c.
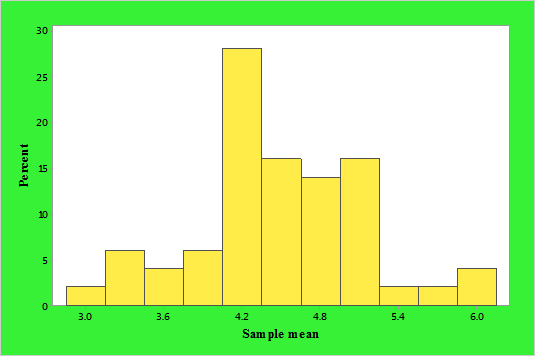
To graph: A probability histogram for the data.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The below is the sample means of
Calculation:
Let the class intervals as
The probability is the frequency divided by the total number of samples.
The below table gives the probability for each class.
Graph:
Below is the histogram of sample means, the vertical axis represents the percentage and the horizontal axis represents the midpoints of the sample mean classes.
Interpretation:
From the above histogram, it can say that the distribution of the sample means is approximately mound-shaped.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
EBK INTRODUCTION TO PROBABILITY AND STA
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
