
Concept explainers
Write Lewis structures that obey the octet rule (duet rule for H) for each of the following molecules. Carbon is the central atom in CH4, nitrogen is the central atom in NH3, and oxygen is the central atom in H2O.
a. F2
b. O2
c. CO
d. CH4
e. NH3
f. H2O
g. HF
(a)
Interpretation: The Lewis structure is to be drawn for the given molecules.
Concept introduction: The Lewis structure is also known as dot structure. This structure depicts the bonding between atoms and the lone pairs of electrons if exists.
The octet rule states that atoms or molecules gain or lose electrons to get the electronic configuration of nearest noble gas.
To determine: The Lewis structure of the molecule
Answer to Problem 81E
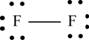
Explanation of Solution
The first step in determining the Lewis structure is to determine the number of valence electrons. The atomic number of fluorine
The valence electron of fluorine is 7
The fluorine molecule
The skeletal structure of
Each fluorine atom requires one electron to complete the octet. Hence, the mutual sharing of two electrons takes place. The 12 valence electrons present are placed as lone pairs in such a way that each atom gets three lone pairs.
The Lewis structure of
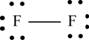
Figure 1
(b)
Interpretation: The Lewis structure is to be drawn for the given molecules.
Concept introduction: The Lewis structure is also known as dot structure. This structure depicts the bonding between atoms and the lone pairs of electrons if exists.
The octet rule states that atoms or molecules gain or lose electrons to get the electronic configuration of nearest noble gas.
To determine: The Lewis structure of the molecule
Answer to Problem 81E
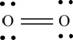
Explanation of Solution
The first step in determining the Lewis structure is to determine the number of valence electrons. The atomic number of oxygen
The valence electron of oxygen is 6
The oxygen molecule
The skeletal structure of
Each oxygen atom requires two electrons to complete the octet. Hence, the mutual sharing of four electrons takes place. The 8 valence electrons present are placed as lone pairs in such a way that each atom gets two lone pairs.
The Lewis structure of
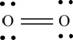
Figure 2
(c)
Interpretation: The Lewis structure is to be drawn for the given molecules.
Concept introduction: The Lewis structure is also known as dot structure. This structure depicts the bonding between atoms and the lone pairs of electrons if exists.
The octet rule states that atoms or molecules gain or lose electrons to get the electronic configuration of nearest noble gas.
To determine: The Lewis structure of the molecule
Answer to Problem 81E

Explanation of Solution
The first step in determining the Lewis structure is to determine the number of valence electrons. The atomic number of oxygen is 8 and its electronic configuration is,
The valence electron of oxygen is 6
The atomic number of carbon
The valence electron of carbon is 4
The molecule
The skeletal structure of
Each oxygen atom requires two electrons to complete the octet whereas carbon requires four electrons to complete the octet. Hence, the mutual sharing of six electrons takes place which is represented by triple bond. The 4 valence electrons left are placed as lone pairs in such a way that each atom gets one lone pair.
The Lewis structure of

Figure 3
(d)
Interpretation: The Lewis structure is to be drawn for the given molecules.
Concept introduction: The Lewis structure is also known as dot structure. This structure depicts the bonding between atoms and the lone pairs of electrons if exists.
The octet rule states that atoms or molecules gain or lose electrons to get the electronic configuration of nearest noble gas.
To determine: The Lewis structure of the molecule
Answer to Problem 81E
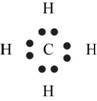
Explanation of Solution
The first step in determining the Lewis structure is to determine the number of valence electrons. The atomic number of carbon is 6 and its electronic configuration is,
The valence electron of carbon is 4
The atomic number of hydrogen
The valence electron of hydrogen is 1
The molecule
The skeletal structure of
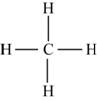
Figure 4
Each hydrogen atom requires one electron to complete the octet whereas carbon requires four electrons to complete the octet. In the molecule
The Lewis structure of

Figure 5
(e)
Interpretation: The Lewis structure is to be drawn for the given molecules.
Concept introduction: The Lewis structure is also known as dot structure. This structure depicts the bonding between atoms and the lone pairs of electrons if exists.
The octet rule states that atoms or molecules gain or lose electrons to get the electronic configuration of nearest noble gas.
To determine: The Lewis structure of the molecule
Answer to Problem 81E
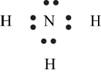
Explanation of Solution
The first step in determining the Lewis structure is to determine the number of valence electrons. The atomic number of nitrogen
The valence electron of nitrogen is 5
The atomic number of hydrogen is 1 and its electronic configuration is,
The valence electron of hydrogen is 1
The molecule
The skeletal structure of
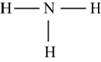
Figure 6
Each hydrogen atom requires one electron to complete the octet whereas nitrogen requires three electrons to complete the octet. In the molecule
The Lewis structure of

