
1.
Describe the classifications of long-lived assets and to explain their differences.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Long-lived assets:
Long-lived assetsrefer to the fixed assets, having a useful life of more than a year that is acquired by a company to be used in its business activities, for generating revenue.
Classifications of Long-lived Assets:
The two major classifications of long-lived assets are as follows:
- Tangible assets
- Intangible assets
Difference between tangible assets and intangible assets:
Tangible Assets:
Tangible assets are the long-term assets used by the company, which have physical existence, and can be seen, touched and felt. Some of the examples of the tangible assets include plant, property, land, and building.
Intangible Assets:
Intangible assets are the long-term assets having no physical existence. However, the benefits provided by these assets are used by the company for a long period of time. These intangible assets represent rights. Some of the examples of the intangible assets include patent, trademark,
2.
Record the purchase and the subsequent payment made and to show their computations.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Journal entry is a set of economic events which can be measured in monetary terms. These are recorded chronologically and systematically.
Accounting rules for Journal entries:
- To record increase balance of account: Debit assets, expenses, losses and credit liabilities, capital, revenue and gains.
- To record decrease balance of account: Credit assets, expenses, losses and debit liabilities, capital, revenue and gains.
Journalize the transaction for the purchase of the equipment.
| Date | Account titles and explanation |
Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| June 1, 2013 | Equipment | 61,500 | ||
| Cash | 1,500 | |||
| Common stock | 4,000 | |||
| Additional paid-in capital | 8,000 | |||
| Note payable | 48,000 | |||
| (To record the purchase of equipment) |
Table (1)
Working Notes:
Computations required for recording the purchase of the machine:
Compute common stock value.
Compute the additional paid-in capital.
Compute the note payable.
Compute the cost of the equipment:
- Equipment is an asset account and the amount has increased because equipment (plant asset) is purchased; therefore, debit Equipment account.
- Cash is an asset account. The amount has decreased because cash is paid for purchase of equipment. Therefore, credit cash account.
- Common Stock is a
stockholders’ equity account and the amount has increased due to the distribution of stock dividends. Therefore, credit common stock account. - Additional paid-in capital is a component of stockholder’s equity and it has increased the value of stockholder’s equity. Hence, credit the additional paid-in capital.
- Note Payable is a liability account. Note is signed for the purchase of the machine. Therefore, credit note payable account.
Journalize the transaction for the subsequent payment made.
| Date | Account titles and explanation |
Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| September 2, 2013 | Note payable | 48,000 | ||
| Interest expense | 1,440 | |||
| Cash | 49,440 | |||
| (To record the subsequent payment made) |
Table (2)
Working Notes:
Computation required for recording the payment made on the machine:
Calculate the amount of interest expense.
- Note Payable is a liability account and it is decreased. Hence, debit the note payable account.
- Interest expense is an expense account and it is increased, which in turn has decreased the stockholder’s equity account. Hence, debit the interest expense account.
- Cash is an asset account, and it is decreased. Therefore, credit cash account.
3.
Indicate the accounts, amounts, and effects of the purchase and subsequent cash payment on the
3.
Explanation of Solution
Accounting equation is the mathematical representation of the relationship among the assets, liabilities, and stockholder’s equity at any given point of time. The components of the accounting equation include the assets, liabilities and stockholder’s Equity. In the accounting equation, the assets, which are placed on the left side of the equation, and the liabilities, and stockholder’s equity which are placed on the right side, must always balance. The accounting equation is as follows:
Indicate the accounts, amounts, and effects of purchase and subsequent cashpaymenton the accounting equation:
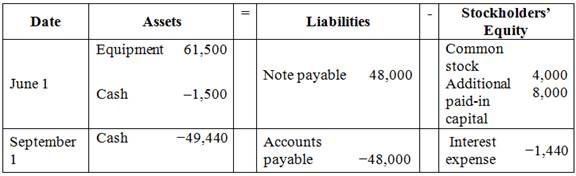
Figure (1)
- On 1st June, Corporation Wpurchased a machine for $61,500 and signed a note payable for $48,000. The payment was made by issuing common stock of $4,000, and additional paid-in capital was $8,000. Hence, this increases the assets (equipment) by $61,500, and liabilities (note payable) by $48,000 and increases the stockholder’s equity (common stock) by $4,000 and (additional paid-in capital) by $8,000. Cash payment on installation costs of the machine decreases the assets (cash) by $1,500.
- On 2nd September, Corporation W paid the balance due on the machine. This decreases the assets (cash) balance by $49,440 and liabilities (accounts payable) by $48,000 and stockholder’s equity (interest expense) by $1,440.
4.
Explain the basis which was used for any questionable items.
4.
Explanation of Solution
The basis which was used for the questionable items are as follows:
- Only installation costs are included in the cost of the machinery. The freight charges are not included in the cost of the machinery as it was paid by the vendor.
- Interest expense of $1,440 is the cost of financing. Hence, it should not be included in the cost of the machinery but it should be recorded as an interest expense.
- For the valuation of the common stock, the market price per share of $6 is used. That is, this amount of $6 is allocated between the common stock at the par value of $2 and additional paid-in capital account at the balance amount of $4.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Financial Accounting - With Access

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