Figure 7
(f)
Interpretation: The Lewis structure is to be drawn for the given molecules.
Concept introduction: The Lewis structure is also known as dot structure. This structure depicts the bonding between atoms and the lone pairs of electrons if exists.
The octet rule states that atoms or molecules gain or lose electrons to get the electronic configuration of nearest noble gas.
To determine: The Lewis structure of the molecule
Answer to Problem 81E
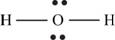
Explanation of Solution
The first step in determining the Lewis structure is to determine the number of valence electrons. The atomic number of oxygen is 8 and its electronic configuration is,
The valence electron of oxygen is 6
The atomic number of hydrogen is 1 and its electronic configuration is,
The valence electron of hydrogen is 1
The molecule
The skeletal structure of
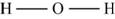
Figure 8
Each hydrogen atom requires one electron to complete the octet whereas oxygen requires two electrons to complete the octet. In the molecule
The Lewis structure of

Figure 9
(g)
Interpretation: The Lewis structure is to be drawn for the given molecules.
Concept introduction: The Lewis structure is also known as dot structure. This structure depicts the bonding between atoms and the lone pairs of electrons if exists.
The octet rule states that atoms or molecules gain or lose electrons to get the electronic configuration of nearest noble gas.
To determine: The Lewis structure of the molecule
Answer to Problem 81E
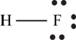
Explanation of Solution
The first step in determining the Lewis structure is to determine the number of valence electrons. The atomic number of fluorine is 9 and its electronic configuration is,
The valence electron of fluorine is 7
The atomic number of hydrogen is 1 and its electronic configuration is,
The valence electron of hydrogen is 1
The molecule
The skeletal structure of
Each hydrogen atom requires one electron to complete the octet whereas fluorine requires one electron to complete the octet. Hence, the mutual sharing of eight electrons takes place.
The Lewis structure of
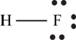
Figure 10
The Lewis dot structure is drawn to satisfy the octets of atoms. The octet rule states that elements gain or lose electrons to get the nearest noble gas configuration.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Chemistry
- What is meant by a chemical bond? Why do atoms form bonds with each other? Why do some elements exist as molecules in nature instead of as free atoms?arrow_forwardWrite Lewis structures for the following: (a) ClF3 (b) PCl5 (c) BF3 (d) PF6arrow_forwardG. N. Lewis developed a model for chemical bonding that you have learned in this chapter. His theory was extremely successful and is used today at all levels of chemistry, from the introductory class to the research laboratory. Why was Lewis theory so successful?arrow_forward
- Lewis structures can be used to understand why some molecules react in certain ways. Write the Lewis structures for the reactants and products in the reactions described below. a. Nitrogen dioxide dimerizes to produce dinitrogen tetroxide. b. Boron trihydride accepts a pair of electrons from ammonia, forming BH3NH3. Give a possible explanation for why these two reactions occur.arrow_forwardWrite Lewis structures that obey the octet rule for each of the following molecules. a. CCl4 b. NCl3 c. SeCl2 d. ICl In each case, the atom listed first is the central atom.arrow_forwardWrite Lewis structures that obey the octet rule for each of the following molecules and ions. (In each case the first atom listed is the central atom.) a. POCl3, SO42-, XeO4, PO43-, ClO4- b. NF3, SO32-, PO33-.Cl3- c. ClO2-, SCl2, PCl2- d. Considering your answers to part a, b, and c, what conclusions can you draw concerning the structures of species containing the same number of atoms and the same number of valence electrons?arrow_forward
- Lewis structure of NI3. Any polar bonds? Polar or non polar?arrow_forwardIn the vapor phase, BeCl2 exists as a discrete molecule. (a) Draw the Lewis structure of this molecule, using only single bonds. Does this Lewis structure satisfy the octet rule? (b) What other resonance structures are possible that satisfy the octet rule? (c) On the basis of the formal charges, which Lewis structure is expected to be dominant for BeCl2?arrow_forwardAlthough I3- is a known ion, F3- is not. (a) Draw the Lewis structure for I3- (it is linear, not a triangle). (b) One of your classmates says that F3 - does not exist because F is too electronegative to make bonds with another atom. Give an example that proves your classmate is wrong. (c) Another classmate says F3- does not exist because it would violate the octet rule.Is this classmate possibly correct? (d) Yet another classmatesays F3- does not exist because F is too small to make bonds tomore than one atom. Is this classmate possibly correct?arrow_forward
- (a) Describe the molecule xenon trioxide, XeO3, using four possible Lewis structures, one each with zero, one, two, or three Xe—O double bonds. (b) Do any of these resonance structures satisfy the octet rule for every atom in the molecule? (c) Do any of the four Lewis structures have multiple resonance structures? If so, how many resonance structures do you find? (d) Which of the Lewis structures in (a) yields the most favorable formal charges for the molecule?arrow_forward1) A) In the Lewis structure for IF2–, how many lone pairs of electrons are around the central iodine atom?a) 0b) 1c) 2d) 3e) 4B) The Cl–Xe–Cl bond angle in XeCl4 is closest toa) 90°b) 120°c) 150°d) 360°e) 109°C) Which of the following atoms cannot exceed the octet rule in a molecule?a) Bb) Snc) Pdd) Ie) All atoms exceed the octet rulearrow_forwardA) what are the correct formal charges on the atoms for structure A? B) what are the correct formal charges on the atoms for structure B? C) what are the correct formal charges on the atoms for structure C? D) based on the formal charges, what is the best structure? D)arrow_forward

 Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax





